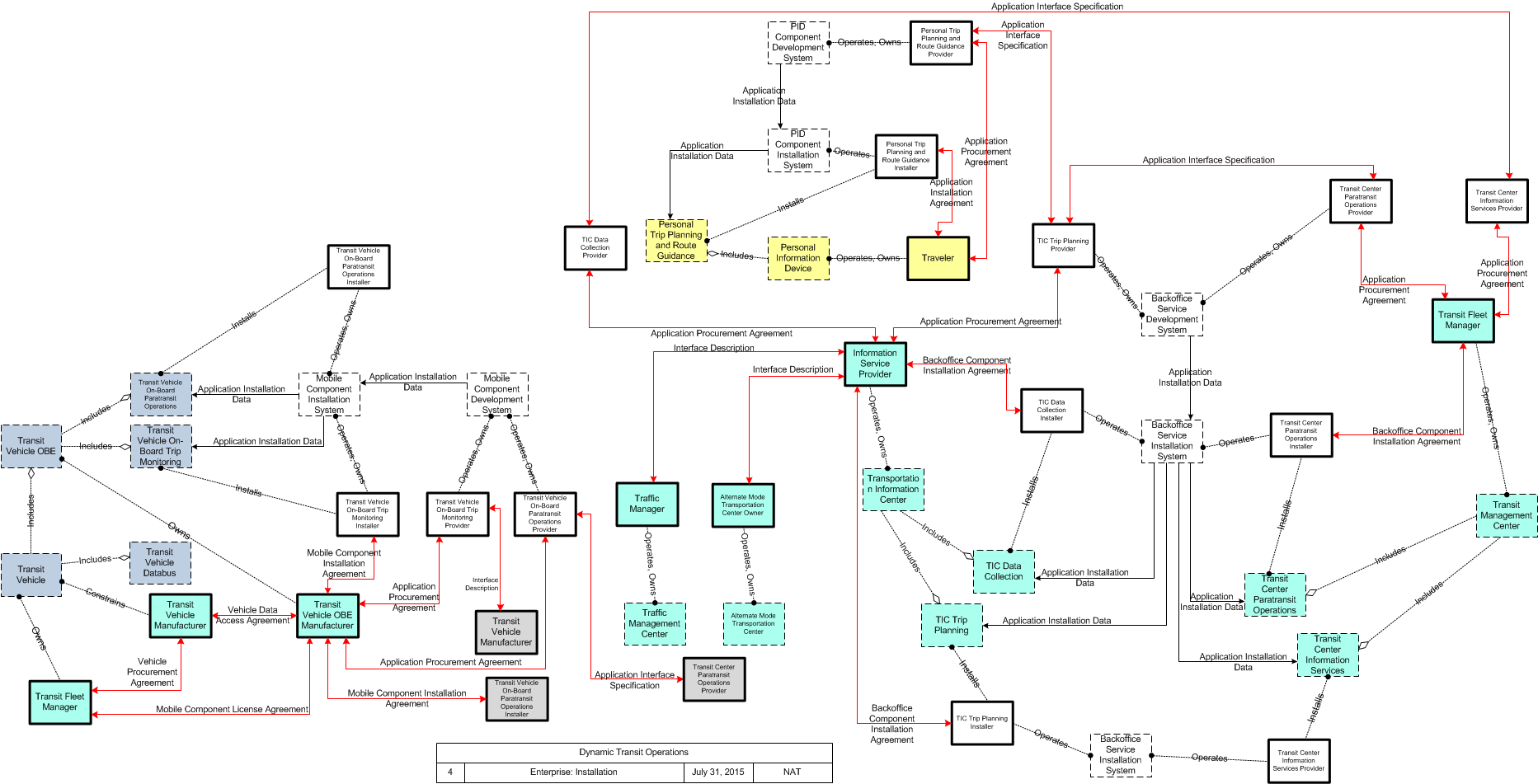
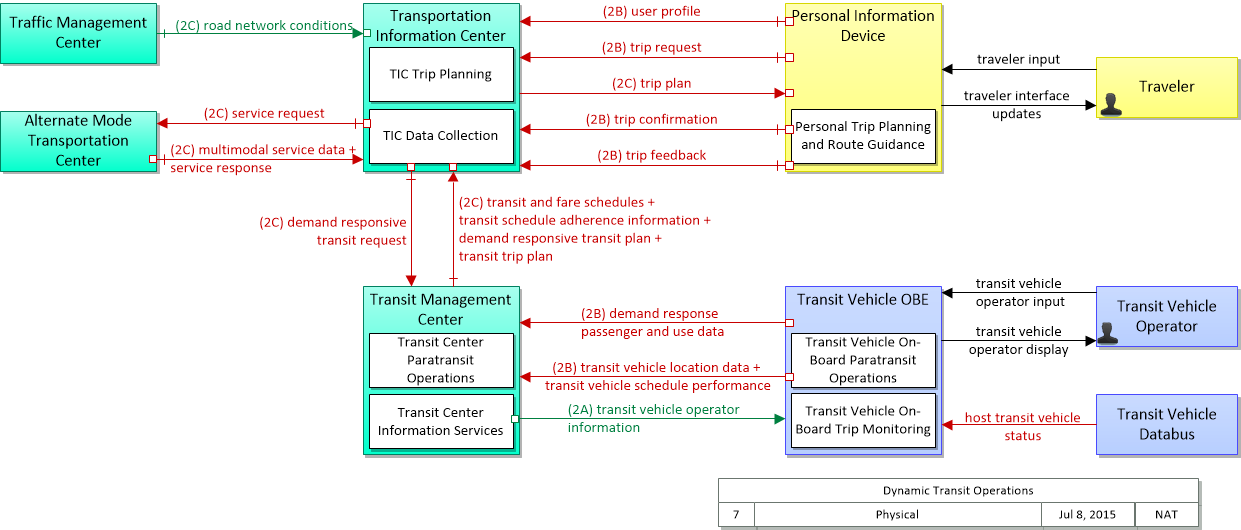
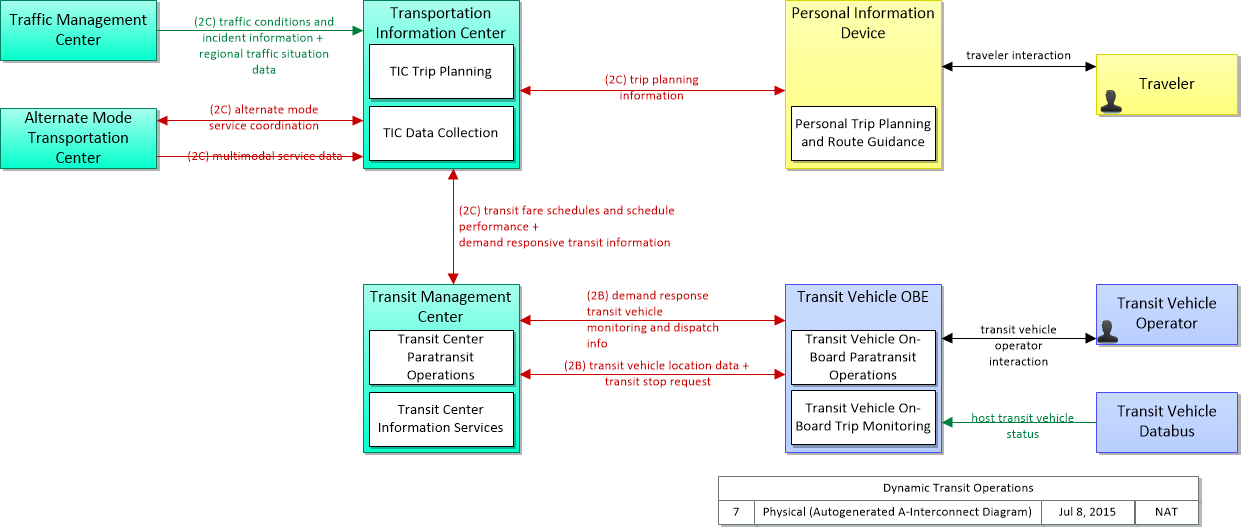
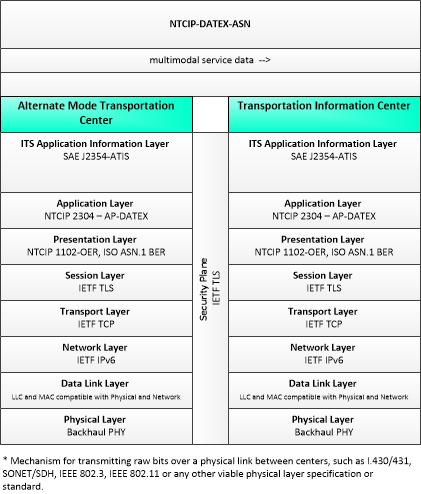
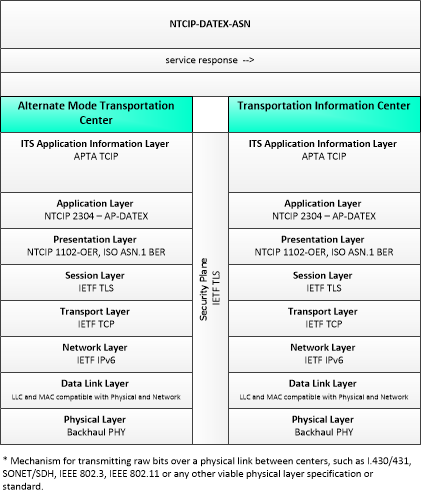
