Type: Support
Groups:- Communications
- Vehicle Safety Communications Applications (VSC-A) Final Report, Final, 9/1/2011
- Core System Concept of Operations (ConOps), Final revE, 10/24/2011
- J2735 Systems Engineering Version, Draft Candidate Std, 12/15/2012
- Harmonization Task Group #1 Service and Security Management to Support safety and sustainability applications: Current Status of Security Standards, Draft, 8/29/2012
Communications Support
Communications Support applications provide the protocol layers to allow communications between connected devices. These communications applications operate in conjunction with the Security and Credentials Management applications to provide effective and secure communications between connected devices.
Enterprise
This is one way this application may be realized, but not the only way. There are other ways to build a given application and accomplish a stated objective.
The enterprise diagram can be viewed in SVG or PNG format and the current format is SVG. Enterprise diagrams have not been developed for this application yet.
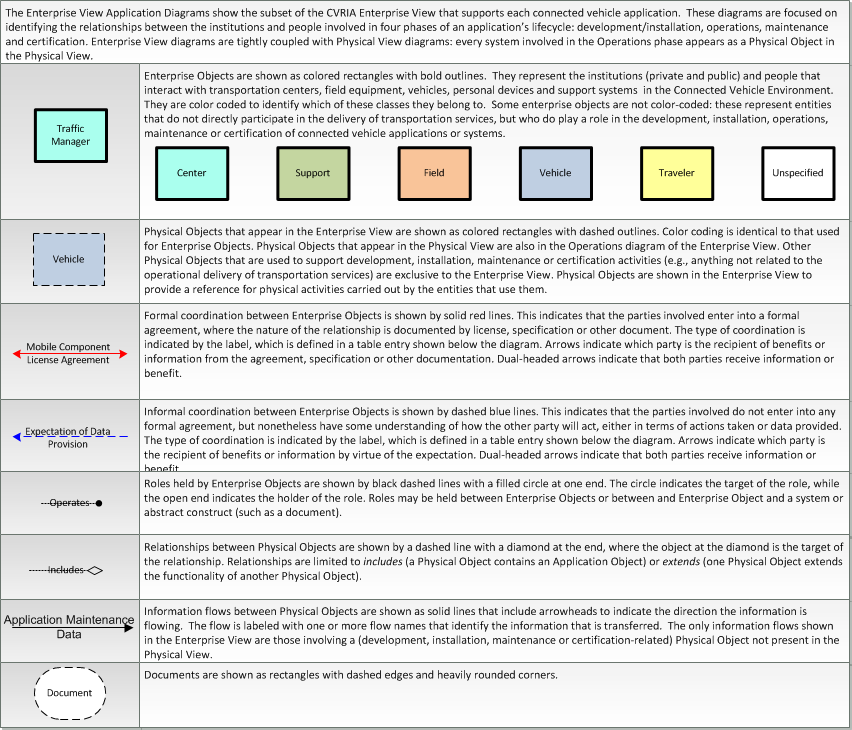
Includes Enterprise Objects:
| Enterprise Object | Description |
|---|
Includes Resources:
| Resource | Description |
|---|
Includes Roles:
| Role | Description |
|---|
Includes Coordination:
| Coordination | Type | Description |
|---|
Functional
Includes Processes:
| Level | Name | Type | Allocated to Application Object |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.1.5.1 | Support Connected Vehicle Center Communications | Pspec |
- Center Communications Support - Center Trust Management |
| 10.1.5.2 | Support Connected Vehicle Field Communications | Pspec |
- RSE Communications Support - RSE Trust Management |
| 10.1.5.3 | Support Connected Vehicle Vehicle Communications | Pspec |
- Vehicle Communications Support - Vehicle Trust Management |
| 10.1.5.4 | Support Connected Vehicle Mobile Communications | Pspec |
- Personal Communications Support - Personal Trust Management |
| 10.1.5.5 | Provide Center Misbehavior Detection | Pspec |
- Center Trust Management |
| 10.1.5.6 | Provide Field Misbehavior Detection | Pspec |
- RSE Trust Management |
| 10.1.5.7 | Provide Vehicle Misbehavior Detection | Pspec |
- Vehicle Trust Management |
| 10.1.5.8 | Provide Mobile Misbehavior Detection | Pspec |
- Personal Trust Management |
Includes Data Flows:
Physical
This is one way this application may be realized, but not the only way. There are other ways to build a given application and accomplish a stated objective.
