Type: Support
Groups:- Core Services
Core Authorization
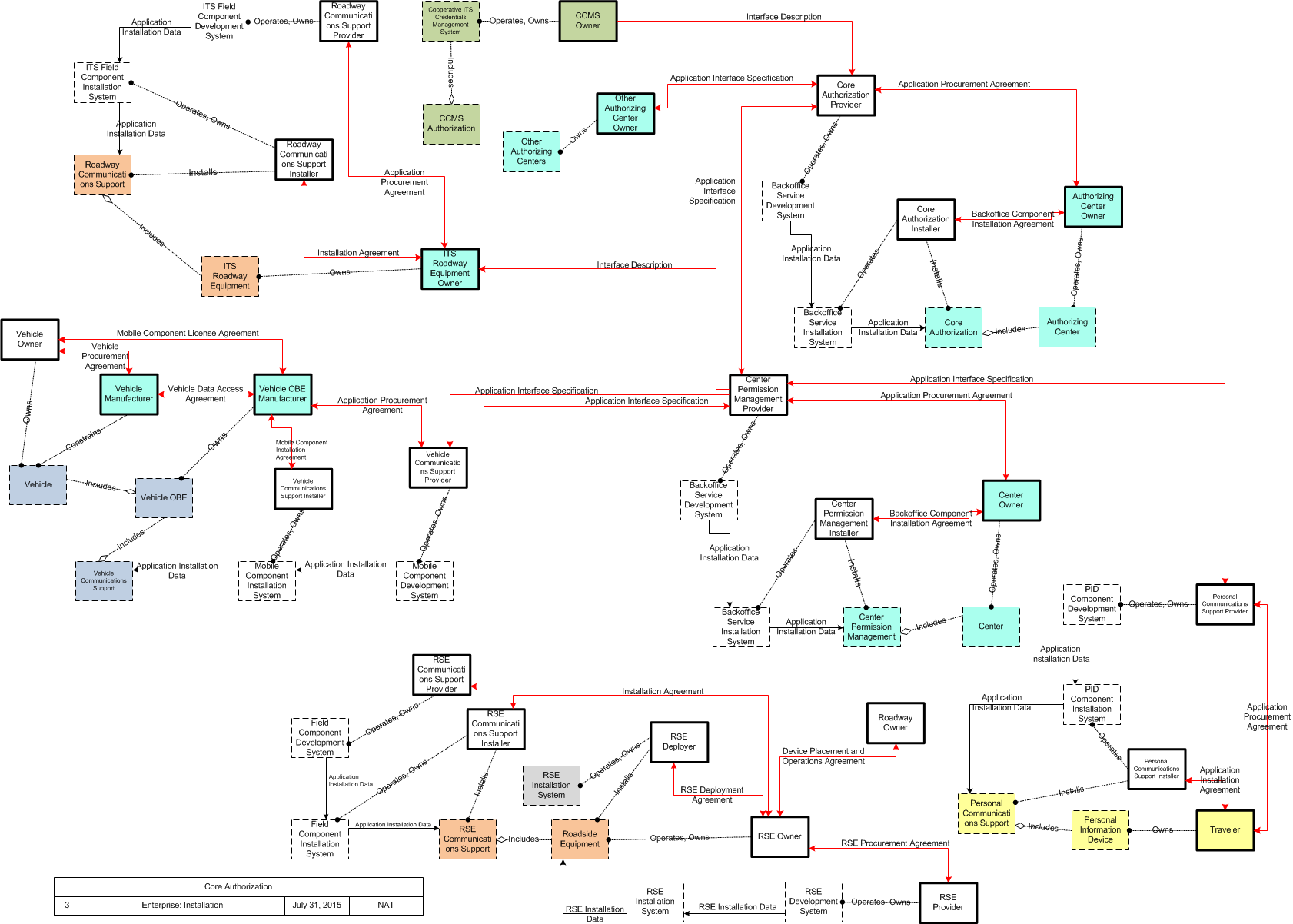
Core Authorization is a connected vehicle support application that manages the authorization mechanisms to define roles, responsibilities and permissions for other connected vehicle applications . This allows system administrators to establish operational environments where different connected vehicle system users may have different capabilities. For instance, some Mobile elements may be authorized to request signal priority, or some Centers may be permitted to use the geographic broadcast service, while those without those permissions would not.
Enterprise
SVG Diagrams: Installation Operations Maintenance Certification
PNG Diagrams: Installation Operations Maintenance Certification
Business Interaction Matrix:
| Core Authorization Operations Stage | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Owner | Vehicle OBE Owner | Roadway Owner | RSE Owner | RSE Operator | ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Operator | Traveler | Center Owner | CCMS Owner | Authorizing Center Owner | Authorizing Center Operator | Other Authorizing Center Owner | |
| Vehicle Owner | Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||
| Vehicle OBE Owner | Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Information Provision and Action Agreement | |||||||||||
| Roadway Owner | Service Delivery Agreement | ||||||||||||
| RSE Owner | Service Delivery Agreement | Operations Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | Information Provision and Action Agreement | |||||||||
| RSE Operator | Operations Agreement | ||||||||||||
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Information Exchange Agreement | Operations Agreement | Information Provision and Action Agreement | ||||||||||
| ITS Roadway Operator | Operations Agreement | ||||||||||||
| Traveler | Information Provision and Action Agreement | ||||||||||||
| Center Owner | Information Provision and Action Agreement | Information Provision and Action Agreement | Information Provision and Action Agreement | Information Provision and Action Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | ||||||||
| CCMS Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | ||||||||||||
| Authorizing Center Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Employment Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | |||||||||
| Authorizing Center Operator | Employment Agreement | ||||||||||||
| Other Authorizing Center Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | ||||||||||||
Includes Enterprise Objects:
| Enterprise Object | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Certification Entity | The body that determines whether an application may be deployed and operated in the Connected Vehicle Environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with application type. For example, applications with human safety component (crash avoidance, movement assistance etc.) may have stringent requirements and extensive testing in a variety of conditions, while applications that provide strictly mobility functionality may have far less testing requirements; possibly as little as just making sure the application doesn't interfere with any other applications. |
| Authorizing Center Operator | The operator of the Authorizing Center. |
| Authorizing Center Owner | The owner of the Authorizing Center. |
| CCMS Owner | The organization that is responsible for the Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System. |
| Center Owner | General representation of the owner of the general "Center" physical object. |
| Center Permission Management Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Center Permission Management Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Center Permission Management Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Core Authorization Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Core Authorization Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Core Authorization Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Device Certification Entity | The body that determines whether a device may be deployed and operated in the Connected Vehicle Environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with device type. |
| Federal Regulatory | Federal regulatory bodies that have legal authority to control and/or provide input to policies regulating transportation infrastructure and operations. This includes entities such as the Federal Communications Commission and US Department of Transportation. |
| ITS Certification Entity | The body that determines whether an ITS device or application may be deployed and operated in the transportation environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with device and application type. Typically not a formal body, assigned on a project-by-project basis depending on the type of infrastructure involved. Since ITS projects are locally-focused (typically state or smaller), the entities that are part of this body are typically those with operational jurisdiction where the ITS is installed (e.g., state or local DOTs, state or local maintenance managers etc.) |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | The entity that owns the Roadway ITS equipment. |
| ITS Roadway Operator | The entity that operates the Roadway ITS equipment. |
| Other Authorizing Center Owner | Representing the owner of another Authorizing Center, "Other Authorizing Center Owner" provides the source and destination for agreements and expectations between Authorizing Centers, enabling application authorization activities to be coordinated across jurisdictional boundaries. |
| Personal Communications Support Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Personal Communications Support Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Personal Communications Support Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| PID Provider | The entity that designs, manufacturers and provides (either to the end user or to a reseller) the personal information device, including its hardware and base operating software. |
