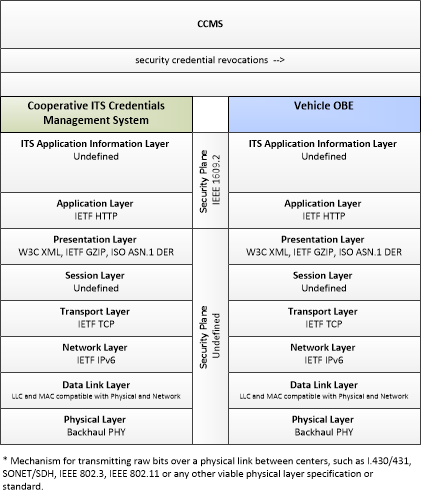
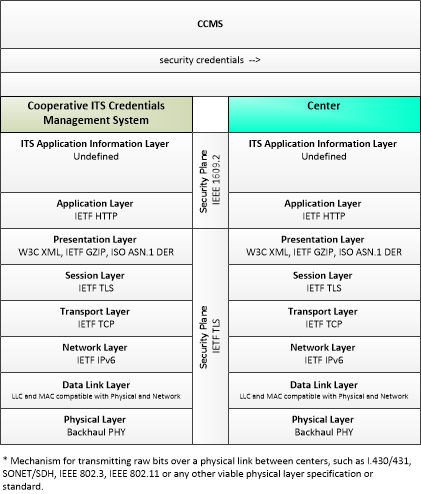
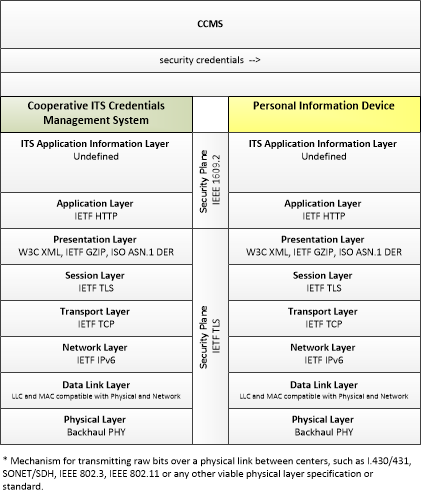
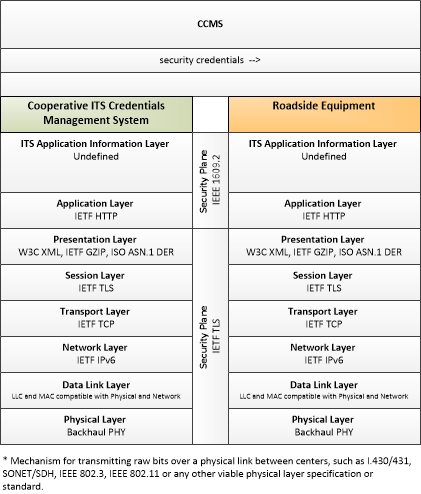
Type: Support
Groups:- Security
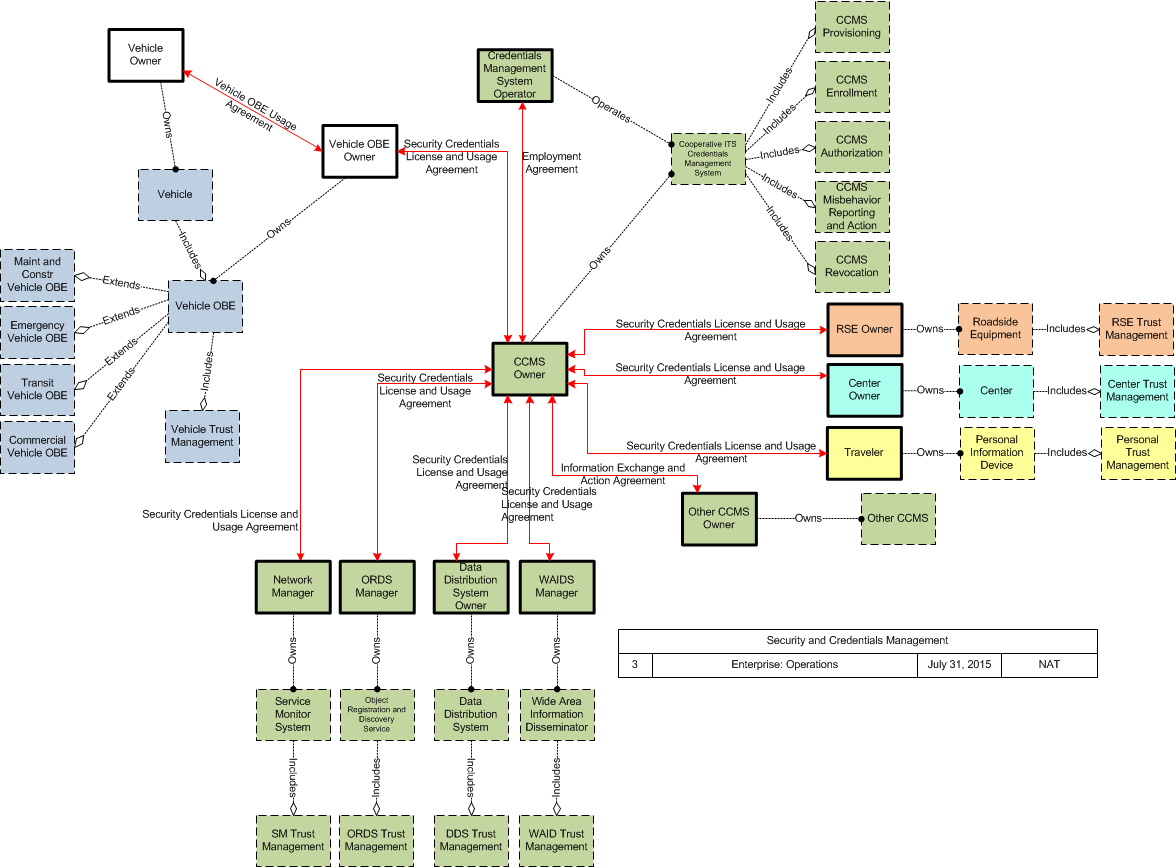
Security and Credentials Management
Security and Credentials Management (SCM) is a support application that is used to ensure the trusted communications between mobile devices and other mobile devices or roadside devices and protect data they handle from unauthorized access. The application grants trust credentials to qualified mobile devices and infrastructure devices in the Connected Vehicle Environment so that those devices may be considered trusted by other devices that receive trust credentials from the SCM application. The application allows credentials to be requested and revoked, as well as to secure the exchange of trust credentials between parties, so that no other party can intercept and use those credentials illegitimately. The application provides security to the transmissions between connected devices, ensuring authenticity and integrity of the transmissions. Additional security features include privacy protection, authorization and privilege class definition, as well as non-repudiation of origin.
