Link Type: Short Range
Roadside Equipment --> Vehicle OBE:
connected vehicle data
This triple is bi-directional. See also
Vehicle OBE --> Roadside Equipment: connected vehicle data
Definitions
connected vehicle data (Information Flow): This flow represents any secure data exchange within the Connected Vehicle Environment. It defines the common data fields that are shared by all secure messages, including a verifiable timestamp, a verifiable geographic location of the sender's origin, and a digital signature. The information may also be encrypted to protect sensitive data content.
Roadside Equipment (Source Physical Object): "Roadside Equipment" (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC). Communications with adjacent ITS Roadway Equipment (see the separate object) and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other roadside equipment, and centers that provide back office support.
Vehicle OBE (Destination Physical Object): The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications.
Four different types of implementations are represented by the Vehicle OBE:
1. Vehicle Awareness Device – This is an aftermarket electronic device, installed in a vehicle without connection to vehicle systems, that is only capable of sending the basic safety message over short range communications. Vehicle awareness devices do not generate warnings.
2. Aftermarket Device – This is an aftermarket electronic device, installed in a vehicle, and capable of sending and receiving messages over a wireless communications link. The self-contained device includes GPS, runs connected vehicle applications, and includes an integrated driver interface that issues audible or visual warnings, alerts, and guidance to the driver of the vehicle.
3. Retrofit Device – This is an electronic device installed in vehicles by an authorized service provider, at a service facility after the vehicle has completed the manufacturing process (retrofit). This type of device provides two-way communications and is connected to a vehicle databus to integrate the device with other on-board systems. Depending on implementation, the device may include an integrated driver interface and GPS or integrate with modules on the vehicle bus that provide these services. Depending on implementation, it may support all of the connected vehicle applications identified in CVRIA.
4. Integrated System – This is a system of one or more electronic devices integrated into vehicles during vehicle production. The Integrated System is connected to proprietary data busses to share information with other on-board systems. The Integrated System may include many control modules and may be configured to support all of the connected vehicle applications identified in CVRIA.
In retrofit and integrated implementations, the Vehicle OBE interfaces to other on-board systems through a vehicle bus (e.g., CAN). Represented in CVRIA as the Vehicle Platform, this interface provides access to on-board sensors, monitoring and control systems, and information systems that support connected vehicle applications. The vehicle bus may also be the source for GPS location and time and the access point for the vehicle's driver-vehicle interface. Self-contained devices include an integrated GPS and driver interface that supports direct visual, audible, or haptic interaction with the driver.
In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars and trucks. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal automobiles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE is used to model the common interfaces and functions that apply to all of these vehicle types.
Included In
This Information Flow is in the following Applications:
This Information Flow is in the following Application Objects:
Communication Diagrams
The communication diagram(s) can be viewed in SVG or PNG format and the current format is SVG. Switch to PNG format.
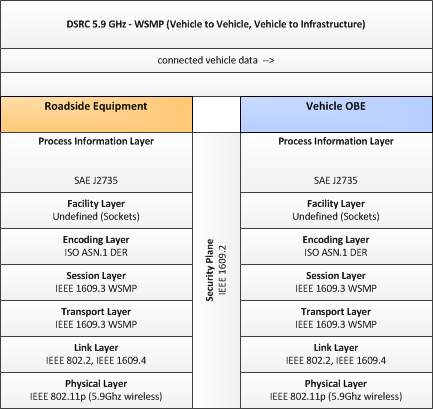
DSRC-5.9-GHz-WSMP (Vehicle-to-Vehicle, Vehicle-to- Infrastructure). This template describes a set of standards applicable to broadcast, near constant, low latency vehicle- to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communications using the WAVE Short Messaging Protocol (WSMP) over the 5.9GHz spectrum.