| Roadway Communications Support Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Communications Support Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Communications Support Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Roadway Owner | The owner of the roadway proximate to which roadside equipment will be/is installed. |
| RSE Communications Support Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Communications Support Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Communications Support Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Deployer | The entity responsible for the deployment, operations and maintenance of roadside equipment. |
| RSE Operator | The entity that operates roadside equipment in the transportation environment. |
| RSE Owner | The owner of roadside equipment. |
| RSE Provider | The "RSE Provider" is the entity that develops and (presumably) sells roadside equipment to other entities for deployment and research. |
| State Regulatory | State regulatory bodies that have legal authority to control and/or provide input to policies regulating vehicles, transportation infrastructure and operations. This includes entities like Departments of Motor Vehicles, property tax authorities and tolling agencies. |
| Traffic Manager | The entity responsible for the management of traffic, both freeway and arterial. |
| Traveler | The 'Traveler' represents any individual who uses transportation services. The interfaces to the traveler provide general pre-trip and en-route information supporting trip planning, personal guidance, and requests for assistance in an emergency that are relevant to all transportation system users. It also represents users of a public transportation system and addresses interfaces these users have within a transit vehicle or at transit facilities such as roadside stops and transit centers. |
| Vehicle Communications Support Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Communications Support Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Communications Support Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Vehicle Manufacturer | The entity that builds, assembles, verifies and validates the Vehicle in which the Vehicle OBE will eventually operate. |
| Vehicle OBE Manufacturer | The entity that builds, assembles, verifies and validates the Vehicle OBE. This can be an OEM-equipped OBE, retrofit or aftermarket equipment. |
| Vehicle OBE Owner | The entity, individual, group or corporation that owns the Vehicle On-Board equipment. This could be the same as the Vehicle Owner, but it could be a third part that licenses the use of the OBE to the Owner. |
| Vehicle Owner | The individual, group of individuals or corporate entity that is identified as the registered owner of the Vehicle under state law. |
Includes Resources:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Component Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of an application component. Certification Requirements must be met in order for an application to be installed in the CVE. |
| Authorizing Center | The 'Authorizing Center' provides the functionality needed to enable data exchange between and among mobile and fixed transportation users. Its primary mission is to enable safety, mobility and environmental communications-based applications for both mobile and non-mobile users. The Authorizing Center has some jurisdiction over limited access resources; typically this includes roadside application access and radio spectrum licensing. It may be implemented as an autonomous center or as a set of supporting services that are co-located within another center. |
| Backoffice Service Development System | The systems used to develop backoffice (center) hardware and software components of applications. |
| Backoffice Service Installation System | The systems used to install and configure backoffice (center) hardware and software components. |
| Backoffice Service Maintenance System | The systems used to maintain and upgrade backoffice (center) hardware and software components. |
| CCMS Authorization | "CCMS Authorization" components provide authorization credentials (e.g., pseudonym certificates) to end entities. The end entity applies for and obtains authorization credentials, enabling the end entity to enter the "Operational" state. This function requires an interactive dialog, including at minimum a Certificate Request from the end entity desiring certificates. This request will be checked for validity, with the embedded enrollment certificate checked against an internal blacklist. If all checks are passed, this function will distribute a bundle of linked pseudonym certificates suitable for use by the requesting end entity, with the characteristics and usage rules of those certificates dependent on the operational policies of the CCMS. It also provides the secure provisioning of a given object's Decryption Key in response to an authorized request from that object. The retrieved Decryption Key will be used by the receiving object to decrypt the "next valid" batch within the set of previously retrieved Security Credential batches. |
| Center | This general physical object is used to model core capabilities that are common to any center. |
| Center Permission Management | "Center Permission Management" enables Connected Vehicle system users to request permission to access connected vehicle services. A center may request permission for the center or the infrastructure devices and vehicles associated with the center. |