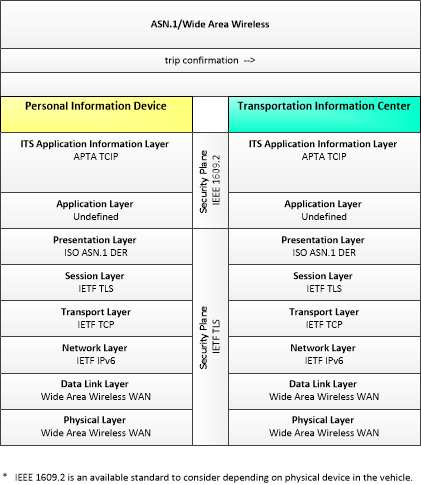
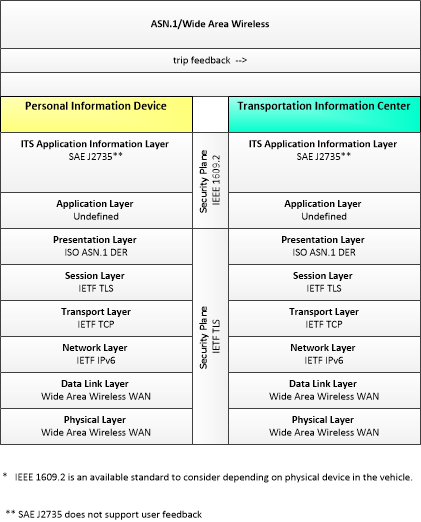
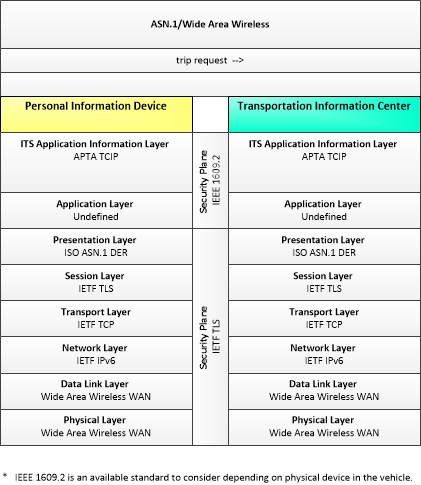
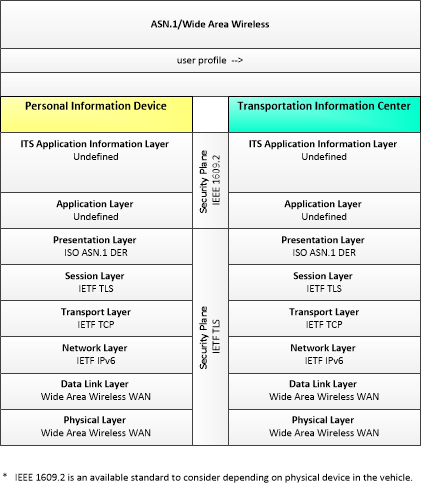
