The communications profiles reflect likely implementation choices have been developed and assigned, where applicable, to triples. The communications profiles have been developed following closely the naming practices of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Model.
| ID |
Name |
Description |
Profile Diagram |
|
CCMS
|
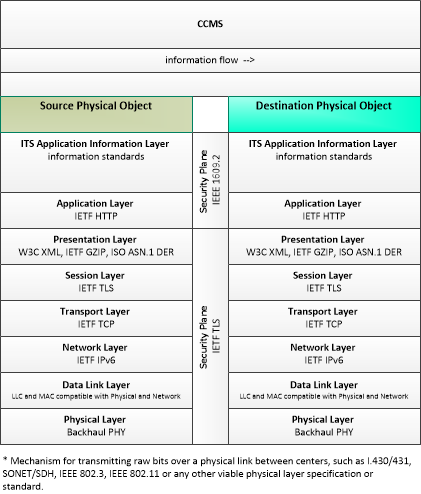
CCMS Communications
|
This profile identifies applicable standards for secure communications with the Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System (CCMS).
|
 |
|
Contact-Proximity-Interface
|
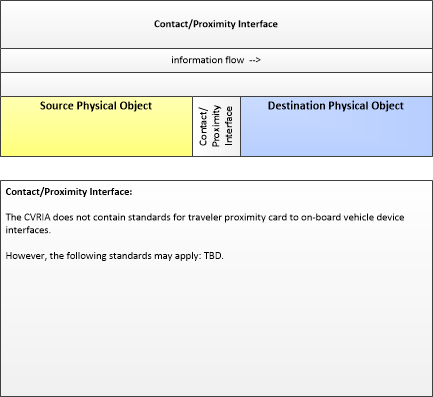
Proximity Communication Interface
|
This profile describe applicable standards used in close proximity communications.
|
 |
|
DSRC-UDP
|
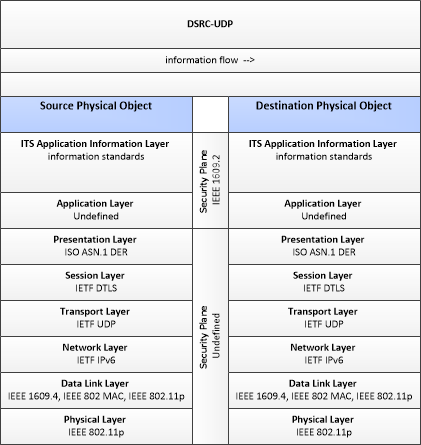
Vehicle-to-Vehicle/Infrastructure using UDP
|
This profile describes a set of standards applicable to broadcast, frequent (non-constant), medium latency vehicle- to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communications using the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) over Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) over the 5.9GHz spectrum.
|
 |
|
DSRC-WSMP
|
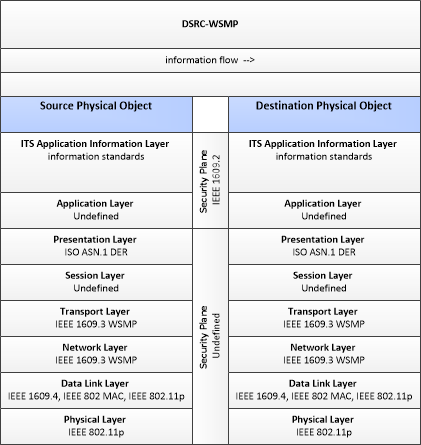
Vehicle-to-Vehicle/Infrastructure using WSMP
|
This profile describes a set of standards applicable to broadcast, near constant, low latency vehicle- to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communications using the WAVE Short Messaging Protocol (WSMP) over the 5.9GHz spectrum.
|
 |
|
GENERIC-TEMPLATE
|
No Standards Identified
|
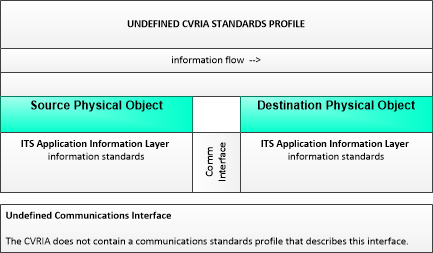
This profile is used to show that the CVRIA does not contain standards applicable for this interface.