Enterprise
SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
Business Interaction Matrix:
| Security and Credentials Management Operations Stage | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Owner | Vehicle OBE Owner | RSE Owner | Traveler | Center Owner | CCMS Owner | Data Distribution System Owner | Credentials Management System Operator | Network Manager | ORDS Manager | WAIDS Manager | Other CCMS Owner | |
| Vehicle Owner | Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | |||||||||||
| Vehicle OBE Owner | Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | ||||||||||
| RSE Owner | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | |||||||||||
| Traveler | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | |||||||||||
| Center Owner | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | |||||||||||
| CCMS Owner | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | Employment Agreement | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | ||
| Data Distribution System Owner | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | |||||||||||
| Credentials Management System Operator | Employment Agreement | |||||||||||
| Network Manager | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | |||||||||||
| ORDS Manager | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | |||||||||||
| WAIDS Manager | Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | |||||||||||
| Other CCMS Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | |||||||||||
Includes Enterprise Objects:
| Enterprise Object | Description |
|---|---|
| CCMS Owner | The organization that is responsible for the Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System. |
| Center Owner | General representation of the owner of the general "Center" physical object. |
| Credentials Management System Operator | The 'Credentials Management System Operator' represents the person or people that monitor and manage the Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System. These personnel monitor and manage the secure distribution, use, and revocation of trust credentials. |
| Data Distribution System Owner | The enterprise charged with providing data distribution services in the connected vehicle environment. This enterprise serves as broker between information and data providers and consumers. |
| Network Manager | The "Network Manager" represents the entity responsible for operating and maintaining the connected vehicle infrastructure including RSE and DDS, charged with monitoring its operational status and responding to operational issues related to monitored applications. |
| ORDS Manager | The "ORDS Manager" represents the entity responsible for operating and maintaining the Object Registration and Discovery Service, charged with monitoring its operational status and responding to operational issues related to it. |
| Other CCMS Owner | Owner of another CCMS |
| RSE Owner | The owner of roadside equipment. |
| Traveler | The 'Traveler' represents any individual who uses transportation services. The interfaces to the traveler provide general pre-trip and en-route information supporting trip planning, personal guidance, and requests for assistance in an emergency that are relevant to all transportation system users. It also represents users of a public transportation system and addresses interfaces these users have within a transit vehicle or at transit facilities such as roadside stops and transit centers. |
| Vehicle OBE Owner | The entity, individual, group or corporation that owns the Vehicle On-Board equipment. This could be the same as the Vehicle Owner, but it could be a third part that licenses the use of the OBE to the Owner. |
| Vehicle Owner | The individual, group of individuals or corporate entity that is identified as the registered owner of the Vehicle under state law. |
| WAIDS Manager | The "WAIDS Manager" represents the entity responsible for operating and maintaining the Wide Area Information Disseminator, charged with monitoring its operational status and responding to operational issues related to it. |
Includes Resources:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| CCMS Authorization | "CCMS Authorization" components provide authorization credentials (e.g., pseudonym certificates) to end entities. The end entity applies for and obtains authorization credentials, enabling the end entity to enter the "Operational" state. This function requires an interactive dialog, including at minimum a Certificate Request from the end entity desiring certificates. This request will be checked for validity, with the embedded enrollment certificate checked against an internal blacklist. If all checks are passed, this function will distribute a bundle of linked pseudonym certificates suitable for use by the requesting end entity, with the characteristics and usage rules of those certificates dependent on the operational policies of the CCMS. It also provides the secure provisioning of a given object's Decryption Key in response to an authorized request from that object. The retrieved Decryption Key will be used by the receiving object to decrypt the "next valid" batch within the set of previously retrieved Security Credential batches. |
| CCMS Enrollment | "CCMS Enrollment" components provide enrollment credentials to end entities. The end entity applies for and obtains enrollment credentials that can be used to communicate with other CCMS components, entering the "Unauthorized" state. CCMS Enrollment components also participate in de-registration processes through interaction with CCMS Revocation components. |
| CCMS Misbehavior Reporting and Action | "CCMS Misbehavior Reporting and Action" components process misbehavior reports from end entities. Misbehavior reports are analyzed and investigated if warranted. Investigated misbehavior reports are correlated with end entities and systemic issues are identified. If revocation is warranted, this component provides information to Authorization or Revocation components to initiate revocation and/or blacklisting, as appropriate. |