The physical diagram can be viewed in SVG or PNG format and the current format is SVG. SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
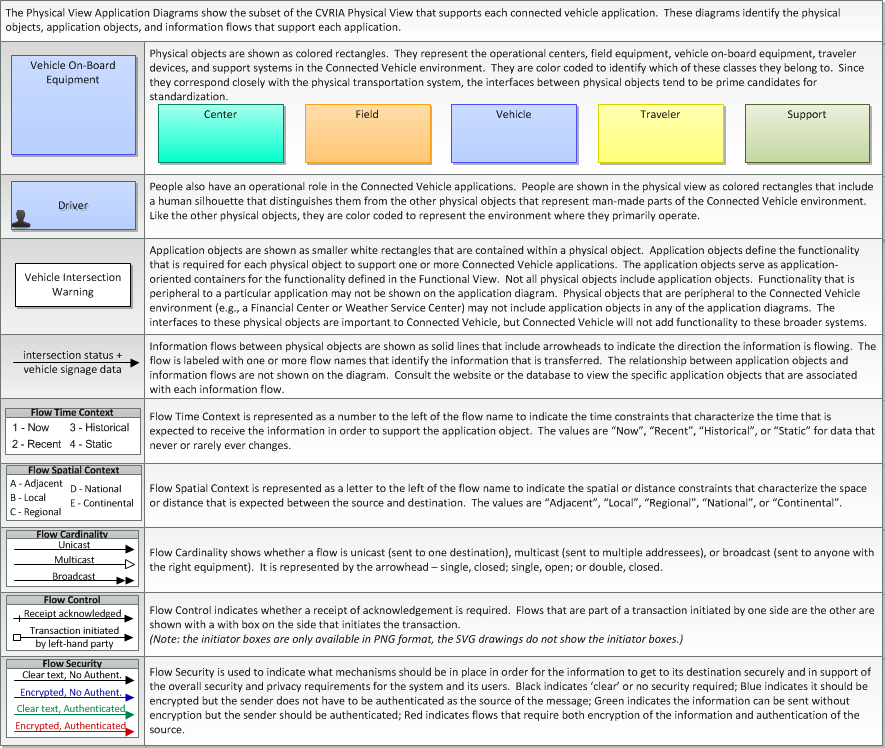
Includes Physical Objects:
| Physical Object | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Center | Center | This general physical object is used to model general functions and core capabilities that may be supported by any center included in CVRIA. |
| Other Centers | Center | "Other Centers" represents any operational center that participates in a regional transportation system. This object is used in CVRIA to model common functionality and interfaces that may be supported by any transportation center, such as the general capability to exchange data with another regional center. |
| Personal Information Device | Traveler | The "Personal Information Device" provides the capability for travelers to receive formatted traveler information wherever they are. Capabilities include traveler information, trip planning, and route guidance. It provides travelers with the capability to receive route planning from the infrastructure at home, at work, or en route using personal devices that may be linked with connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| Remote Vehicle OBEs | Vehicle | "Remote Vehicle OBEs" represents other connected vehicles that are communicating with the host vehicle. In CVRIA, this object provides a source and destination for information transfers between connected vehicles. The host vehicle on-board equipment, represented by the Vehicle OBE physical object, sends information to, and receives information from the Remote Vehicle OBEs to model all connected vehicle V2V communications in CVRIA. |
| Roadside Equipment | Field | "Roadside Equipment" (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC). Communications with adjacent ITS Roadway Equipment (see the separate object) and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other roadside equipment, and centers that provide back office support. |
| Security and Credentials Management System | Support | The "Security and Credentials Management System" is a high-level aggregate representation of the interconnected systems that enable trusted communications between mobile devices and other mobile devices, roadside devices, and centers and protect data they handle from unauthorized access. This physical object will be implemented as an interconnected system of support applications that enable the secure distribution, use, and revocation of trust credentials. |
| Vehicle OBE | Vehicle | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. Four different types of implementations are represented by the Vehicle OBE: 1. Vehicle Awareness Device – This is an aftermarket electronic device, installed in a vehicle without connection to vehicle systems, that is only capable of sending the basic safety message over short range communications. Vehicle awareness devices do not generate warnings. 2. Aftermarket Device – This is an aftermarket electronic device, installed in a vehicle, and capable of sending and receiving messages over a wireless communications link. The self-contained device includes GPS, runs connected vehicle applications, and includes an integrated driver interface that issues audible or visual warnings, alerts, and guidance to the driver of the vehicle. 3. Retrofit Device – This is an electronic device installed in vehicles by an authorized service provider, at a service facility after the vehicle has completed the manufacturing process (retrofit). This type of device provides two-way communications and is connected to a vehicle databus to integrate the device with other on-board systems. Depending on implementation, the device may include an integrated driver interface and GPS or integrate with modules on the vehicle bus that provide these services. Depending on implementation, it may support all of the connected vehicle applications identified in CVRIA. 