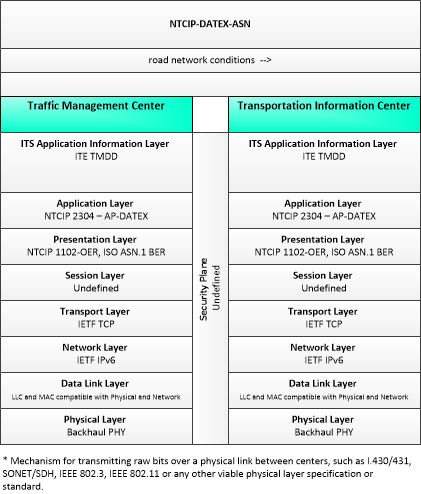
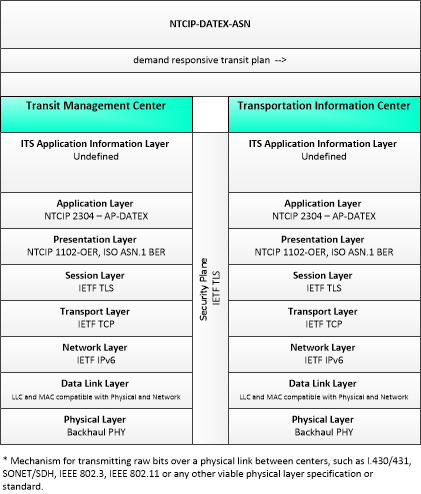
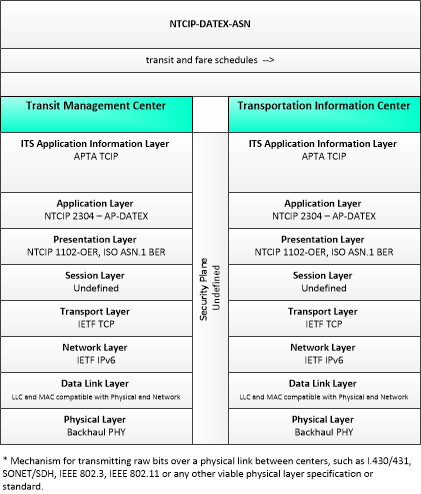
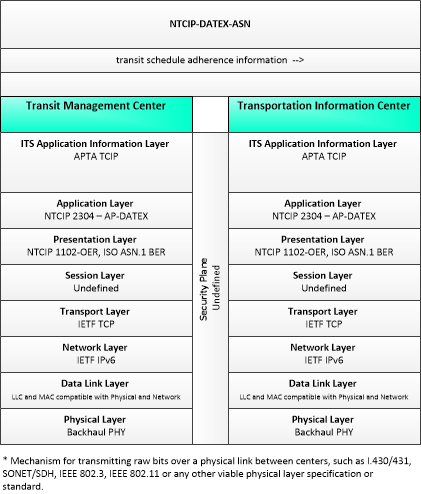
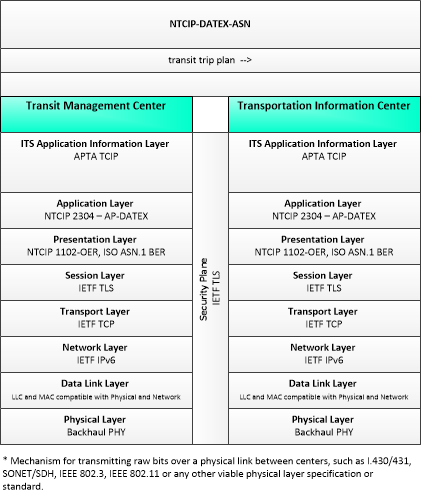