| Commercial Vehicle OBE | The Commercial Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) resides in a commercial vehicle and provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support safe and efficient commercial vehicle operations. It provides two-way communications between the commercial vehicle drivers, their fleet managers, attached freight equipment, and roadside officials. In CVRIA, a separate 'Vehicle OBE' physical object supports the general V2V and V2I safety applications and other applications that apply to all vehicles, including commercial vehicles. The Commercial Vehicle OBE supplements these general capabilities with capabilities that are specific to commercial vehicles. |
| Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System | The 'Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System' (CCMS) is a high-level aggregate representation of the interconnected systems that enable trusted communications between mobile devices and other mobile devices, roadside devices, and centers and protect data they handle from unauthorized access. Representing the different interconnected systems that make up a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), this physical object represents an end user view of the credentials management system with focus on the exchanges between the CCMS and user devices that support the secure distribution, use, and revocation of trust credentials. |
| Core Authorization | "Core Authorization" manages authorization mechanisms to define permissions for System Users. This enables the Core System to establish operational environments where different System Users may have different capabilities in terms of accessing Core services and interacting with one another. For instance, some Mobile elements may be authorized to request signal priority, or some Centers may be permitted to use the geographic broadcast service, while those without those permissions would not. |
| Device Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of a connected vehicle device. Certification Requirements must be met in order for the device to be granted the credentials necessary to operate in the Connected Vehicle Environment. |
| Emergency Vehicle OBE | The Emergency Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) resides in an emergency vehicle and provides the processing, storage, and communications functions that support public safety-related connected vehicle applications. It represents a range of vehicles including those operated by police, fire, and emergency medical services. In addition, it represents other incident response vehicles including towing and recovery vehicles and freeway service patrols. It includes two-way communications to support coordinated response to emergencies. In CVRIA, a separate 'Vehicle OBE' physical object supports the general V2V and V2I safety applications and other applications that apply to all vehicles, including emergency vehicles. The Emergency Vehicle OBE supplements these general capabilities with capabilities that are specific to emergency vehicles. |
| Field Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the field component of the application. |
| Field Component Installation System | The system used to install a field component of a connected vehicle application. |
| Field Component Maintenance System | The system used to install and configure changes and updates to the field component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| ITS Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of an ITS device or ITS application. Applicability varies with jurisdictions, but typically devices and applications must meet pre-defined acceptance criteria prior to usage in the transportation environment. |
| ITS Field Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the ITS field component of the application. |
| ITS Field Component Installation System | The system used to install a field component of a connected vehicle application. |
| ITS Field Component Maintenance System | The system used to install and configure changes and updates to the ITS field component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway itself. In CVRIA, this physical object represents all of the other ITS field equipment that interfaces with and supports the Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE). This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| Maint and Constr Vehicle OBE | The 'Maint and Constr Vehicle OBE' resides in a maintenance, construction, or other specialized service vehicle or equipment and provides the processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support highway maintenance and construction. All types of maintenance and construction vehicles are covered, including heavy equipment and supervisory vehicles. The MCV OBE provides two-way communications between drivers/operators and dispatchers and maintains and communicates current location and status information. A wide range of operational status is monitored, measured, and made available, depending on the specific type of vehicle or equipment. A snow plow for example, would monitor whether the plow is up or down and material usage information. The Maint and Constr Vehicle OBE may also contain capabilities to monitor vehicle systems to support maintenance of the vehicle itself and include sensors that monitor environmental conditions such as road condition and surface weather information. This can include a diverse set of mobile environmental sensing platforms, including wheeled vehicles and any other vehicle that collects and reports environmental information. In CVRIA, a separate 'Vehicle OBE' physical object supports the general V2V and V2I safety applications and other applications that apply to all vehicles, including maintenance and construction vehicles. The Maint and Constr Vehicle OBE supplements these general applications with applications that are specific to maintenance and construction vehicles. |
| Mobile Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the mobile component of the application. |
| Mobile Component Installation System | The system that interacts with the Vehicle OBE other mobile device and installs the mobile component of the application. |