|
 |
|
NTCIP-DATEX
|
NTCIP using DATEX
|
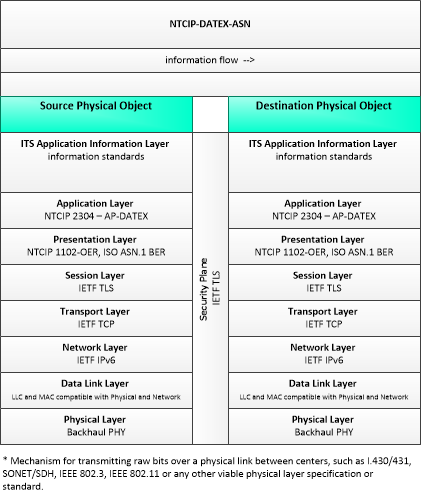
This profile describes an alternative set of standards applicable to communications between entities using ISO TC204 WG9 DATa Exchange(DATEX). Information messages are encoded using the NTCIP Octet Encoding Rules (OER).
|
 |
|
NTCIP-SMTP
|
NTCIP using SMTP
|
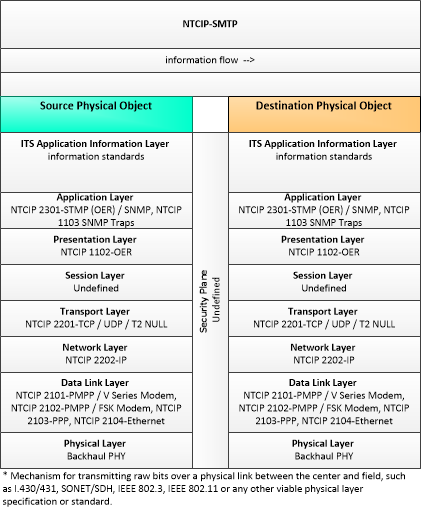
This profile describes an alternative set of standards used to communicate with ITS Roadway Devices that uses the NTCIP Octet Encoding Rules (OER), a standard developed specifically for the transportation industry. This template is used primarily for communication with traffic signal controllers, where second-per-second communications is required. This template also includes standards for SNMP traps, that allows an ITS Roadway Device to initiate event-driven communications with a receiver.
|
 |
|
NTCIP-SNMP
|
NTCIP using SNMP
|
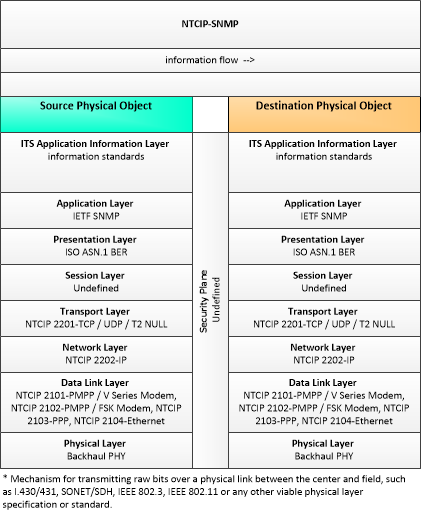
This profile describes applicable standards for communicating between with ITS Roadway devices using the simple network management protocol (SNMP).
|
 |
|
Position-Location-Interface
|
Position-Location Interface
|
This partial profile, showing only physical objects and flow, describes communications between connected vehicle equipment and on board geolocation equipment such as a GPS receiver.
|
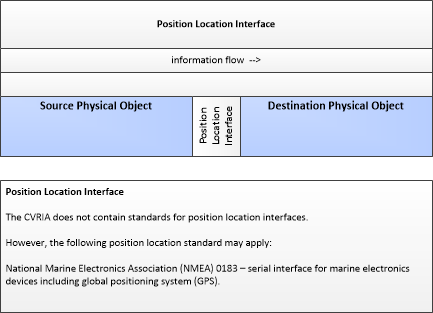 |
|
RSE-C2F
|
RSE - Center to Field Communications
|
This profile describes applicable standards for Center to Field communications with RSEs. Common internet standards (HTTPS and TCP) are used in this profile.