| CCMS Provisioning | "CCMS Provisioning" components provide the end entity with material that allows it to enter the "Unenrolled" state. This consists of root certificates and the crypto material that allows it to communicate securely with the Enrollment components. This function ensures the requesting entity meets requirements for provisioning and provides the certificates and relevant policy information to entities that meet the requirements. |
| CCMS Revocation | "CCMS Revocation" components generate the internal blacklist and Certificate Revocation List (CRL) and distribute them to other CCMS components and end entities. Once placed on the CRL, an end entity is in the Unauthorized state. Once placed on the blacklist, an end entity is in the Unenrolled state. |
| Center | This general physical object is used to model core capabilities that are common to any center. |
| Center Trust Management | "Center Trust Management" manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Security and Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to the Connected Vehicle Environment security. |
| Commercial Vehicle OBE | The Commercial Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) resides in a commercial vehicle and provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support safe and efficient commercial vehicle operations. It provides two-way communications between the commercial vehicle drivers, their fleet managers, attached freight equipment, and roadside officials. In CVRIA, a separate 'Vehicle OBE' physical object supports the general V2V and V2I safety applications and other applications that apply to all vehicles, including commercial vehicles. The Commercial Vehicle OBE supplements these general capabilities with capabilities that are specific to commercial vehicles. |
| Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System | The 'Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System' (CCMS) is a high-level aggregate representation of the interconnected systems that enable trusted communications between mobile devices and other mobile devices, roadside devices, and centers and protect data they handle from unauthorized access. Representing the different interconnected systems that make up a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), this physical object represents an end user view of the credentials management system with focus on the exchanges between the CCMS and user devices that support the secure distribution, use, and revocation of trust credentials. |
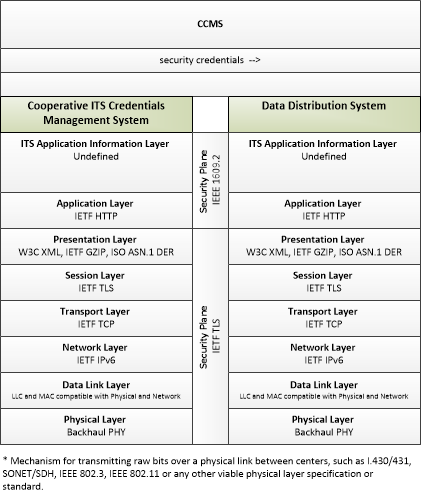
| Data Distribution System | The 'Data Distribution System' collects, processes, and distributes connected vehicle data, connecting data producers with data consumers and facilitating data exchange in the Connected Vehicle Environment. |
| DDS Trust Management | 'DDS Trust Management' manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to the Connected Vehicle Environment security. |
| Emergency Vehicle OBE | The Emergency Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) resides in an emergency vehicle and provides the processing, storage, and communications functions that support public safety-related connected vehicle applications. It represents a range of vehicles including those operated by police, fire, and emergency medical services. In addition, it represents other incident response vehicles including towing and recovery vehicles and freeway service patrols. It includes two-way communications to support coordinated response to emergencies. In CVRIA, a separate 'Vehicle OBE' physical object supports the general V2V and V2I safety applications and other applications that apply to all vehicles, including emergency vehicles. The Emergency Vehicle OBE supplements these general capabilities with capabilities that are specific to emergency vehicles. |
| Maint and Constr Vehicle OBE | The 'Maint and Constr Vehicle OBE' resides in a maintenance, construction, or other specialized service vehicle or equipment and provides the processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support highway maintenance and construction. All types of maintenance and construction vehicles are covered, including heavy equipment and supervisory vehicles. The MCV OBE provides two-way communications between drivers/operators and dispatchers and maintains and communicates current location and status information. A wide range of operational status is monitored, measured, and made available, depending on the specific type of vehicle or equipment. A snow plow for example, would monitor whether the plow is up or down and material usage information. The Maint and Constr Vehicle OBE may also contain capabilities to monitor vehicle systems to support maintenance of the vehicle itself and include sensors that monitor environmental conditions such as road condition and surface weather information. This can include a diverse set of mobile environmental sensing platforms, including wheeled vehicles and any other vehicle that collects and reports environmental information. In CVRIA, a separate 'Vehicle OBE' physical object supports the general V2V and V2I safety applications and other applications that apply to all vehicles, including maintenance and construction vehicles. The Maint and Constr Vehicle OBE supplements these general applications with applications that are specific to maintenance and construction vehicles. |
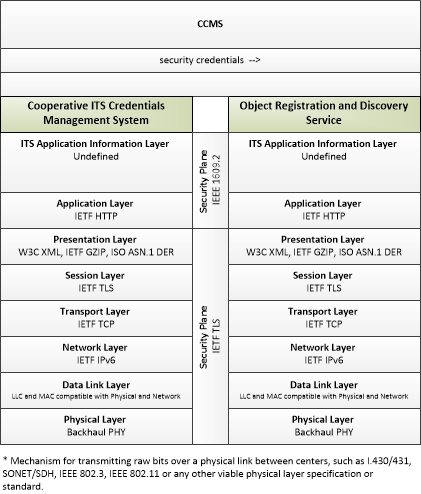
| Object Registration and Discovery Service | The 'Object Registration and Discovery Service' represents one or more center-based applications that provide registration and lookup services necessary to allow objects to locate (for communications purposes) other objects operating within the Connected Vehicle Environment. These registration and discovery services are support services that enable other applications. |
| ORDS Trust Management | 'ORDS Trust Management' manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and keys and identifies, logs and reports events that may indicate a threat to Connected Vehicle security. |