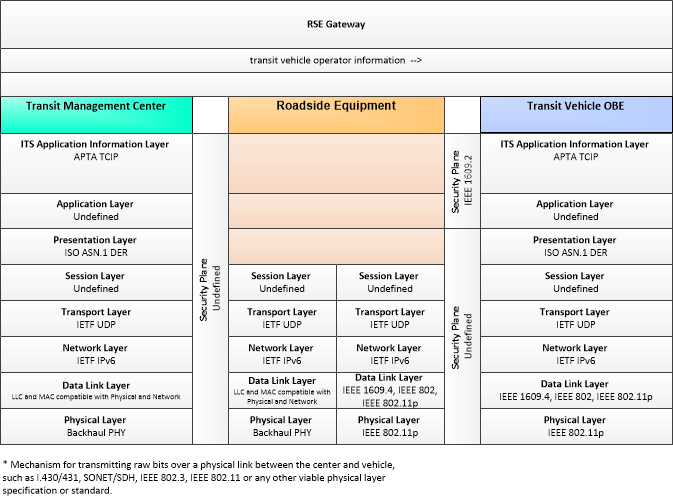
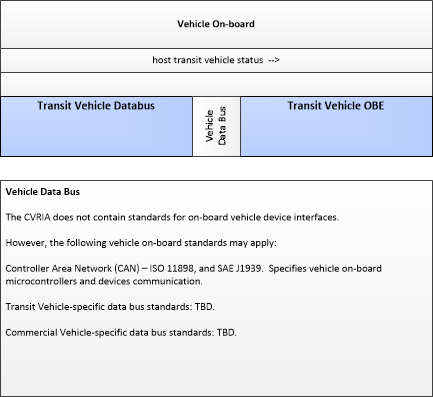
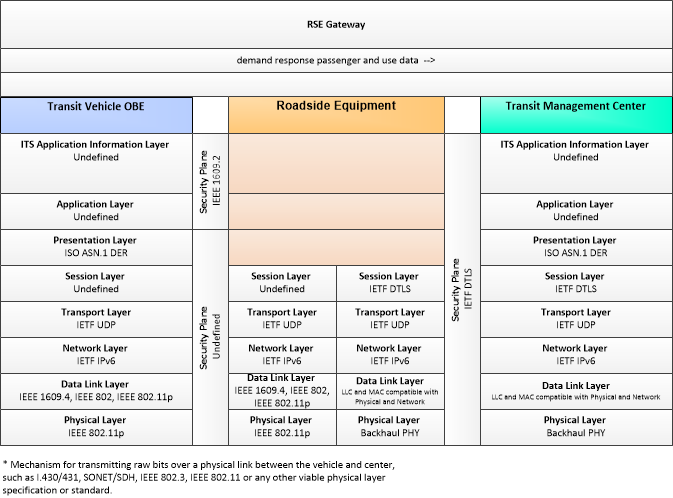
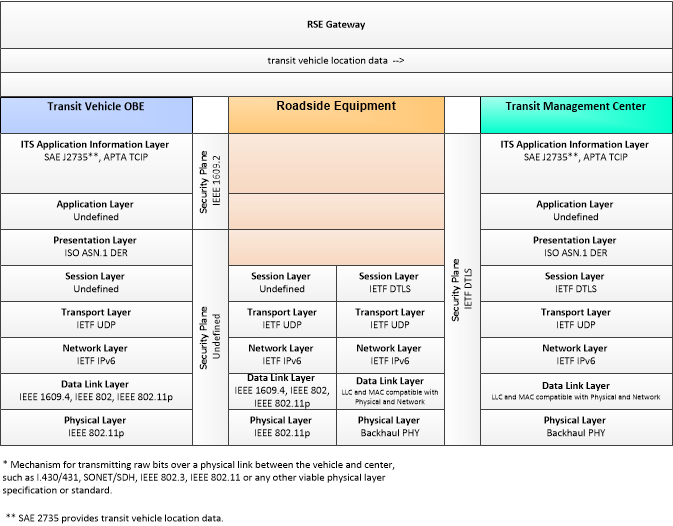
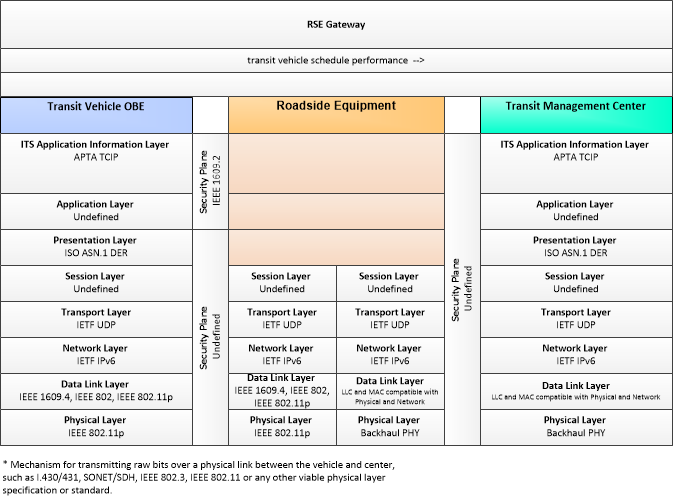