|
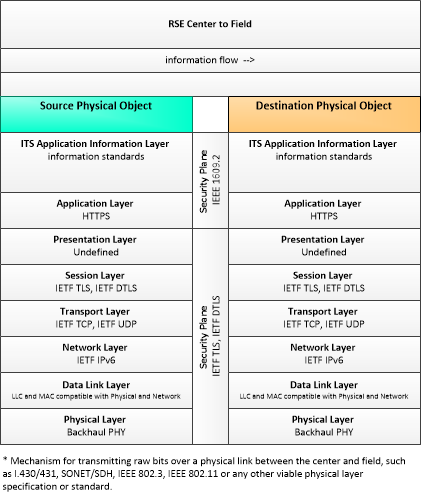 |
|
RSE-C2F-SNMP
|
RSE - Center to Field Communications - SNMP
|
This profile identifies applicable standards for Center to Field communications with RSEs. This profile uses the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), an Internet-standard protocol for managing devices on IP networks.
|
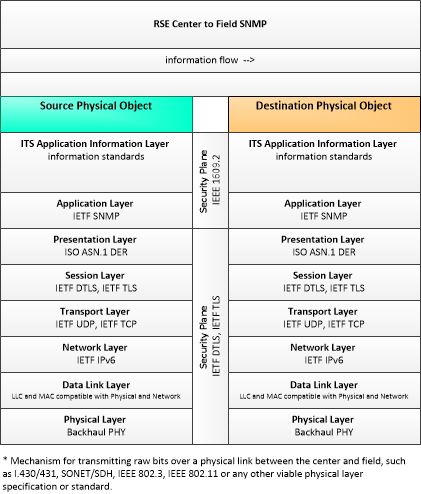 |
|
RSE-F2F
|
Roadside Equipment to ITS Roadway Equipment
|
This profile describes standards applicable to communications between roadside equipment and other field equipment such as traffic signal controllers that is represented by ITS Roadway Equipment in CVRIA.
|
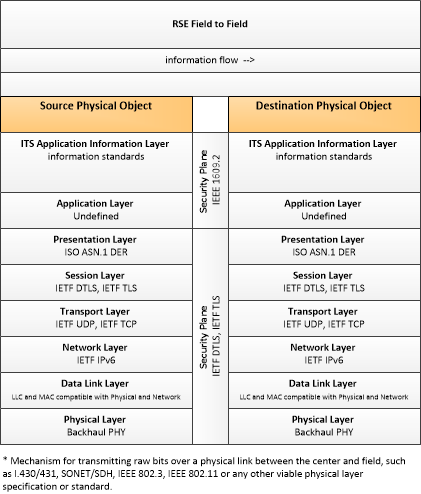 |
|
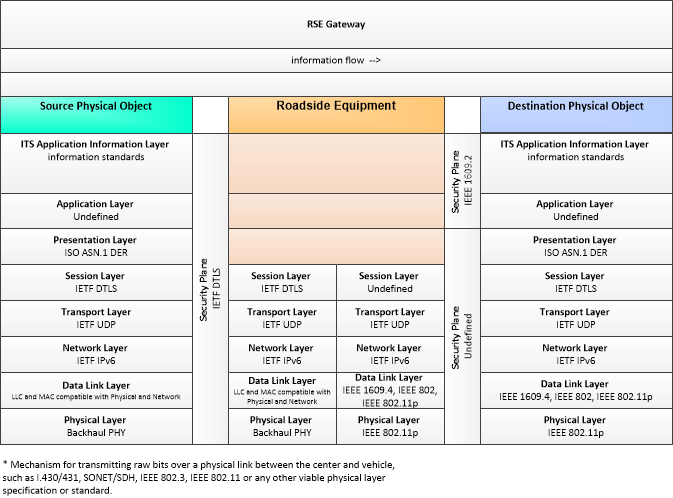
RSEGateway-VehicleDestination
|
Vehicle Communications via RSEs, Vehicle Destination
|
This profile describes an alternative set of standards used in vehicle communications where one or more RSEs act as a gateway with the vehicle as destination.