| Other CCMS | Representing another Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System (CCMS), 'Other CCMS' is intended to provide a source and destination for information exchange between peer credentials management systems. It supports modeling of projects or regions that include multiple interconnected CCMS that manage credentials distribution and management in the connected vehicle environment. |
| Personal Information Device | The 'Personal Information Device' provides the capability for travelers to receive formatted traveler information wherever they are. Capabilities include traveler information, trip planning, and route guidance. Frequently a smart phone, the Personal Information Device provides travelers with the capability to receive route planning and other personally focused transportation services from the infrastructure in the field, at home, at work, or while en-route. Personal Information Devices may operate independently or may be linked with connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| Personal Trust Management | "Personal Trust Management" manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Security and Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to the Connected Vehicle Environment security. |
| Roadside Equipment | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| RSE Trust Management | "RSE Trust Management" manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Security and Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and keys and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to Connected Vehicle Environment security. |
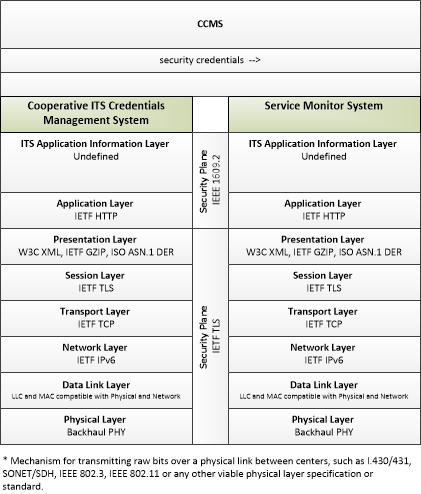
| Service Monitor System | The 'Service Monitor System' represents one or more center-based systems that provide monitoring, management and control services necessary to other applications and/or devices operating within the Connected Vehicle Environment. These support services enable other applications to provide transportation services. |
| SM Trust Management | 'SM Trust Management' manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and keys and identifies, logs and reports events that may indicate a threat to Connected Vehicle security. |
| Transit Vehicle OBE | The Transit Vehicle On-Board equipment (OBE) resides in a transit vehicle and provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support safe and efficient movement of passengers. The types of transit vehicles containing this physical object include buses, paratransit vehicles, light rail vehicles, other vehicles designed to carry passengers, and supervisory vehicles. It collects ridership levels and supports electronic fare collection. It supports a traffic signal prioritization function that communicates with the roadside physical object to improve on-schedule performance. Automated vehicle location enhances the information available to the transit operator enabling more efficient operations. On-board sensors support transit vehicle maintenance. The physical object supports on-board security and safety monitoring. This monitoring includes transit user or vehicle operator activated alarms (silent or audible), as well as surveillance and sensor equipment. The surveillance equipment includes video (e.g. CCTV cameras), audio systems and/or event recorder systems. It also furnishes travelers with real-time travel information, continuously updated schedules, transfer options, routes, and fares. In CVRIA, a separate 'Vehicle OBE' physical object supports the general V2V and V2I safety applications and other applications that apply to all vehicles, including transit vehicles. The Transit Vehicle OBE supplements these general capabilities with capabilities that are specific to transit vehicles. |
| Vehicle | The conveyance that provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support efficient, safe, and convenient travel. These functions reside in general vehicles including personal automobiles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, or other vehicle types. |
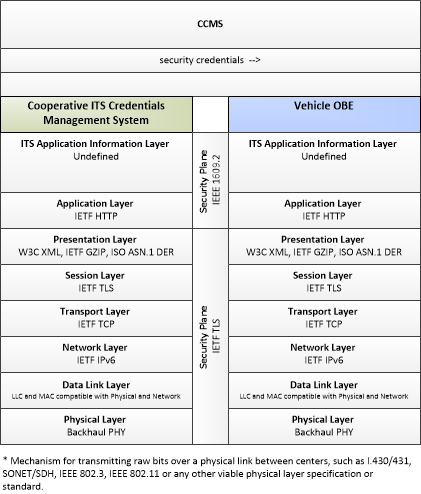
| Vehicle OBE | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
| Vehicle Trust Management | "Vehicle Trust Management" manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Security and Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to the Connected Vehicle Environment security. |
| WAID Trust Management | 'WAID Trust Management' manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to the Connected Vehicle Environment security. |
| Wide Area Information Disseminator | The 'Wide Area Information Disseminator' represents the Connected Vehicle center based systems and communications equipment that is used to send messages to equipped vehicles using wide-area wireless communications such as satellite radio, terrestrial FM broadcast subcarrier, or cellular data networks. |
Includes Roles:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Operates | An Enterprise controls the functionality and state of the target Resource. An Enterprise that Operates a resource is considered Responsible. |
| Owns | An Enterprise has financial ownership and control over the Resource. An Enterprise that Owns a resource is considered Accountable. |
Includes Coordination:
| Coordination | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Employment Agreement | Agreement | An agreement between an individual and a corporation or government entity, whereupon the individual agrees to provide labor to the corporation/agency, which in turn compensates the employee. Stipulates level of compensation, working conditions, necessary equipment and training and expectations of employee performance. |
| Extends | Includes | Indicates that one component includes all of the functionality of another component, and in provides additional functionality beyond that other component's. |
| Includes | Includes | Indicates that one component is entirely contained within another component. |
| Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Agreement | An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. This also includes a specification for action that shall, should or may be taken by one party in response to this information. |
| Security Credentials License and Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which a connected vehicle device owner gains access to security credentials, and agrees to protect and use those credentials in accordance with restrictions and safeguards documented in this agreement. |
| Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one entity permission to use a Vehicle OBE that the other party controls. |
Functional
Includes Processes:
Includes Data Flows:
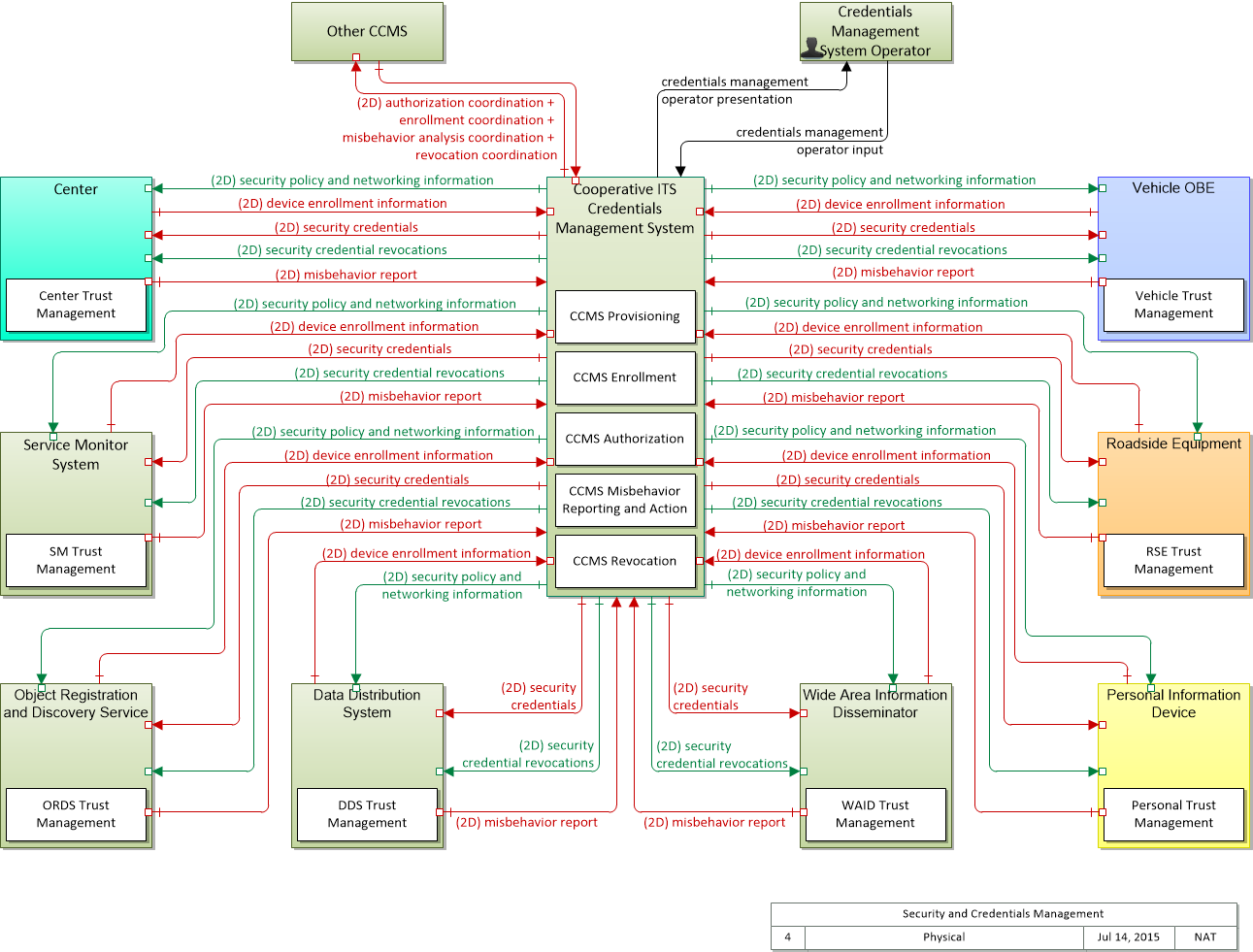
Physical
SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
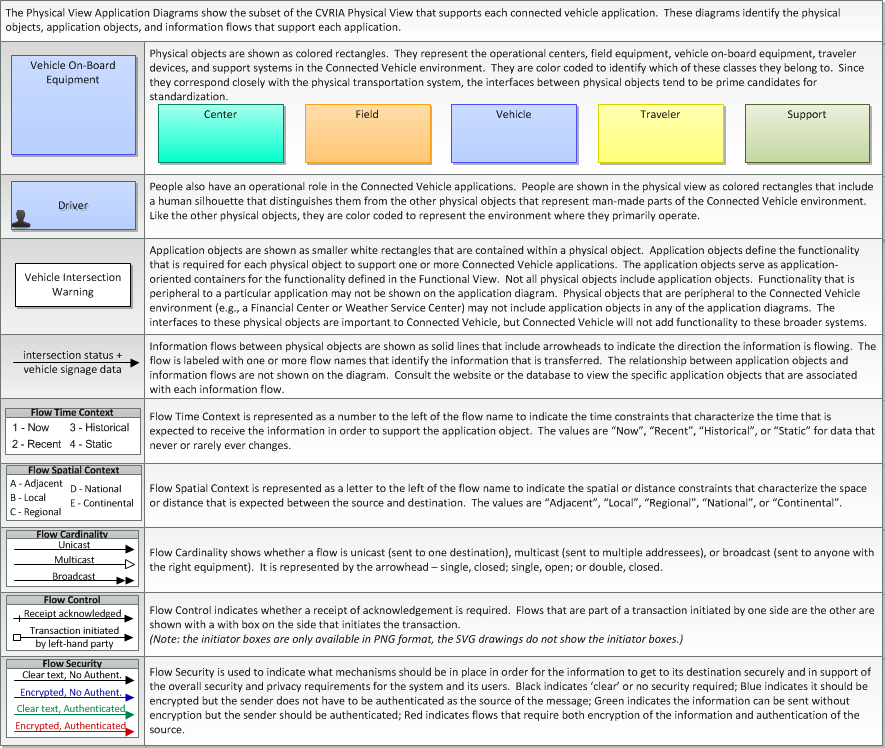
Includes Physical Objects:
| Physical Object | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Center | Center | This general physical object is used to model core capabilities that are common to any center. |
| Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System | Support | The 'Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System' (CCMS) is a high-level aggregate representation of the interconnected systems that enable trusted communications between mobile devices and other mobile devices, roadside devices, and centers and protect data they handle from unauthorized access. Representing the different interconnected systems that make up a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), this physical object represents an end user view of the credentials management system with focus on the exchanges between the CCMS and user devices that support the secure distribution, use, and revocation of trust credentials. |
| Credentials Management System Operator | Support | The 'Credentials Management System Operator' represents the person or people that monitor and manage the Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System. These personnel monitor and manage the secure distribution, use, and revocation of trust credentials. |
| Data Distribution System | Support | The 'Data Distribution System' collects, processes, and distributes connected vehicle data, connecting data producers with data consumers and facilitating data exchange in the Connected Vehicle Environment. |
| Object Registration and Discovery Service | Support | The 'Object Registration and Discovery Service' represents one or more center-based applications that provide registration and lookup services necessary to allow objects to locate (for communications purposes) other objects operating within the Connected Vehicle Environment. These registration and discovery services are support services that enable other applications. |
| Other CCMS | Support | Representing another Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System (CCMS), 'Other CCMS' is intended to provide a source and destination for information exchange between peer credentials management systems. It supports modeling of projects or regions that include multiple interconnected CCMS that manage credentials distribution and management in the connected vehicle environment. |
| Personal Information Device | Traveler | The 'Personal Information Device' provides the capability for travelers to receive formatted traveler information wherever they are. Capabilities include traveler information, trip planning, and route guidance. Frequently a smart phone, the Personal Information Device provides travelers with the capability to receive route planning and other personally focused transportation services from the infrastructure in the field, at home, at work, or while en-route. Personal Information Devices may operate independently or may be linked with connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| Roadside Equipment | Field | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Service Monitor System | Support | The 'Service Monitor System' represents one or more center-based systems that provide monitoring, management and control services necessary to other applications and/or devices operating within the Connected Vehicle Environment. These support services enable other applications to provide transportation services. |
| Vehicle OBE | Vehicle | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
| Wide Area Information Disseminator | Support | The 'Wide Area Information Disseminator' represents the Connected Vehicle center based systems and communications equipment that is used to send messages to equipped vehicles using wide-area wireless communications such as satellite radio, terrestrial FM broadcast subcarrier, or cellular data networks. |
Includes Application Objects:
| Application Object | Description | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| CCMS Authorization | "CCMS Authorization" components provide authorization credentials (e.g., pseudonym certificates) to end entities. The end entity applies for and obtains authorization credentials, enabling the end entity to enter the "Operational" state. This function requires an interactive dialog, including at minimum a Certificate Request from the end entity desiring certificates. This request will be checked for validity, with the embedded enrollment certificate checked against an internal blacklist. If all checks are passed, this function will distribute a bundle of linked pseudonym certificates suitable for use by the requesting end entity, with the characteristics and usage rules of those certificates dependent on the operational policies of the CCMS. It also provides the secure provisioning of a given object's Decryption Key in response to an authorized request from that object. The retrieved Decryption Key will be used by the receiving object to decrypt the "next valid" batch within the set of previously retrieved Security Credential batches. | Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System |