| Mobile Component Maintenance System | The system used to configure changes and updates to the mobile component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| Other Authorizing Centers | 'Other Authorizing Centers' provides a source and destination for information flows between multiple authorizing centers that manage permissions for the Connected Vehicle Environment. The interface represented by this object enables coordination of permissions between centers in different regions, jurisdictions, or application areas. |
| Personal Communications Support | "Personal Communications Support" supports secure, reliable communications with other connected devices. It provides the communications functions that add a timestamp, the message origin, and a digital signature in outbound messages and processes, verifies, and authenticates the same fields in inbound messages. It also encrypts (outbound) and decrypts (inbound) sensitive data. |
| Personal Information Device | The 'Personal Information Device' provides the capability for travelers to receive formatted traveler information wherever they are. Capabilities include traveler information, trip planning, and route guidance. Frequently a smart phone, the Personal Information Device provides travelers with the capability to receive route planning and other personally focused transportation services from the infrastructure in the field, at home, at work, or while en-route. Personal Information Devices may operate independently or may be linked with connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| PID Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the PID component of the application. |
| PID Component Installation System | The system used to install the PID component of a connected vehicle application. |
| PID Component Maintenance System | The system used to configure changes and updates to the PID component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| Roadside Equipment | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Roadway Communications Support | "Roadway Communications Support" supports secure, reliable communications with other connected devices. It provides the communications functions that add a timestamp, the message origin, and a digital signature in outbound messages and processes, verifies, and authenticates the same fields in inbound messages. It also encrypts (outbound) and decrypts (inbound) sensitive data. |
| RSE Communications Support | "RSE Communications Support" supports secure, reliable communications with other connected devices. It provides the communications functions that add a timestamp, the message origin, and a digital signature in outbound messages and processes, verifies, and authenticates the same fields in inbound messages. It also encrypts (outbound) and decrypts (inbound) sensitive data. |
| RSE Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the roadside equipment. |
| RSE Installation System | The system used to install and configure the roadside equipment. |
| RSE Maintenance System | The system used to configure changes and updates to the roadside equipment. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the RSE's configuration and performance. |
| Transit Vehicle OBE | The Transit Vehicle On-Board equipment (OBE) resides in a transit vehicle and provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support safe and efficient movement of passengers. The types of transit vehicles containing this physical object include buses, paratransit vehicles, light rail vehicles, other vehicles designed to carry passengers, and supervisory vehicles. It collects ridership levels and supports electronic fare collection. It supports a traffic signal prioritization function that communicates with the roadside physical object to improve on-schedule performance. Automated vehicle location enhances the information available to the transit operator enabling more efficient operations. On-board sensors support transit vehicle maintenance. The physical object supports on-board security and safety monitoring. This monitoring includes transit user or vehicle operator activated alarms (silent or audible), as well as surveillance and sensor equipment. The surveillance equipment includes video (e.g. CCTV cameras), audio systems and/or event recorder systems. It also furnishes travelers with real-time travel information, continuously updated schedules, transfer options, routes, and fares. In CVRIA, a separate 'Vehicle OBE' physical object supports the general V2V and V2I safety applications and other applications that apply to all vehicles, including transit vehicles. The Transit Vehicle OBE supplements these general capabilities with capabilities that are specific to transit vehicles. |
| Vehicle | The conveyance that provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support efficient, safe, and convenient travel. These functions reside in general vehicles including personal automobiles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, or other vehicle types. |
| Vehicle Communications Support | "Vehicle Communications Support" supports secure, reliable communications with other connected devices. It provides the communications functions that add a timestamp, the message origin, and a digital signature in outbound messages and processes, verifies, and authenticates the same fields in inbound messages. It also encrypts (outbound) and decrypts (inbound) sensitive data. |
| Vehicle OBE | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
Includes Roles:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Certifies | An Enterprise verifies that a target Resource meets relevant performance, functional, environmental and quality requirements. |
| Constrains | A Resource or Enterprise applies requirements, constraints and associated tests to another Resource. |
| Installs | An Enterprise performs the initial delivery, integration and configuration of the target Resource. |