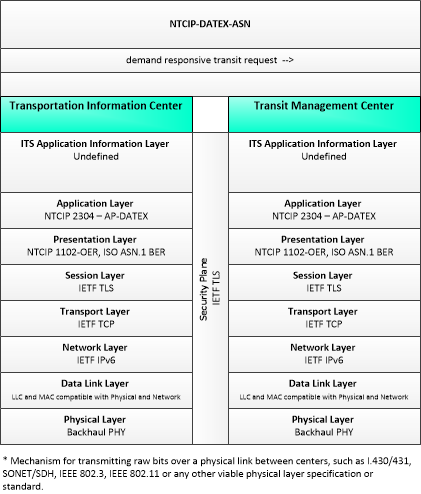
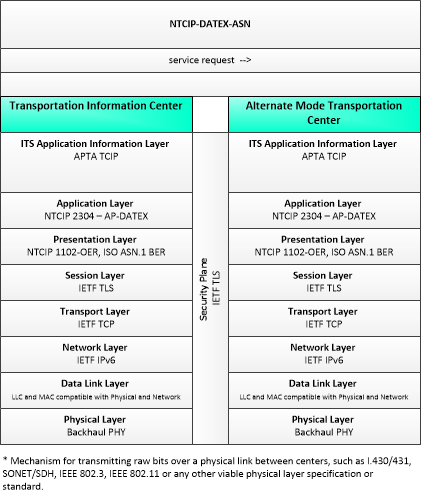
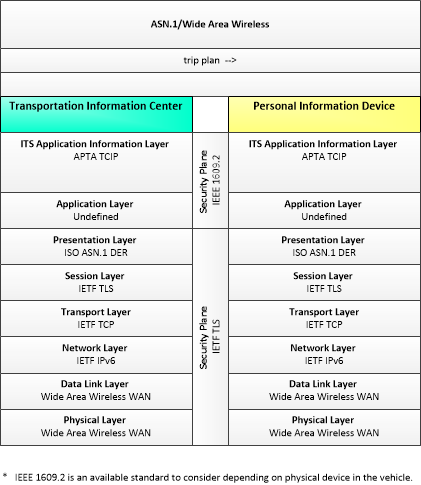
This is one way this application may be realized, but not the only way. There are other ways to build a given application and accomplish a stated objective.
The enterprise diagram can be viewed in SVG or PNG format and the current format is
.