|
 |
|
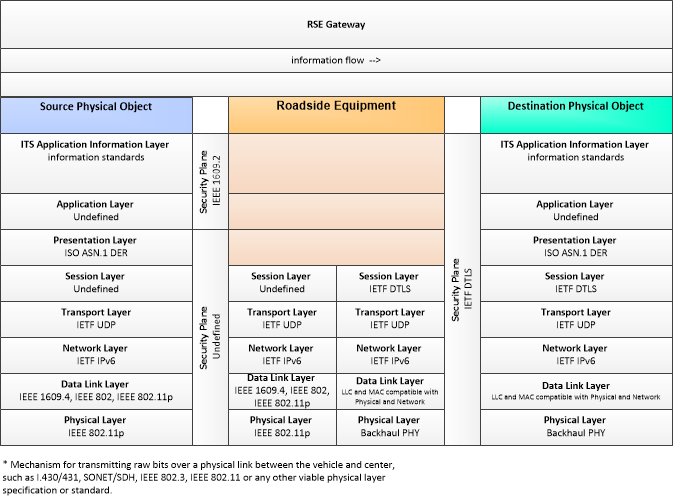
RSEGateway-VehicleSource
|
Vehicle Communications via RSEs, Vehicle Source
|
This profile describes an alternative set of standards used in vehicle communications where one or more RSEs act as a gateway with the vehicle as source.
|
 |
|
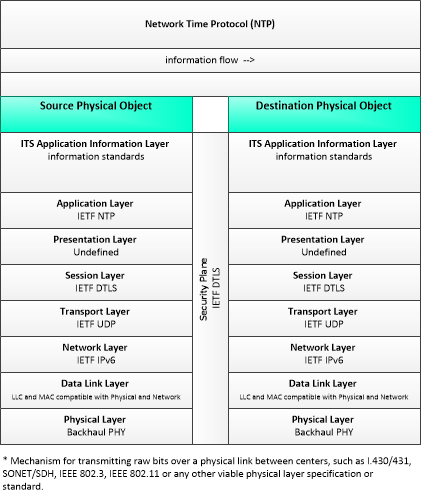
Time
|
Network Time Protocol
|
This profile includes a collection of standards that support the Network Time Protocol that allows NTP servers to provide time synchronization services to other NTP servers and clients.
|
 |
|
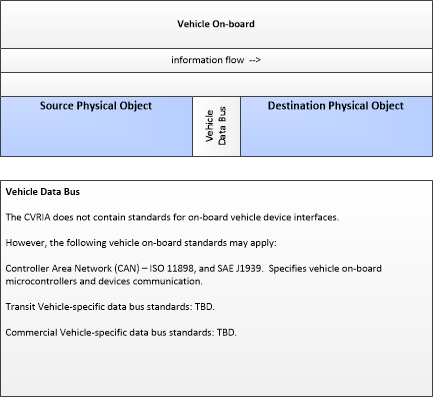
Vehicle-On-Board
|
Vehicle-On-Board
|
This partial profile, showing only physical objects and flow, describes communications between equipment that reside on the vehicle. The CVRIA does not contain any specific information on standards for on-board vehicle communications.
|
 |
|
WAB
|
Wide-Area-Broadcast
|
This profile shows a wide area wireless communications system that offers broadcast services with regional, national, or continental coverage, enabling communications with vehicles and traveler mobile devices at any location on or off the road network. Examples of this link include satellite and terrestrial radio digital broadcast services.
|
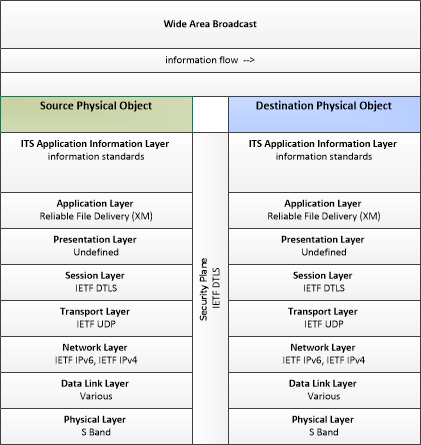 |
|
WAB-Via-WAID
|
Wide-Area-Broadcast-Via-WAID
|
This profile shows a wide area wireless communications system that offers broadcast services with regional, national, or continental coverage, enabling communications with vehicles and traveler mobile devices at any location on or off the road network. In this profile, the Wide-Area Information Disseminator (WAID) CVRIA Physical Object provides broadcast communications services enabling transportation centers to communicate with all equipped transportation users in their region. Examples of this link include satellite and terrestrial radio digital broadcast services.