| Maintains | An Enterprise administers the hardware and software that comprise the target Resource. |
| Member | An Enterprise is part of another larger, target Enterprise. |
| Operates | An Enterprise controls the functionality and state of the target Resource. An Enterprise that Operates a resource is considered Responsible. |
| Owns | An Enterprise has financial ownership and control over the Resource. An Enterprise that Owns a resource is considered Accountable. |
Includes Coordination:
| Coordination | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Application Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one party permission to install an application component on a device controlled by the other party. |
| Application Installation Data | Information Sharing | Data needed to install the application, including the application executable code and any configuration data. Unidirectional flow. |
| Application Interface Specification | Agreement | The definition of an interface between two application components that operate on two distinct pieces of hardware. The Application Interface Specification is specific to the application in question. |
| Application Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of a software application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Application Maintenance Data | Information Sharing | Data used to facilitate the upgrade, patching and general health maintenance of an application component. |
| Application Performance Data | Information Sharing | Data used to characterize application performance, including such measures as availability, known errors and known uses. |
| Application Procurement Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity provides a copy of an application component to another entity. This component is capable of being installed and functioning, according to its requirements that passed through the application's certification process. |
| Backoffice Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one party permission to install a backoffice application component on a center-based device controlled by the other party. |
| Backoffice Component Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the backoffice component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Device Placement and Operations Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that enables the controller of a physical device to install it (so as to make it operational) at a fixed location controlled by another entity. |
| Employment Agreement | Agreement | An agreement between an individual and a corporation or government entity, whereupon the individual agrees to provide labor to the corporation/agency, which in turn compensates the employee. Stipulates level of compensation, working conditions, necessary equipment and training and expectations of employee performance. |
| Extends | Includes | Indicates that one component includes all of the functionality of another component, and in provides additional functionality beyond that other component's. |
| Includes | Includes | Indicates that one component is entirely contained within another component. |
| Information Exchange Agreement | Agreement | An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. |
| Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Agreement | An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. This also includes a specification for action that shall, should or may be taken by one party in response to this information. |
| Information Provision and Action Agreement | Agreement | An agreement where one party agrees to provide information to another party. This is a unidirectional agreement. This also includes a specification for action that shall, should or may be taken by one party in response to this information. |
| Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity installs an application component on a device controlled by another entity. |
| Interface Description | Agreement | Documentation of the interface between two systems, where one system does not have an application component that is part of the application, but does provide and/or receive data and/or information that is used by or sourced from the application. In many cases this is an existing interface used by the application, so the description of the interface already exists and is imposed by the terminator. |
| Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of a system under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that states one entity will provide data related to maintenance of an application component to the other entity. |
| Mobile Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon the controller of OBE gives another party permission to install, configure and make operational a component that enables the mobile portion of an application. |
| Mobile Component License Agreement | Agreement | An end-user license agreement allowing the operator of the mobile device to use the mobile application component that is part of the application in question. |
| Mobile Component Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the mobile component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Operations Agreement | Agreement | An agreement where one entity agrees to operate a device or application on behalf of another, device/application controlling entity. |
| RSE Deployment Agreement | Agreement | Agreement to install, configure and make operational roadside equipment, between the provider of that equipment and the entity that controls access to the roadside. May define locations, expectation of power provision, backhaul responsibility and installation restrictions. |
| RSE Installation Data | Information Sharing | Data necessary to configure and make RSE operational. Uni-directional. |
| RSE Maintenance Data | Information Sharing | Data necessary to modify the operational configuration of RSE; assumes RSE is already configured. Uni-directional. |