| Enterprise Object |
Description |
| Alternate Mode Transportation Center Owner |
The entity that owns and is responsible for operating non-roadway-based transportation systems (e.g. airlines, ferry services, passenger-carrying heavy rail). |
| Application Certification Entity |
The body that determines whether an application may be deployed and operated in the Connected Vehicle Environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with application type. For example, applications with human safety component (crash avoidance, movement assistance etc.) may have stringent requirements and extensive testing in a variety of conditions, while applications that provide strictly mobility functionality may have far less testing requirements; possibly as little as just making sure the application doesn't interfere with any other applications. |
| Device Certification Entity |
The body that determines whether a device may be deployed and operated in the Connected Vehicle Environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with device type. |
| Federal Regulatory |
Federal regulatory bodies that have legal authority to control and/or provide input to policies regulating transportation infrastructure and operations. This includes entities such as the Federal Communications Commission and US Department of Transportation. |
| Information Service Provider |
The "Information Service Provider" represents the owner of the Transportation Information Center. The Information Service Provider is responsible for collecting and disseminating information relevant to the traveling public. |
| Personal Interactive Traveler Information Provider |
Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Personal Trip Planning and Route Guidance Installer |
Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Personal Trip Planning and Route Guidance Maintainer |
Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Personal Trip Planning and Route Guidance Provider |
Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| PID Provider |
The entity that designs, manufacturers and provides (either to the end user or to a reseller) the personal information device, including its hardware and base operating software. |
| State Regulatory |
State regulatory bodies that have legal authority to control and/or provide input to policies regulating vehicles, transportation infrastructure and operations. This includes entities like Departments of Motor Vehicles, property tax authorities and tolling agencies. |
| TIC Data Collection Installer |
Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TIC Data Collection Maintainer |
Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TIC Data Collection Provider |
Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| TIC Trip Planning Installer |
Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TIC Trip Planning Maintainer |
Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TIC Trip Planning Provider |
Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Traffic Manager |
The entity responsible for the management of traffic, both freeway and arterial. |
| Transit Center Information Services Provider |
Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Transit Center Paratransit Operations Installer |
Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Transit Center Paratransit Operations Maintainer |
Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Transit Center Paratransit Operations Provider |
Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Transit Fleet Manager |
The agency or organization that operates transit vehicles. This includes administration, routing, driver instruction, maintenance and any other responsibilities associated with the operations and maintenance of a transit system. |
| Transit Vehicle Manufacturer |
The entity which builds transit vehicles. This entity is complementary to the Vehicle Manufacturer entity in that it represents those aspects of vehicle manufacture which are unique to transit vehicles. |
| Transit Vehicle OBE Manufacturer |
The Transit Vehicle OBE Manufacturer is the provider of the transit vehicle on-board equipment. This entity may design and build the OBE, or may integrate other components to form the OBE, or may use some combination of approaches to provide the on-board equipment. Since the OBE could be aftermarket, retrofit, built-in or nomadic, this entity is the one that builds whatever that-is. In some cases it may be a smart phone manufacturer, or in others a top tier parts supplier, or any other entity in the production chain, depending on the device and commercial vehicle in question. |
| Transit Vehicle On-Board Paratransit Operations Installer |
Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Transit Vehicle On-Board Paratransit Operations Maintainer |
Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Transit Vehicle On-Board Paratransit Operations Provider |
Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Transit Vehicle On-Board Trip Monitoring Installer |
Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Transit Vehicle On-Board Trip Monitoring Maintainer |
Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Transit Vehicle On-Board Trip Monitoring Provider |
Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Transit Vehicle Operator |
The 'Transit Vehicle Operator' represents the person that receives and provides additional information that is specific to operating the ITS functions in all types of transit vehicles. The information received by the operator would include status of on-board systems. Additional information received depends upon the type of transit vehicle. In the case of fixed route transit vehicles, the Transit Vehicle Operator would receive operator instructions that might include actions to take to correct schedule deviations. In the case of flexible fixed routes and demand response routes the information would also include dynamic routing or passenger pickup information. |
| Traveler |
The 'Traveler' represents any individual who uses transportation services. The interfaces to the traveler provide general pre-trip and en-route information supporting trip planning, personal guidance, and requests for assistance in an emergency that are relevant to all transportation system users. It also represents users of a public transportation system and addresses interfaces these users have within a transit vehicle or at transit facilities such as roadside stops and transit centers. |
| Resource |
Description |
| Alternate Mode Transportation Center |