| CCMS Enrollment | "CCMS Enrollment" components provide enrollment credentials to end entities. The end entity applies for and obtains enrollment credentials that can be used to communicate with other CCMS components, entering the "Unauthorized" state. CCMS Enrollment components also participate in de-registration processes through interaction with CCMS Revocation components. | Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System |
| CCMS Misbehavior Reporting and Action | "CCMS Misbehavior Reporting and Action" components process misbehavior reports from end entities. Misbehavior reports are analyzed and investigated if warranted. Investigated misbehavior reports are correlated with end entities and systemic issues are identified. If revocation is warranted, this component provides information to Authorization or Revocation components to initiate revocation and/or blacklisting, as appropriate. | Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System |
| CCMS Provisioning | "CCMS Provisioning" components provide the end entity with material that allows it to enter the "Unenrolled" state. This consists of root certificates and the crypto material that allows it to communicate securely with the Enrollment components. This function ensures the requesting entity meets requirements for provisioning and provides the certificates and relevant policy information to entities that meet the requirements. | Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System |
| CCMS Revocation | "CCMS Revocation" components generate the internal blacklist and Certificate Revocation List (CRL) and distribute them to other CCMS components and end entities. Once placed on the CRL, an end entity is in the Unauthorized state. Once placed on the blacklist, an end entity is in the Unenrolled state. | Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System |
| Center Trust Management | "Center Trust Management" manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Security and Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to the Connected Vehicle Environment security. | Center |
| DDS Trust Management | 'DDS Trust Management' manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to the Connected Vehicle Environment security. | Data Distribution System |
| ORDS Trust Management | 'ORDS Trust Management' manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and keys and identifies, logs and reports events that may indicate a threat to Connected Vehicle security. | Object Registration and Discovery Service |
| Personal Trust Management | "Personal Trust Management" manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Security and Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to the Connected Vehicle Environment security. | Personal Information Device |
| RSE Trust Management | "RSE Trust Management" manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Security and Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and keys and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to Connected Vehicle Environment security. | Roadside Equipment |
| SM Trust Management | 'SM Trust Management' manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and keys and identifies, logs and reports events that may indicate a threat to Connected Vehicle security. | Service Monitor System |
| Vehicle Trust Management | "Vehicle Trust Management" manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Security and Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to the Connected Vehicle Environment security. | Vehicle OBE |
| WAID Trust Management | 'WAID Trust Management' manages the certificates and associated keys that are used to sign, encrypt, decrypt, and authenticate messages. It communicates with the Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System to maintain a current, valid set of security certificates and identifies, logs, and reports events that may indicate a threat to the Connected Vehicle Environment security. | Wide Area Information Disseminator |
Includes Information Flows:
| Information Flow | Description |
|---|---|
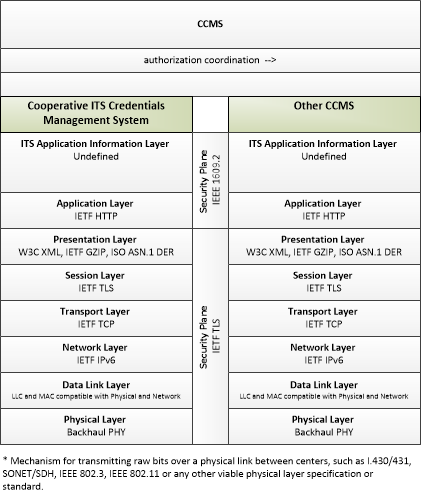
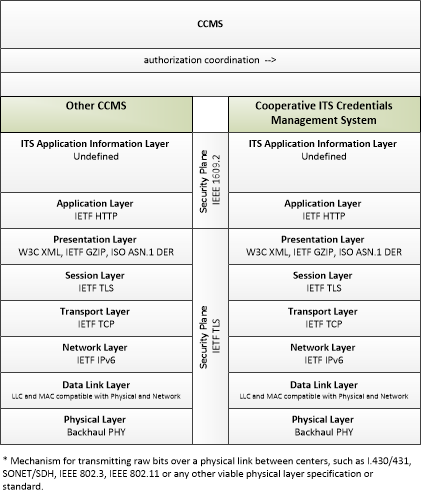
| authorization coordination | Sharing of pseudonym certificate policies and end entity enrollments and revocations to support authorization of end entities that are enrolled with another trusted CCMS. |
| credentials management operator input | User input from the credentials management system operator including requests to monitor current system operation and inputs to affect system operation. |
| credentials management operator presentation | Presentation of information to the credentials management system operator including current operational status of the credentials management system. |
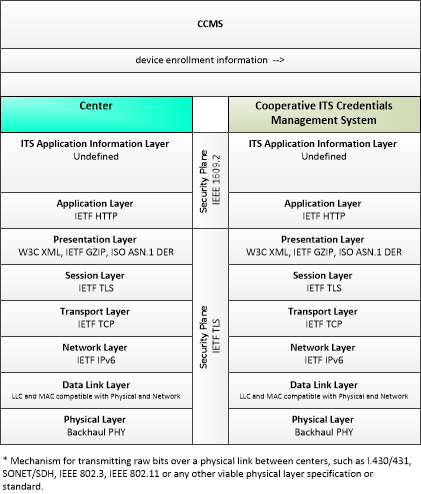
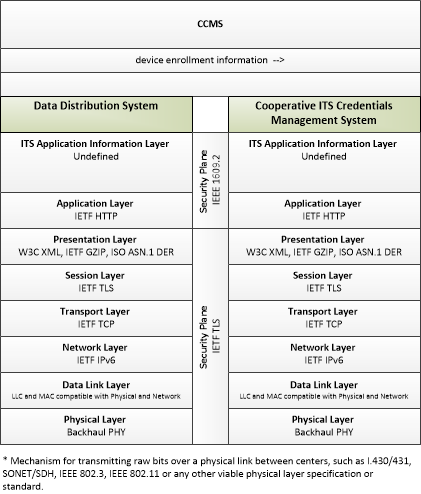
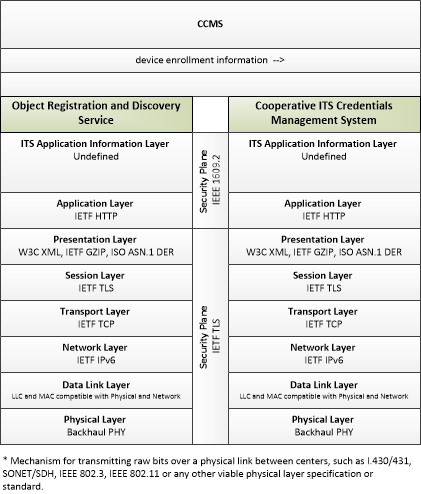
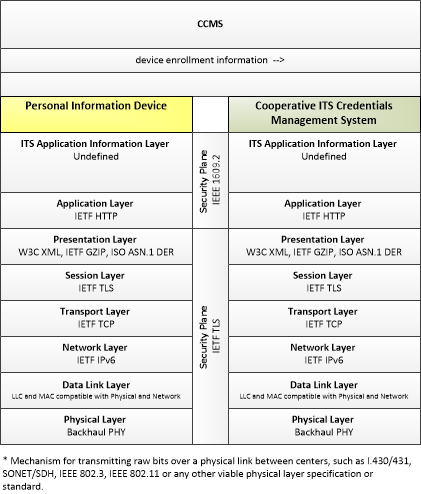
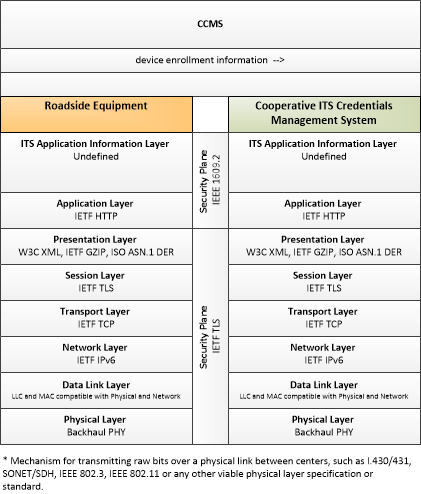
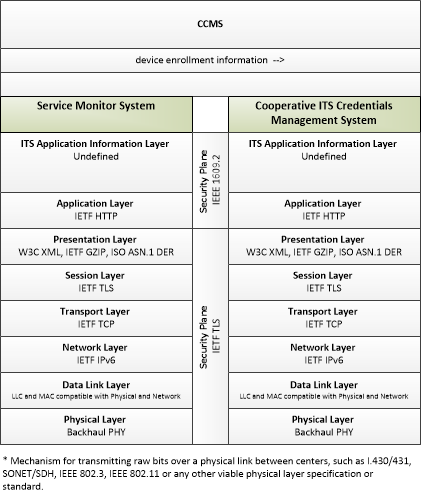
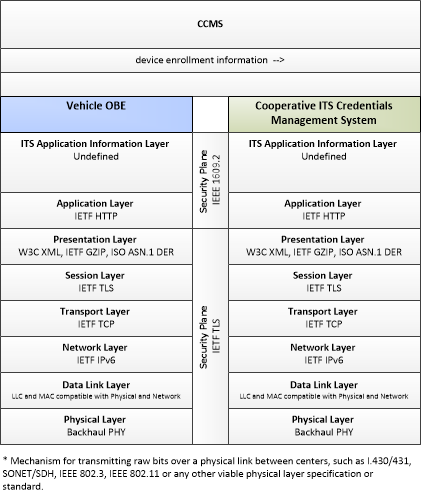
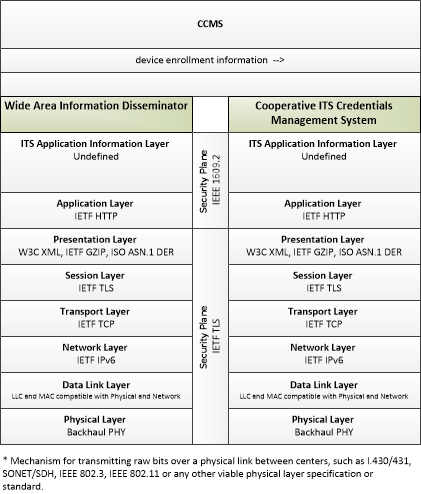
| device enrollment information | Information provided by an end entity to support enrollment and authorization for the Connected Vehicle environment. This includes device identification, requested permissions and restrictions, and security credentials used to establish the current level of trust and eligibility for enrollment and authorization. |
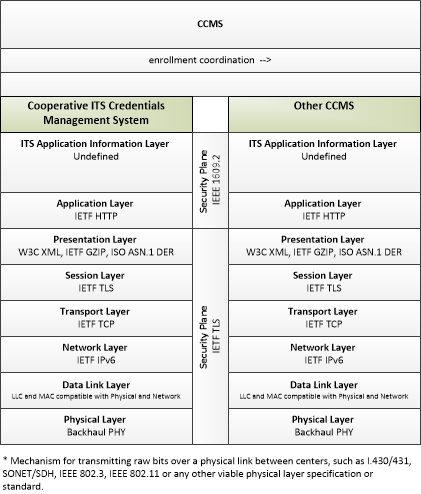
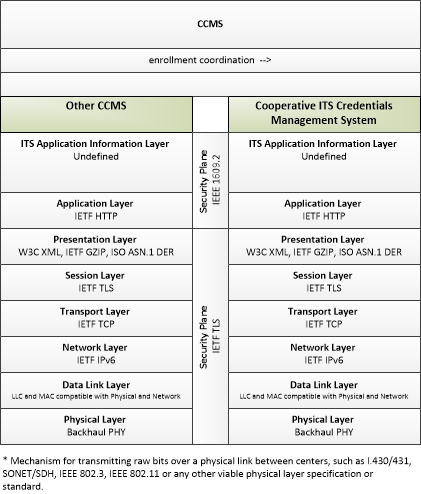
| enrollment coordination | Sharing of enrollment policies, certification mechanisms, registration and deregistration identifier types, registered and deregistered end entities, and other information that supports enrollment process coordination with another CCMS. |
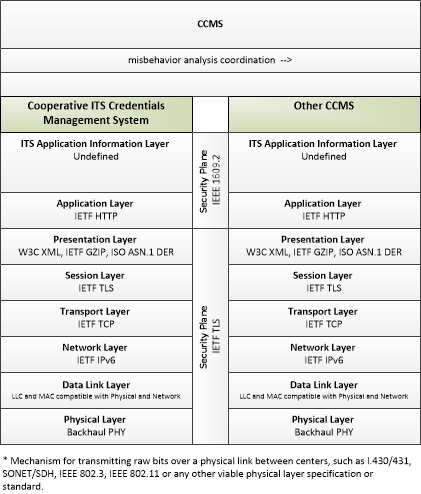
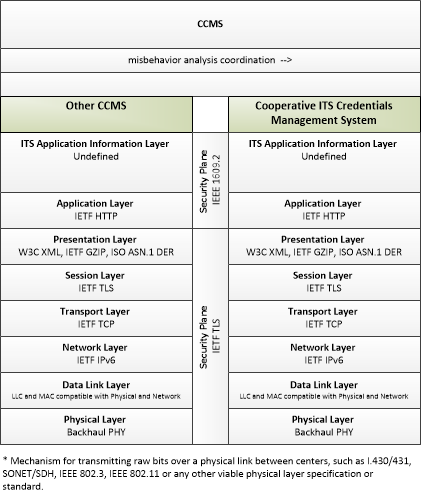
| misbehavior analysis coordination | Sharing of misbehavior policy, reports, and analysis results, including suspected and convicted end entities and other information that coordinates misbehavior detection, analysis, and resolution with another CCMS. |
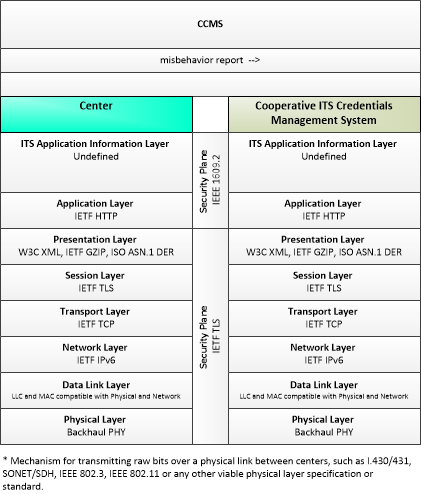