| RSE Performance Data | Information Sharing | Data that includes metrics of RSE performance. Could include fields such as uptime, packets received/transmitted, distance vector from which packets received, as well as application-specific performance measures. |
| RSE Procurement Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity provides roadside equipment to another entity. The RSE is capable of being installed and functioning, according to its requirements that passed through the device's certification process. |
| Service Delivery Agreement | Agreement | A relationship where one party agrees to provide a service to the other party. This agreement may specify the expected performance of this service in terms of availability and/or actions/time-type performance specifications. |
| Vehicle Data Access Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereby the party that controls access to on-board vehicle data grants another party the right and ability to access that data. Includes the conditions under which data may be accessed, and specifies the mechanisms, including physical and functional access methods, data formats and any other considerations necessary for the accessing party to acquire data. May also include caveats regarding responsibility for data quality and responsibility for use of the data. |
| Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one entity permission to use a Vehicle OBE that the other party controls. |
| Vehicle Procurement Agreement | Agreement | The exchange of a vehicle for compensation. One entity purchases the vehicle from the other. |
| Warranty | Agreement | A guarantee or promise made by one entity to another, that provides assurance of the functionality and performance over time of an application component. |
Functional
Includes Processes:
| Level | Name | Type | Allocated to Application Object |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2 | Provide Device Control | Collection | |
| 1.2.7 | Provide Roadside Control Facilities | Collection | |
| 1.2.7.2 | Monitor Roadside Equipment Operation | Pspec |
- Roadway Communications Support |
| 1.2.7.7 | Process Vehicle Safety and Environmental Data for Output | Pspec |
- RSE Communications Support |
| 3 | Provide Vehicle Monitoring and Control | Collection | |
| 3.7 | Support Vehicle Secure Communications | Pspec |
- Vehicle Communications Support |
| 6.8 | Provide Traveler Personal Services | Collection | |
| 6.8.3 | Provide Traveler Services at Personal Devices | Collection | |
| 6.8.3.1 | Get Traveler Personal Request | Pspec |
- Personal Communications Support |
| 10.1.1 | Support Center Application Authorization | Pspec |
- Center Permission Management |
| 10.2 | Authorize Connected Vehicle Environment Applications | Pspec |
- Core Authorization |
| 10.3.3 | Authorize Connected Vehicle Devices | Pspec |
- CCMS Authorization |
| 10.5 | Satisfy Implementation Requirements | Pspec |
Includes Data Flows:
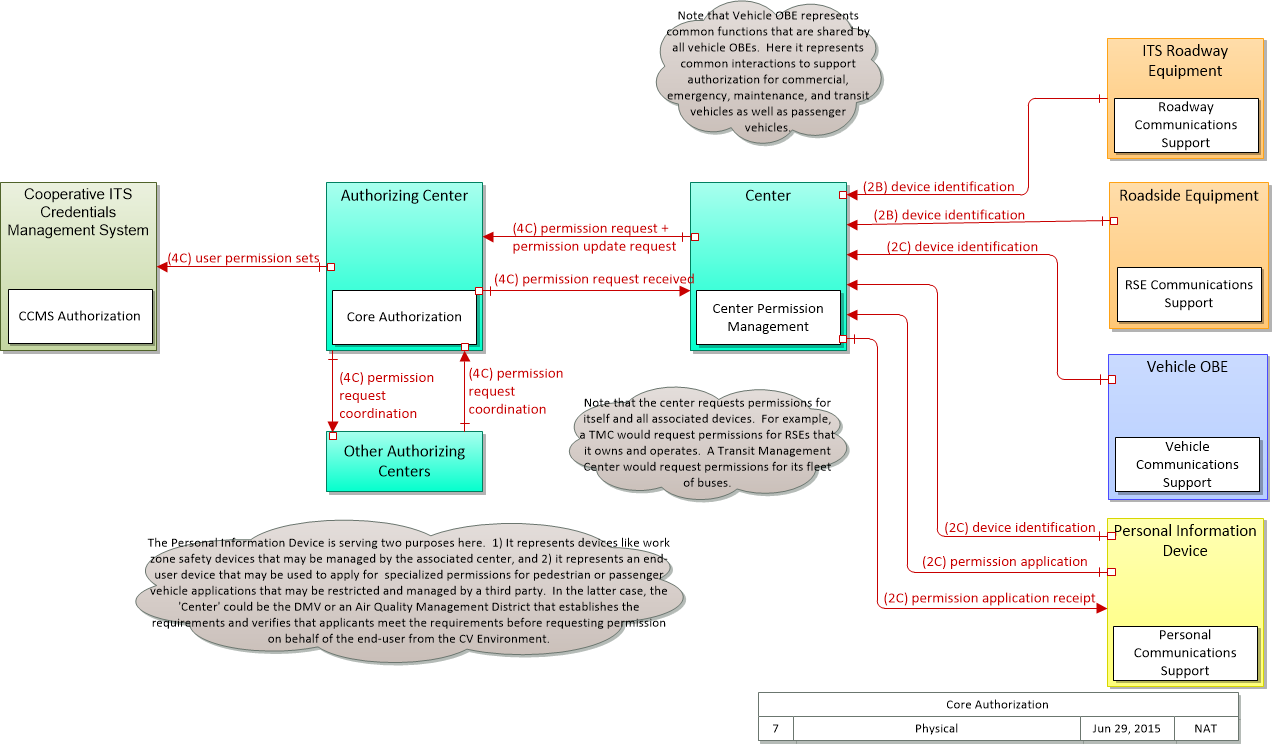
Physical
SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
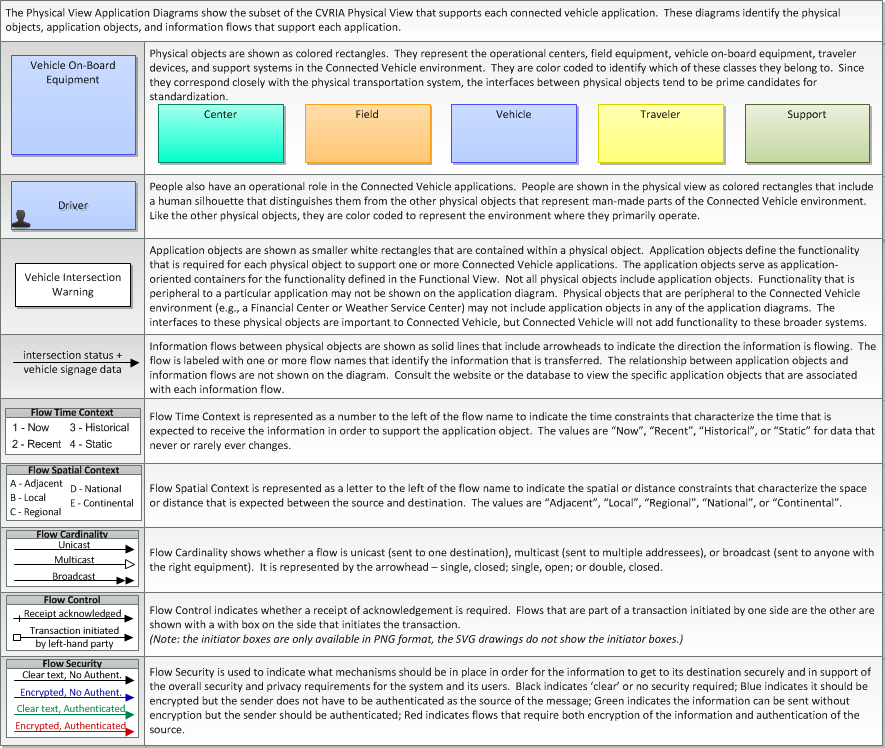
Includes Physical Objects:
| Physical Object | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Authorizing Center | Center | The 'Authorizing Center' provides the functionality needed to enable data exchange between and among mobile and fixed transportation users. Its primary mission is to enable safety, mobility and environmental communications-based applications for both mobile and non-mobile users. The Authorizing Center has some jurisdiction over limited access resources; typically this includes roadside application access and radio spectrum licensing. It may be implemented as an autonomous center or as a set of supporting services that are co-located within another center. |
| Center | Center | This general physical object is used to model core capabilities that are common to any center. |
| Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System | Support | The 'Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System' (CCMS) is a high-level aggregate representation of the interconnected systems that enable trusted communications between mobile devices and other mobile devices, roadside devices, and centers and protect data they handle from unauthorized access. Representing the different interconnected systems that make up a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), this physical object represents an end user view of the credentials management system with focus on the exchanges between the CCMS and user devices that support the secure distribution, use, and revocation of trust credentials. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Field | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway itself. In CVRIA, this physical object represents all of the other ITS field equipment that interfaces with and supports the Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE). This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| Other Authorizing Centers | Center | 'Other Authorizing Centers' provides a source and destination for information flows between multiple authorizing centers that manage permissions for the Connected Vehicle Environment. The interface represented by this object enables coordination of permissions between centers in different regions, jurisdictions, or application areas. |
| Personal Information Device | Traveler | The 'Personal Information Device' provides the capability for travelers to receive formatted traveler information wherever they are. Capabilities include traveler information, trip planning, and route guidance. Frequently a smart phone, the Personal Information Device provides travelers with the capability to receive route planning and other personally focused transportation services from the infrastructure in the field, at home, at work, or while en-route. Personal Information Devices may operate independently or may be linked with connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| Roadside Equipment | Field | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Vehicle OBE | Vehicle | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