4. Integrated System – This is a system of one or more electronic devices integrated into vehicles during vehicle production. The Integrated System is connected to proprietary data busses to share information with other on-board systems. The Integrated System may include many control modules and may be configured to support all of the connected vehicle applications identified in CVRIA. In retrofit and integrated implementations, the Vehicle OBE interfaces to other on-board systems through a vehicle bus (e.g., CAN). Represented in CVRIA as the Vehicle Platform, this interface provides access to on-board sensors, monitoring and control systems, and information systems that support connected vehicle applications. The vehicle bus may also be the source for GPS location and time and the access point for the vehicle's driver-vehicle interface. Self-contained devices include an integrated GPS and driver interface that supports direct visual, audible, or haptic interaction with the driver. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars and trucks. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal automobiles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE is used to model the common interfaces and functions that apply to all of these vehicle types. |
Includes Application Objects:
| Application Object | Description | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| Center Communications Support | "Center Communications Support" supports secure, reliable communications with other connected devices. It provides the communications functions that add a timestamp, the message origin, and a digital signature in outbound messages and processes, verifies, and authenticates the same fields in inbound messages. It also encrypts (outbound) and decrypts (inbound) sensitive data. | Center |
| Center Trust Management | "Center Trust Management" manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Security and Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to the Connected Vehicle Environment security. | Center |
| Personal Communications Support | "Personal Communications Support" supports secure, reliable communications with other connected devices. It provides the communications functions that add a timestamp, the message origin, and a digital signature in outbound messages and processes, verifies, and authenticates the same fields in inbound messages. It also encrypts (outbound) and decrypts (inbound) sensitive data. | Personal Information Device |
| Personal Trust Management | "Personal Trust Management" manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Security and Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to the Connected Vehicle Environment security. | Personal Information Device |
| RSE Communications Support | "RSE Communications Support" supports secure, reliable communications with other connected devices. It provides the communications functions that add a timestamp, the message origin, and a digital signature in outbound messages and processes, verifies, and authenticates the same fields in inbound messages. It also encrypts (outbound) and decrypts (inbound) sensitive data. | Roadside Equipment |
| RSE Trust Management | "RSE Trust Management" manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Security and Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and keys and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to Connected Vehicle Environment security. | Roadside Equipment |
| Vehicle Communications Support | "Vehicle Communications Support" supports secure, reliable communications with other connected devices. It provides the communications functions that add a timestamp, the message origin, and a digital signature in outbound messages and processes, verifies, and authenticates the same fields in inbound messages. It also encrypts (outbound) and decrypts (inbound) sensitive data. | Vehicle OBE |
| Vehicle Trust Management | "Vehicle Trust Management" manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Security and Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to the Connected Vehicle Environment security. | Vehicle OBE |
Includes Information Flows:
| Information Flow | Description |
|---|---|
| connected vehicle data | This flow represents any secure data exchange within the Connected Vehicle Environment. It defines the common data fields that are shared by all secure messages, including a verifiable timestamp, a verifiable geographic location of the sender's origin, and a digital signature. The information may also be encrypted to protect sensitive data content. |
| misbehavior report | Notification of potential security issues encountered in processing messages, including message authentication failures. |
| security credential revocations | A list of security credentials that have been revoked. |
| security credentials | Cryptographic keys and associated data that supports secure communications. |
Requirements