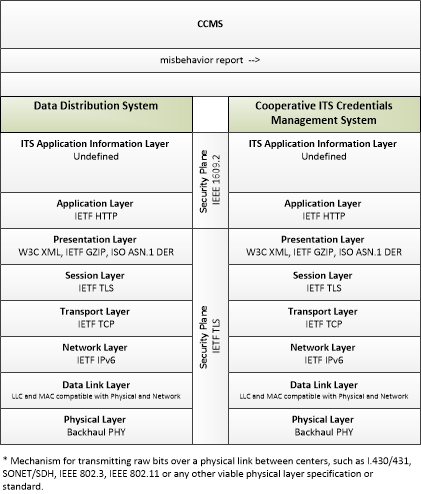
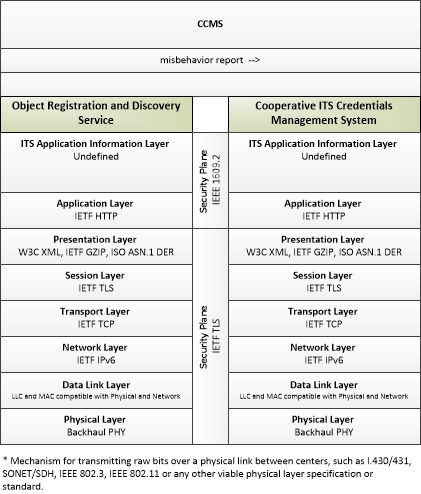
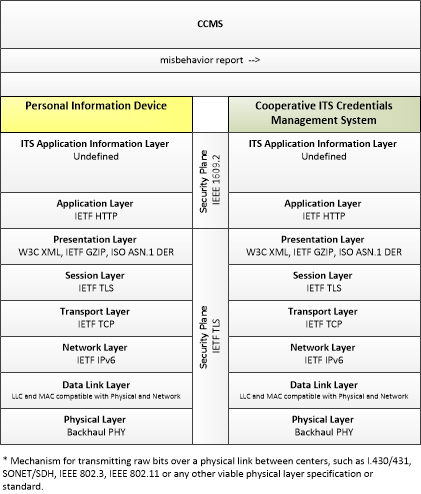
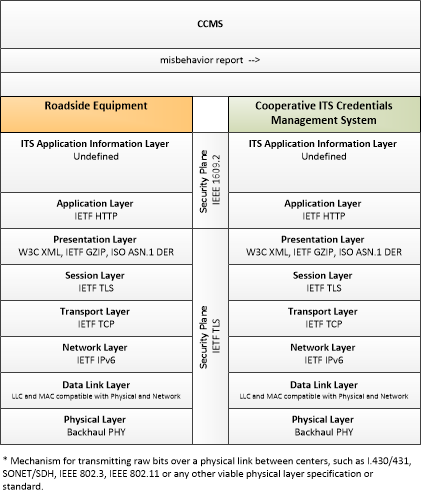
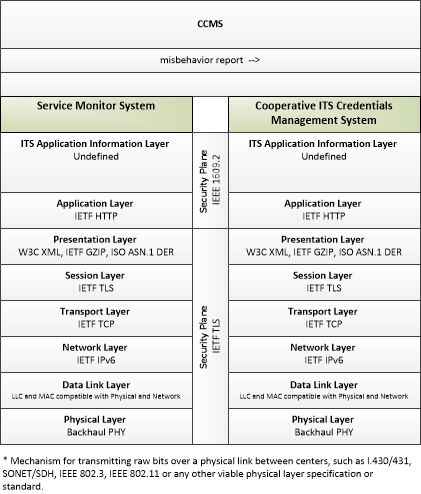
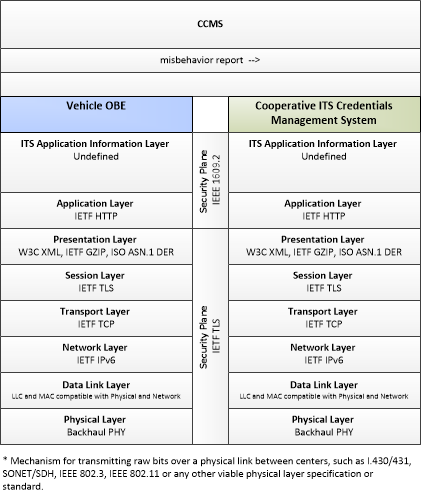
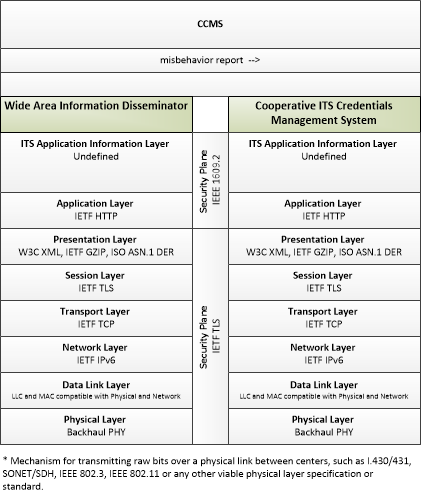
| misbehavior report | Notification of potential security issues encountered in processing messages, including message authentication or integrity failures, plausibility failures, or other issues appropriate to the CCMS' misbehavior policies. |
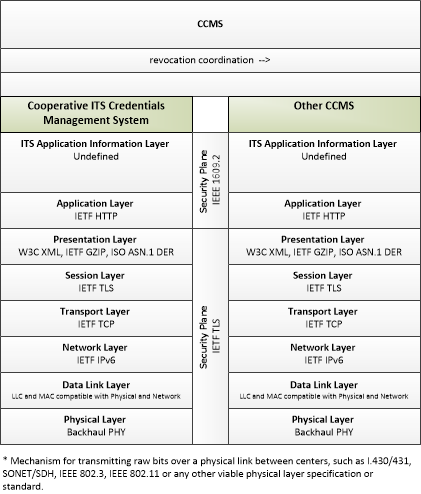
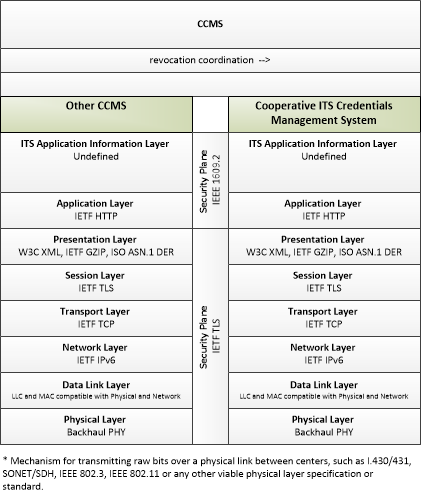
| revocation coordination | Sharing of revocation policies, Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs), and internal blacklists, and other information that supports revocation process coordination with another CCMS. |
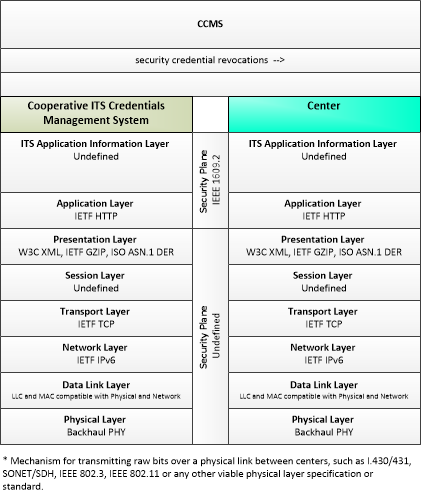
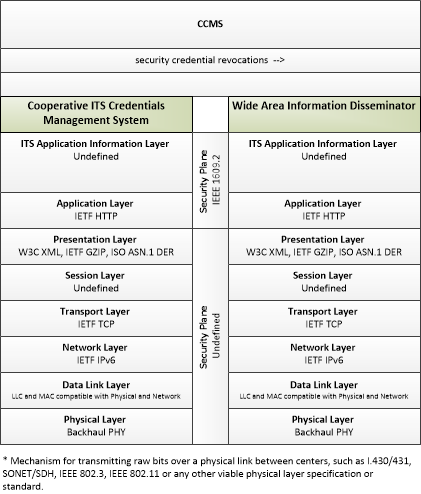
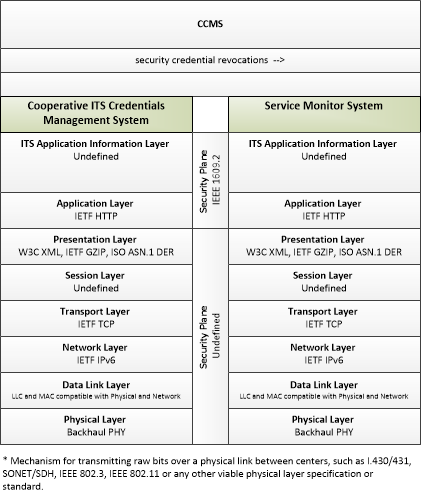
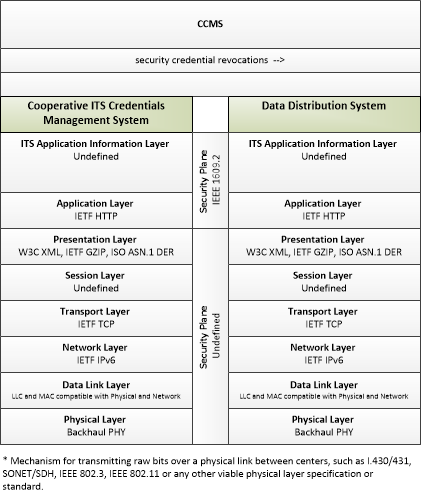
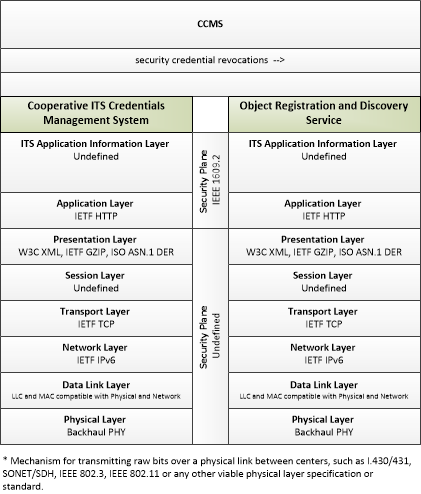
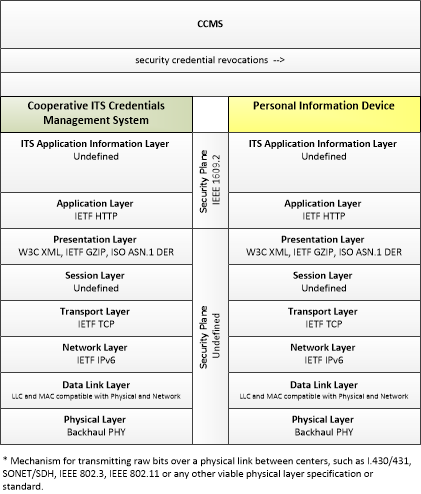
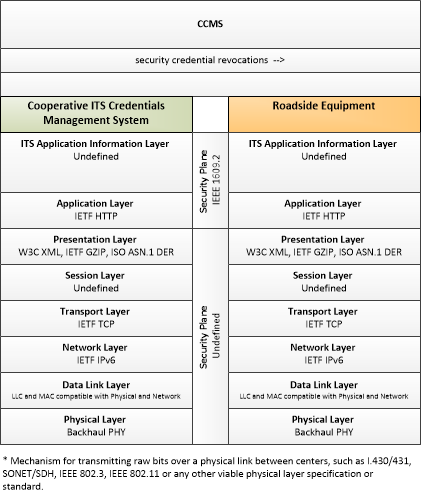
| security credential revocations | Certificate Revocation List; lists the certificates whose trust has been revoked by the CCMS. |
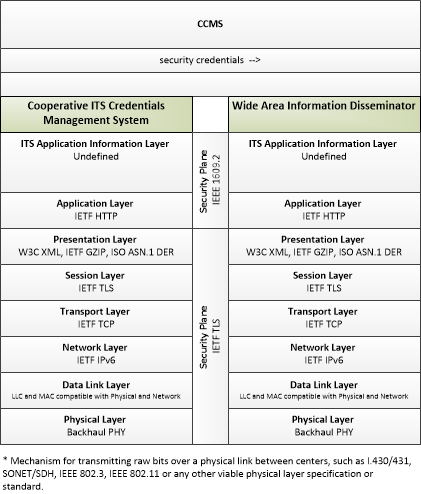
| security credentials | The material used by an end-entity (vehicle, personal device, field device, center system etc.) to ensure privacy, integrity and authenticability of its data transmissions. This includes certificates with associated public and private verifying/signing and decrypting/encrypting keys. |
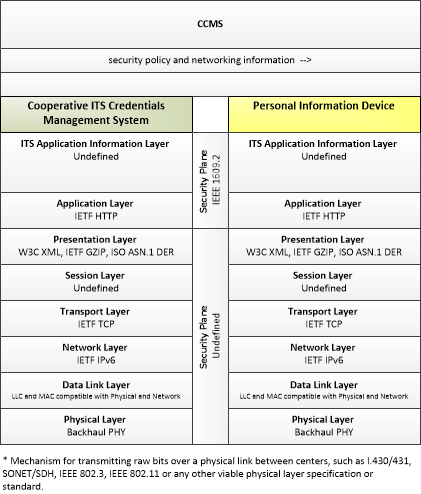
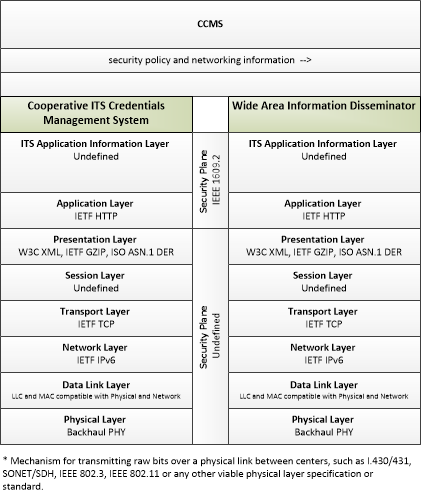
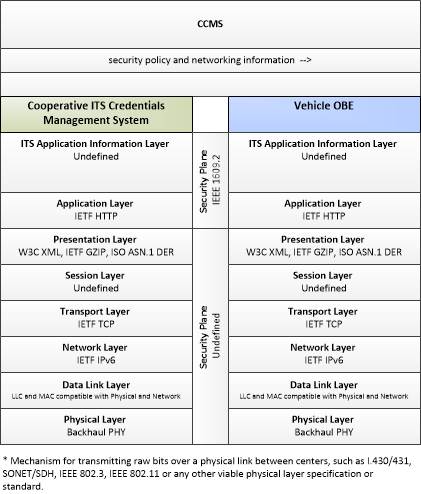
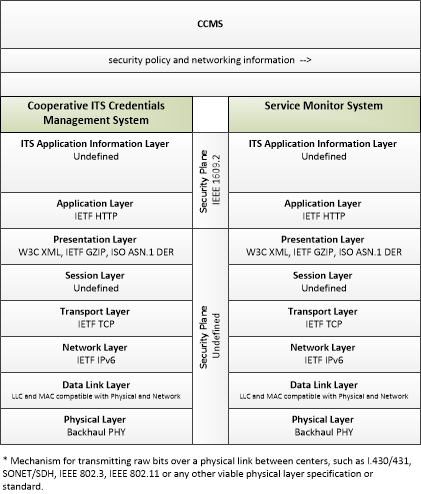
| security policy and networking information | Security policy information describing the CCMS' enrollment, authorization, misbehavior and revocation policies, and communications information related to CCMS components; including contact information and public credentials of those components. |
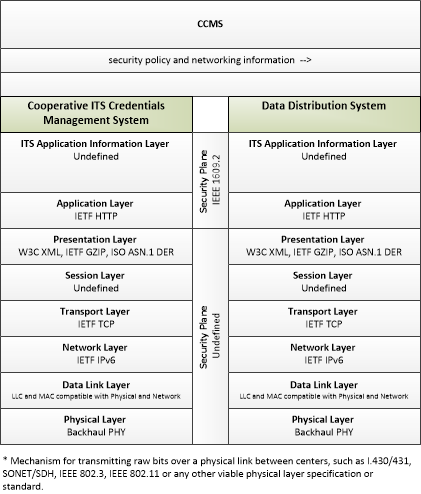
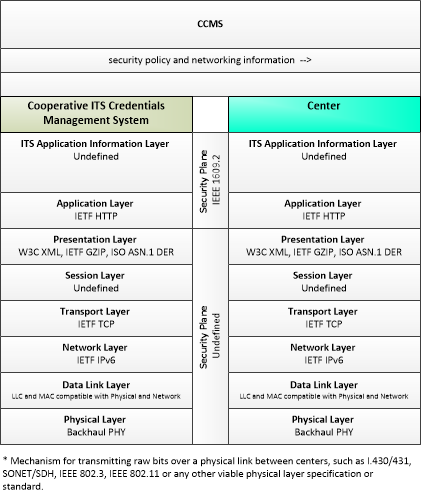
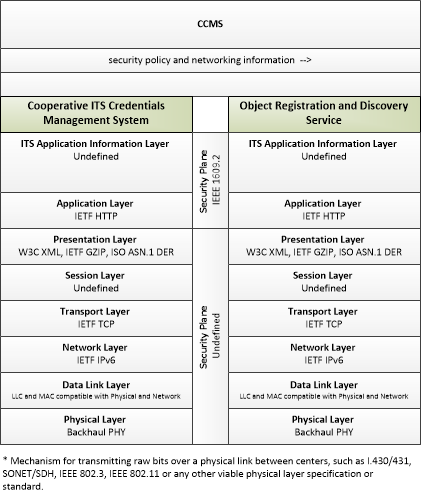
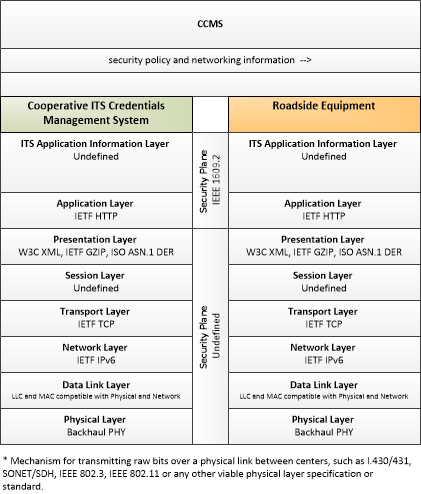
Application Interconnect Diagram
SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
Application Triples
Requirements
| Need | Requirement | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N4.001 | Applications need to protect data they handle from unauthorized access. This is required to support applications that exchange sensitive information, such as personally identifying or financial information, which if intercepted could compromise the privacy or financial records of the user. | 4.001 | Applications that function by exchanging data between entities shall be able to exchange encrypted data between those entities. |
| N4.002 | Applications need to establish trust between entities that operate components of the application. Such trust relationships are necessary so that applications can be assured that entities are who they say they are, and therefore trust the source and data it receives. | 4.002 | Applications shall verify that, for each entity on which an application component is installed, that entity is trusted by the provider of the application. |
| 4.003 | Applications shall be able to digitally sign all messages sent between entities. | ||
| 4.004 | Applications shall be able to verify the digital signature of received messages. | ||
| 4.005 | Digital signatures used to ensure trust shall be generated independently of the application sending the message to be signed. | ||
| N4.003 | Applications need to revoke the trust relationship they have between entities when necessary. A trusted entity may operate in a fashion that indicates it should no longer be trusted, in which case applications must have a way of revoking that trust. | 4.006 | Applications shall identify entities that provide messages to the application that are improperly formatted. |
| 4.007 | Applications shall identify entities that provide messages to the application that are logically inconsistent. | ||
| 4.008 | Applications shall revoke personal trust (trust by the application) when a repeated pattern of messages from a given entity falls outside of the applications tolerances. | ||
| 4.009 | Applications shall be able to report suspicious behavior to third party authentication providers. | ||
| 4.010 | Applications shall be able to accept messages from the third party authentication provider that identifies entities unworthy of trust. | ||
| 4.011 | Applications shall be able to revoke trust between itself and an entity if that entity is identified by the third party authentication provider as untrustworthy. | ||
| N4.004 | All participants in the Connected Vehicle Environment need to operate on a common time base. Coordination of time between the entities that operate applications as well as those providing Core services prevents internal errors and enables time-sensitive interactions between application components. | 4.012 | All applications shall use the same time source as the basis for timing. |
| N4.013 | The SCMS needs to grant trust credentials to qualified end entities including mobile devices so that those devices may be considered trusted by other devices that receive trust credentials from the SCMS. | 4.037 | The SCMS shall manage the distribution of IEEE 1609.2 certificates to field, center and mobile users. |
| 4.038 | The SCMS shall include a registration authority (RA) that collects requests for credentials from field, center and mobile users. | ||
| 4.039 | The Registration Authority (RA) shall request credentials from the CA on behalf of the requester. | ||
| 4.040 | The RA shall bundle certificates and send them to the requesting user as a group. | ||
| 4.041 | The RA shall accept requests for decryption keys from field, center and mobile users. | ||
| 4.042 | The RA shall provide decryption keys to field, center and mobile users that properly request and are entitled to those keys. | ||