Includes Application Objects:
| Application Object | Description | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| CCMS Authorization | "CCMS Authorization" components provide authorization credentials (e.g., pseudonym certificates) to end entities. The end entity applies for and obtains authorization credentials, enabling the end entity to enter the "Operational" state. This function requires an interactive dialog, including at minimum a Certificate Request from the end entity desiring certificates. This request will be checked for validity, with the embedded enrollment certificate checked against an internal blacklist. If all checks are passed, this function will distribute a bundle of linked pseudonym certificates suitable for use by the requesting end entity, with the characteristics and usage rules of those certificates dependent on the operational policies of the CCMS. It also provides the secure provisioning of a given object's Decryption Key in response to an authorized request from that object. The retrieved Decryption Key will be used by the receiving object to decrypt the "next valid" batch within the set of previously retrieved Security Credential batches. | Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System |
| Center Permission Management | "Center Permission Management" enables Connected Vehicle system users to request permission to access connected vehicle services. A center may request permission for the center or the infrastructure devices and vehicles associated with the center. | Center |
| Core Authorization | "Core Authorization" manages authorization mechanisms to define permissions for System Users. This enables the Core System to establish operational environments where different System Users may have different capabilities in terms of accessing Core services and interacting with one another. For instance, some Mobile elements may be authorized to request signal priority, or some Centers may be permitted to use the geographic broadcast service, while those without those permissions would not. | Authorizing Center |
| Personal Communications Support | "Personal Communications Support" supports secure, reliable communications with other connected devices. It provides the communications functions that add a timestamp, the message origin, and a digital signature in outbound messages and processes, verifies, and authenticates the same fields in inbound messages. It also encrypts (outbound) and decrypts (inbound) sensitive data. | Personal Information Device |
| Roadway Communications Support | "Roadway Communications Support" supports secure, reliable communications with other connected devices. It provides the communications functions that add a timestamp, the message origin, and a digital signature in outbound messages and processes, verifies, and authenticates the same fields in inbound messages. It also encrypts (outbound) and decrypts (inbound) sensitive data. | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| RSE Communications Support | "RSE Communications Support" supports secure, reliable communications with other connected devices. It provides the communications functions that add a timestamp, the message origin, and a digital signature in outbound messages and processes, verifies, and authenticates the same fields in inbound messages. It also encrypts (outbound) and decrypts (inbound) sensitive data. | Roadside Equipment |
| Vehicle Communications Support | "Vehicle Communications Support" supports secure, reliable communications with other connected devices. It provides the communications functions that add a timestamp, the message origin, and a digital signature in outbound messages and processes, verifies, and authenticates the same fields in inbound messages. It also encrypts (outbound) and decrypts (inbound) sensitive data. | Vehicle OBE |
Includes Information Flows:
| Information Flow | Description |
|---|---|
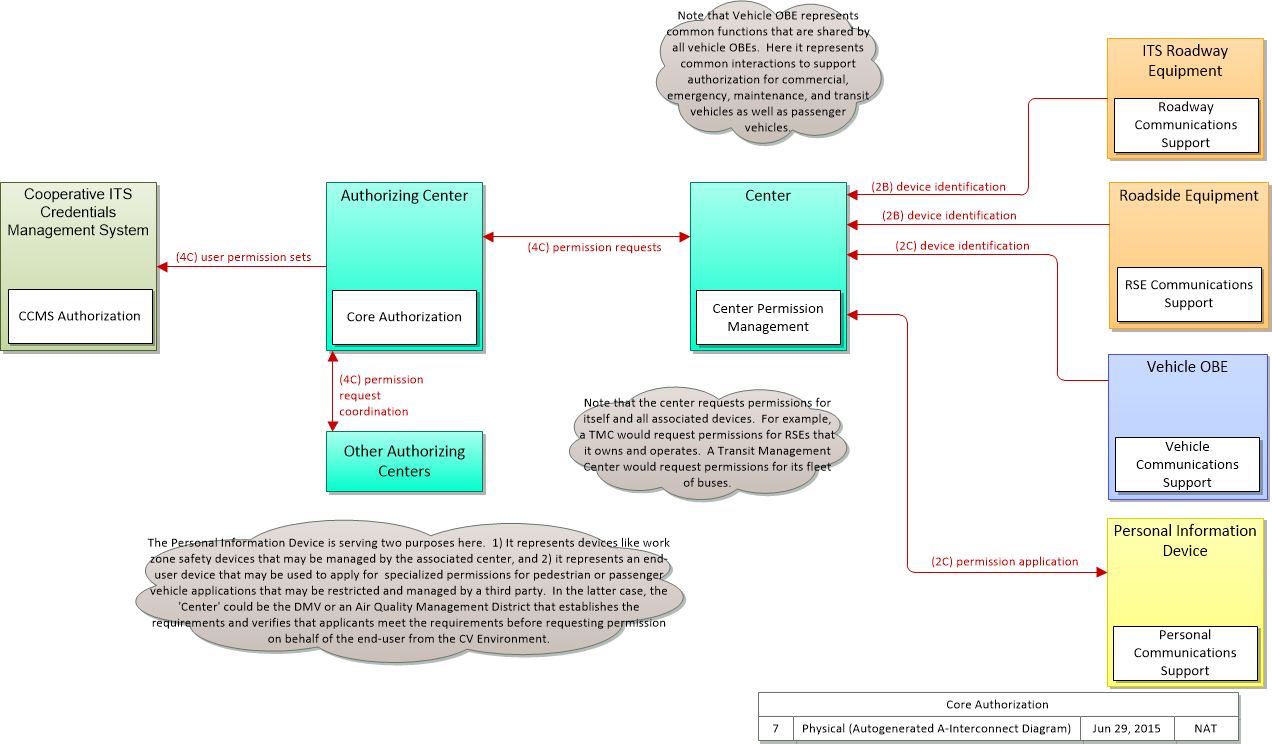
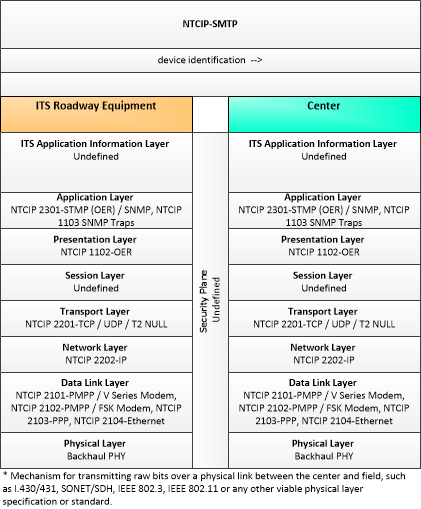
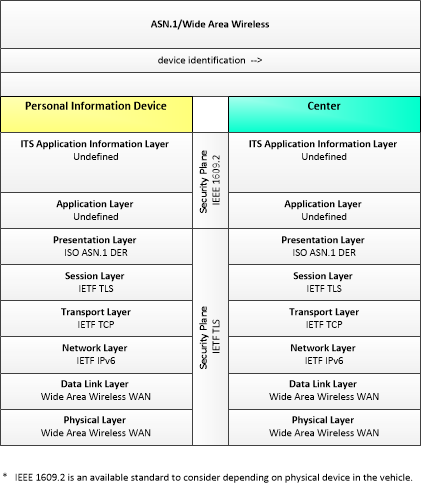
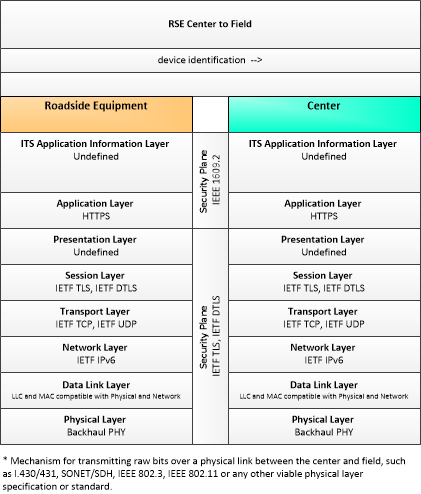
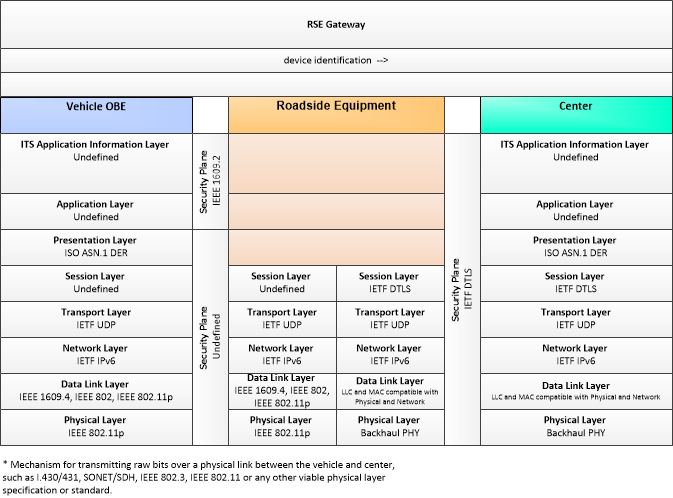
| device identification | An identifier and device type designation that is used to uniquely identify a device in the Connected Vehicle Environment. |
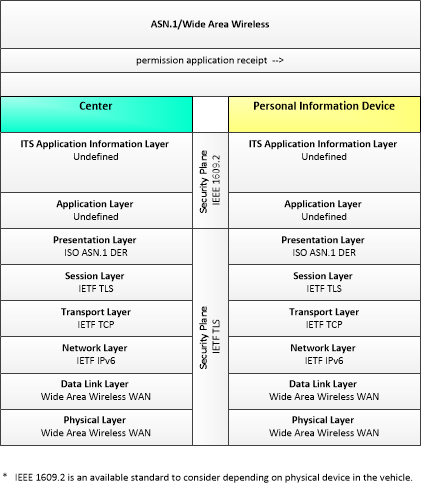
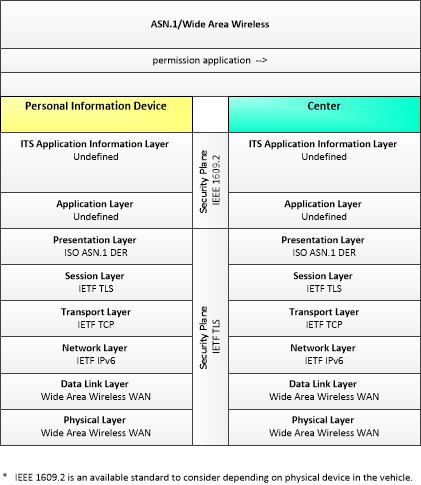
| permission application | A request for permission to access a Connected Vehicle service by an end-user that requires enrollment. This may include services granted to drivers of low emissions vehicles or pedestrians with special needs that require extended crossing times for example. |
| permission application receipt | An acknowledgment that an end-user application for a Connected Vehicle service was received and processed. |
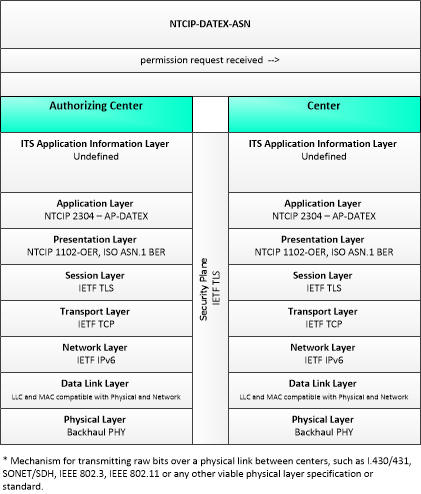
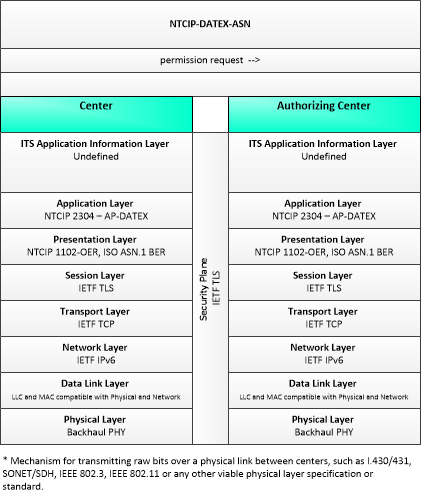
| permission request | A request for permission to access or use connected vehicle applications or services. The request identifies the users that require permission, the applications or services that are requested, and the geographic coverage where the permission is required. In this context, the 'users' may be a center, infrastructure equipment (e.g., RSEs), or vehicles that are owned and operated by the requestor. This request is for an initial set of permissions. See also permission update request. |
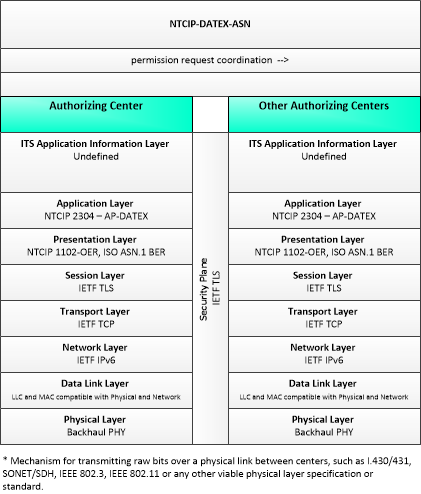
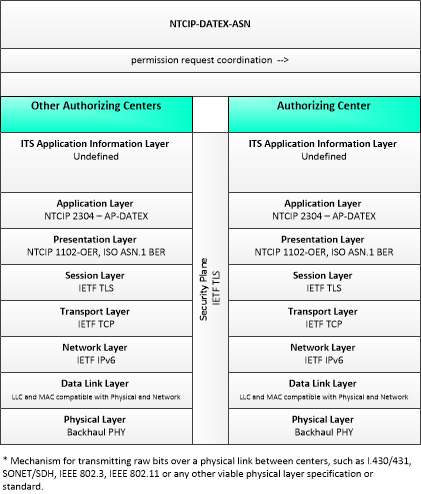
| permission request coordination | Coordination of permission requests between jurisdictions or regions that allow permissions to be managed that may span more than one jurisdiction. |
| permission request received | An acknowledgement that the permission request or permission update request was received. |