| Need | Requirement | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N4.001 | Applications need to protect data they handle from unauthorized access. This is required to support applications that exchange sensitive information, such as personally identifying or financial information, which if intercepted could compromise the privacy or financial records of the user. | 4.001 | Applications that function by exchanging data between entities shall be able to exchange encrypted data between those entities. |
| N4.002 | Applications need to establish trust between entities that operate components of the application. Such trust relationships are necessary so that applications can be assured that entities are who they say they are, and therefore trust the source and data it receives. | 4.002 | Applications shall verify that, for each entity on which an application component is installed, that entity is trusted by the provider of the application. |
| 4.003 | Applications shall be able to digitally sign all messages sent between entities. | ||
| 4.004 | Applications shall be able to verify the digital signature of received messages. | ||
| 4.005 | Digital signatures used to ensure trust shall be generated independently of the application sending the message to be signed. | ||
| N4.003 | Applications need to revoke the trust relationship they have between entities when necessary. A trusted entity may operate in a fashion that indicates it should no longer be trusted, in which case applications must have a way of revoking that trust. | 4.006 | Applications shall identify entities that provide messages to the application that are improperly formatted. |
| 4.007 | Applications shall identify entities that provide messages to the application that are logically inconsistent. | ||
| 4.008 | Applications shall revoke personal trust (trust by the application) when a repeated pattern of messages from a given entity falls outside of the applications tolerances. | ||
| 4.009 | Applications shall be able to report suspicious behavior to third party authentication providers. | ||
| 4.010 | Applications shall be able to accept messages from the third party authentication provider that identifies entities unworthy of trust. | ||
| 4.011 | Applications shall be able to revoke trust between itself and an entity if that entity is identified by the third party authentication provider as untrustworthy. | ||
| N4.004 | All participants in the Connected Vehicle Environment need to operate on a common time base. Coordination of time between the entities that operate applications as well as those providing Core services prevents internal errors and enables time-sensitive interactions between application components. | 4.012 | All applications shall use the same time source as the basis for timing. |
| N4.043 | Every DSRC message need to be constructed in such a way as to make replay attacks impractical, in order to minimize the number of such attacks. | 4.107 | Every DSRC message shall include the verifiable geographic location of the sender's origin. |
| 4.108 | Every DSRC message shall include a verifiable timestamp. | ||
| 4.111 | Every DSRC message shall include a verifiable timestamp. | ||
| N4.044 | Every V2V DSRC message needs to be non-repudiatable in origin; that is, that the originator cannot deny having sent the message. This is so that when a received message invokes actions on the receiver it may be necessary to show that the behavior was in response to a specific transmitted message. Similarly messages may be received that indicate misbehavior of the transmitting vehicle or its equipment that will give rise to a misbehavior report. Non-repudiation of origin ensures that the originator of information cannot successfully deny having sent the information. | 4.109 | Every DSRC message shall include a digital signature. |
| 4.110 | Digital signatures shall be unique to the user of the signature. | ||
| N4.046 | V2V DSRC messages need to use pseudonyms to help protect user's privacy. | 4.114 | Any identifier used in a DSRC message shall be based on a random seed (not the user's identity). |
| N4.047 | DSRC messages need to be able to be relayed from one DSRC device to another, so that in areas where no direct access to infrastructure (DSRC or otherwise) is available, an emergency DSRC message may eventually be relayed to infrastructure. | 4.115 | DSRC messages shall be constructed in such a way so as to be relay-able. |