| 4.043 | The SCMS shall include a certificate authority (CA) that receives requests for credentials from the RA. | ||
| 4.044 | The CA shall issue trust credentials for users to the RA. | ||
| N4.014 | The SCMS needs to be able to revoke the credentials it distributes, so that a misbehaving or malfunctioning device can be recognized as such. | 4.045 | The CA shall analyze misbehavior reports to determine a user whose credentials warrant revocation. |
| 4.046 | The CA shall revoke the credentials of users by putting their credentials on a list of revoked users (the certificate revocation list, or CRL). | ||
| 4.047 | The CA shall distribute the CRL to field, center and mobile users. | ||
| N4.015 | The SCMS needs to secure the exchange of trust credentials between itself and its intended user, so that no other party can intercept and use those credentials illegitimately. | 4.048 | All communications between the Linkage Authorities (Las), CA and RA shall be encrypted using the destination's public-key. |
| 4.049 | All communications between the LAs, CA and RA shall be able to be decrypted by the private-key of the destination. | ||
| N4.016 | The SCMS needs to be constructed in such a way that the cooperation of at least two parties within the SCMS' structure are required to link the identity of a user with a set of trust credentials, to protect user privacy. | 4.050 | The RA shall shuffle requests for credentials prior to requesting credentials from the CA. |
| 4.051 | The CA shall associate all trust credentials intended for a single end user (field, mobile or center) with a single combined linkage value assembled from the values provided by LA1 and LA2. | ||
| 4.052 | The CA shall receive linkage values from the LAs. | ||
| N4.017 | The SCMS needs to be constructed in such a way that the cooperation of at least two parties within the SCMS' structure are required to associate multiple credentials that were distributed to a user, to protect user privacy. | 4.053 | The SCMS shall include two linkage authorities (LA1 and LA2)that issue linkage values to the CA that can be associated with a group of certificates. |
| N4.018 | The SCMS needs to accept misbehavior reports from users, so that malfunctioning and misbehaving users may be identified and their privileges within the CVE revoked if necessary. | 4.054 | The CA shall accept misbehavior reports from field, center and mobile users. |
| 4.055 | The CA shall verify that a misbehavior report's sender is itself trustworthy. | ||
| N4.019 | The SCMS needs to provide a mechanism for a user without credentials to request credentials, so that the user may participate in the CVE. | 4.056 | The RA shall accept requests for long term certificates. |
| 4.057 | The RA shall forward requests for long term certificates to the CA if the request is received from an OBE in a secure environment local to the RA. | ||
| 4.058 | The CA shall issue a long term certificate if it receives a request for a long term certificate. | ||
| N4.020 | Every message received by a participant in the CVE needs to be able to be authenticated by the receiver, so the receiver knows that the originator is a trusted source. | 4.059 | Applications shall be capable of signing every message with a digital signature unique to the originator. |
| N4.021 | Every DSRC message needs to specify the privilege class of the originator, for example to distinguish emergency vehicles from general vehicles. | 4.060 | Every DSRC message shall include a Provider Service Identifier (PSID) and Service Specific Permissions associated with the originator. |
| 4.061 | Security and Credentials Management shall associate PSIDs with applications. | ||
| 4.062 | Security and Credentials Management shall associate service specific permissions with entities and applications. | ||
| 4.063 | Security and Credentials Management shall be able to receive service specific permissions entity/application associations from Core Authorization. | ||
| 4.064 | Core Authorization shall provide service specific permissions entity/application associations to Security and Credentials Management. | ||
| N4.045 | Messages need to be constructed in such a way as to make it difficult to associate messages with one another, to help maintain user privacy. | 4.112 | Every message generator shall be able to change signing keys often enough to ensure a reasonable expectation of user privacy. |
| 4.113 | Signing key changes shall occur with sufficient frequency to ensure a reasonable expectation of user privacy, given the originator's environment (number of other transmitters, frequency of use of other transmitters, laws affecting privacy and anonymity). | ||
Related Sources
- Harmonization Task Group #1 Service and Security Management to Support safety and sustainability applications: Current Status of Security Standards, Draft, 8/29/2012
- Harmonization Task Group #6, HTG6-3 Cooperative-ITS Credential Management System Functional Analysis and Recommendations for Harmonization, 2015-04-03, 4/3/2015
- Security Credential Management System Design, Draft, 4/13/2012
- Security Credentials Distribution ConOps
- Security Credentials Distribution System Requirements
- Security Credentials Management Entity ConOps (CME Task 2 Report)
Security
In order to participate in this application, each physical object should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Physical Object Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Object | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability | Security Class |
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | ||||
In order to participate in this application, each information flow triple should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Information Flow Security | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Destination | Information Flow | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability |
| Basis | Basis | Basis | |||
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | |||||