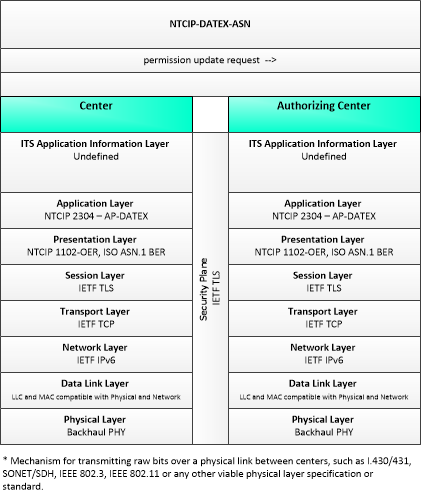
| permission update request | A request for an update to current permission to access or use connected vehicle applications or services. The request identifies the users that require updated permissions, the applications or services that are requested, and the geographic coverage where the permission is required. In this context, the 'users' may be a center, infrastructure equipment (e.g., RSEs), or vehicles that are owned and operated by the requestor. This request is for an update to existing permissions. See also permission request. |
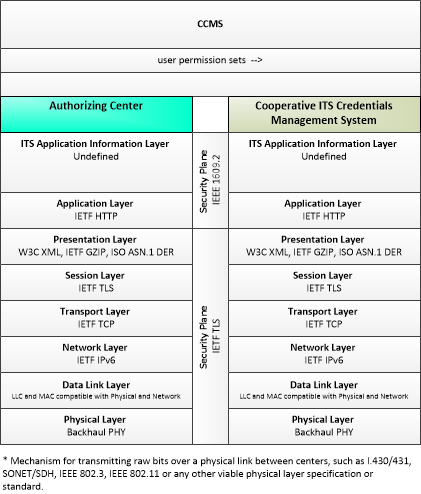
| user permission sets | This flow identifies users, user groups, and associated user permission sets for a geographic area or jurisdiction and set of connected vehicle applications or services. |
Application Interconnect Diagram
SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
Application Triples
Requirements
| Need | Requirement | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N4.001 | Applications need to protect data they handle from unauthorized access. This is required to support applications that exchange sensitive information, such as personally identifying or financial information, which if intercepted could compromise the privacy or financial records of the user. | 4.001 | Applications that function by exchanging data between entities shall be able to exchange encrypted data between those entities. |
| N4.002 | Applications need to establish trust between entities that operate components of the application. Such trust relationships are necessary so that applications can be assured that entities are who they say they are, and therefore trust the source and data it receives. | 4.002 | Applications shall verify that, for each entity on which an application component is installed, that entity is trusted by the provider of the application. |
| 4.003 | Applications shall be able to digitally sign all messages sent between entities. | ||
| 4.004 | Applications shall be able to verify the digital signature of received messages. | ||
| 4.005 | Digital signatures used to ensure trust shall be generated independently of the application sending the message to be signed. | ||
| N4.003 | Applications need to revoke the trust relationship they have between entities when necessary. A trusted entity may operate in a fashion that indicates it should no longer be trusted, in which case applications must have a way of revoking that trust. | 4.006 | Applications shall identify entities that provide messages to the application that are improperly formatted. |
| 4.007 | Applications shall identify entities that provide messages to the application that are logically inconsistent. | ||
| 4.008 | Applications shall revoke personal trust (trust by the application) when a repeated pattern of messages from a given entity falls outside of the applications tolerances. | ||
| 4.009 | Applications shall be able to report suspicious behavior to third party authentication providers. | ||
| 4.010 | Applications shall be able to accept messages from the third party authentication provider that identifies entities unworthy of trust. | ||
| 4.011 | Applications shall be able to revoke trust between itself and an entity if that entity is identified by the third party authentication provider as untrustworthy. | ||
| N4.004 | All participants in the Connected Vehicle Environment need to operate on a common time base. Coordination of time between the entities that operate applications as well as those providing Core services prevents internal errors and enables time-sensitive interactions between application components. | 4.012 | All applications shall use the same time source as the basis for timing. |
| N4.005 | Core Authorization needs to manage authorization mechanisms to define roles, responsibilities and permissions for applications. This enables Core Authorization to establish operational environments where different System Users may have different capabilities in terms of accessing Core services and interacting with one another. For instance, some mobile entities may be authorized to request signal priority, or some Centers may be permitted to use the geographic broadcast service, while those without those permissions would not. | 4.013 | Core Authorization shall define its operational scope by a geographic boundary. |
| 4.014 | Core Authorization shall maintain a listing of all applications it manages permissions for within its operational scope. | ||
| 4.015 | Core Authorization shall provide a mechanism for modifying permissions of applications. | ||
| 4.016 | Core Authorization shall provide a mechanism for entities to verify the permissions of applications. | ||
| 4.017 | Core Authorization shall provide a mechanism for applications to verify the permissions of entities. | ||
| N4.006 | Core Authorization needs to connect to the Internet. This allows Core Authorization to provide services to any entity capable of connecting to the Internet. | 4.018 | Core Authorization shall provide all of its services through the Internet. |
Related Sources
- Core System Concept of Operations (ConOps), Final revE, 10/24/2011
Security
In order to participate in this application, each physical object should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Physical Object Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Object | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability | Security Class |
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | ||||
In order to participate in this application, each information flow triple should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Information Flow Security | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Destination | Information Flow | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability |
| Basis | Basis | Basis | |||
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | |||||