|
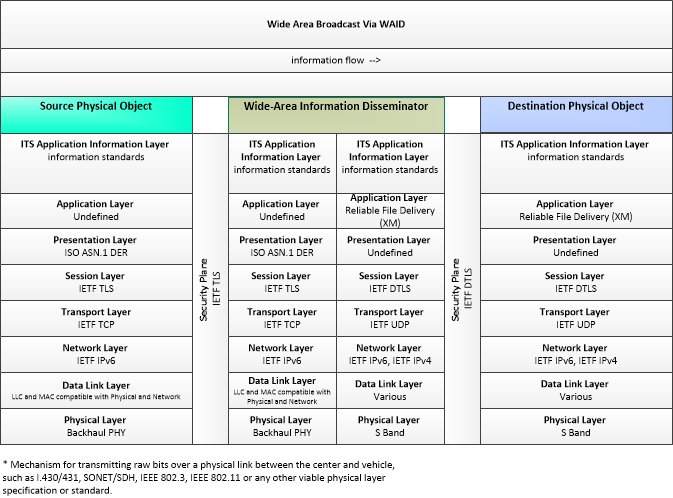 |
|
WAW-ASN1
|
Wide Area Wireless using ASN.1 as encoding method
|
This profile describes applicable ASN.1 standards used in transmissions over wide area wireless communications.
|
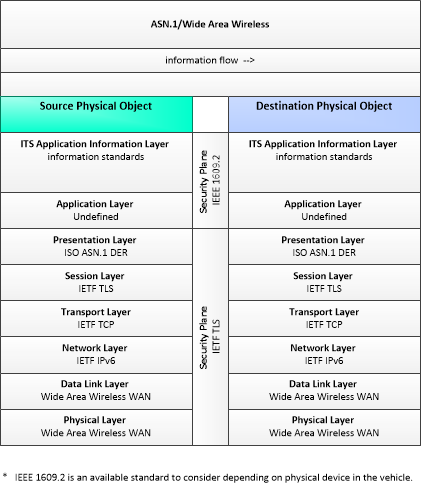 |
|
WAW-WWWBrowser-JSON
|
Wide Area Wireless using JSON as encoding method
|
This profile describes applicable IETF JSON and W3C web browser standards (e.g., HTML5 and Web Sockets) for transmissions over wide area wireless communications.
|
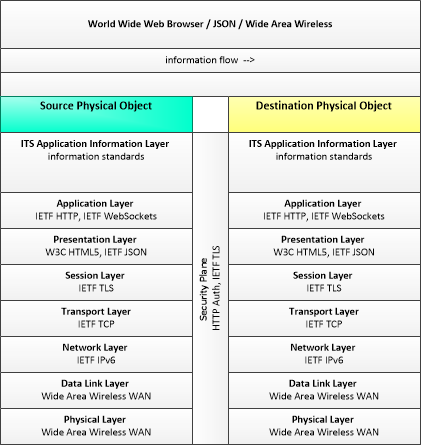 |
|
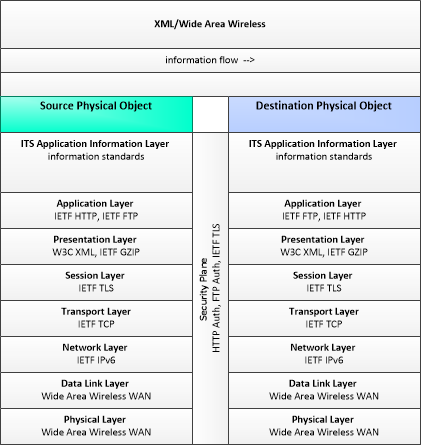
WAW-XML
|
Wide Area Wireless using XML as encoding method
|
This profile describes applicable XML and W3C web services standards used in transmissions over wide area wireless communications.
|
 |
|
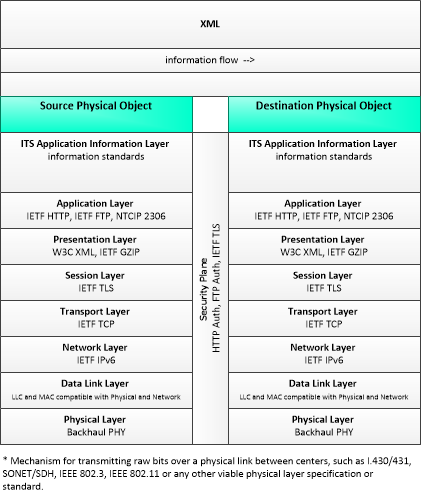
XML
|
eXtensible Markup Language
|
This profile describes a set of standards applicable to communications between entities using the Web Services standards of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force). Information messages are encoded using the eXtensible Markup Language (XML).
|
 |





