The 'Alternate Mode Transportation Center' provides the interface through which non-ITS transportation systems (e.g., airlines, ferry services, passenger-carrying heavy rail) can exchange data with ITS.. This two-way interface enables coordination for efficient movement of people across multiple transportation modes. It also enables the traveler to efficiently plan itineraries which include segments using other modes. |
| Application Component Certification Requirements |
The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of an application component. Certification Requirements must be met in order for an application to be installed in the CVE. |
| Backoffice Service Development System |
The systems used to develop backoffice (center) hardware and software components of applications. |
| Backoffice Service Installation System |
The systems used to install and configure backoffice (center) hardware and software components. |
| Backoffice Service Maintenance System |
The systems used to maintain and upgrade backoffice (center) hardware and software components. |
| Device Certification Requirements |
The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of a connected vehicle device. Certification Requirements must be met in order for the device to be granted the credentials necessary to operate in the Connected Vehicle Environment. |
| Mobile Component Development System |
The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the mobile component of the application. |
| Mobile Component Installation System |
The system that interacts with the Vehicle OBE other mobile device and installs the mobile component of the application. |
| Mobile Component Maintenance System |
The system used to configure changes and updates to the mobile component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| Personal Information Device |
The 'Personal Information Device' provides the capability for travelers to receive formatted traveler information wherever they are. Capabilities include traveler information, trip planning, and route guidance. Frequently a smart phone, the Personal Information Device provides travelers with the capability to receive route planning and other personally focused transportation services from the infrastructure in the field, at home, at work, or while en-route. Personal Information Devices may operate independently or may be linked with connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| Personal Trip Planning and Route Guidance |
"Personal Trip Planning and Route Guidance" provides a personalized trip plan to the traveler. The trip plan is calculated based on preferences and constraints supplied by the traveler and provided to the traveler for confirmation. Coordination may continue during the trip so that the route plan can be modified to account for new information. Many equipment configurations are possible including systems that provide a basic trip plan to the traveler as well as more sophisticated systems that can provide transition by transition guidance to the traveler along a multi-modal route with transfers. Devices represented by this application object include desktop computers at home, work, or at major trip generation sites, plus personal devices such as tablets and smart phones. |
| PID Component Development System |
The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the PID component of the application. |
| PID Component Installation System |
The system used to install the PID component of a connected vehicle application. |
| PID Component Maintenance System |
The system used to configure changes and updates to the PID component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| TIC Data Collection |
"TIC Data Collection" collects transportation-related data from other centers, performs data quality checks on the collected data and then consolidates, verifies, and refines the data and makes it available in a consistent format to applications that support operational data sharing between centers and deliver traveler information to end-users. A broad range of data is collected including traffic and road conditions, transit data, emergency information and advisories, weather data, special event information, traveler services, parking, multimodal data, and toll/pricing data. It also shares data with other transportation information centers. |
| TIC Trip Planning |
"TIC Trip Planning" provides pre-trip and en-route trip planning services for travelers. It receives origin, destination, constraints, and preferences and returns trip plan(s) that meet the supplied criteria. Trip plans may be based on current traffic and road conditions, transit schedule information, and other real-time traveler information. Candidate trip plans are multimodal and may include vehicle, transit, and alternate mode segments (e.g., rail, ferry, bicycle routes, and walkways) based on traveler preferences. It also confirms the trip plan for the traveler and supports reservations and advanced payment for portions of the trip. The trip plan includes specific routing information and instructions for each segment of the trip and may also include information and reservations for additional services (e.g., parking) along the route. |
| Traffic Management Center |
The 'Traffic Management Center' monitors and controls traffic and the road network. It represents centers that manage a broad range of transportation facilities including freeway systems, rural and suburban highway systems, and urban and suburban traffic control systems. It communicates with ITS Roadway Equipment and Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE) to monitor and manage traffic flow and monitor the condition of the roadway, surrounding environmental conditions, and field equipment status. It manages traffic and transportation resources to support allied agencies in responding to, and recovering from, incidents ranging from minor traffic incidents through major disasters. |
| Transit Center Information Services |
"Transit Center Information Services" collects the latest available information for a transit service and makes it available to transit customers and to Transportation Information Centers for further distribution. Customers are provided information at transit stops and other public transportation areas before they embark and on-board the transit vehicle once they are enroute. Information provided can include the latest available information on transit routes, schedules, transfer options, fares, real-time schedule adherence, current incidents, weather conditions, yellow pages, and special events. In addition to general service information, tailored information (e.g., itineraries) are provided to individual transit users. |
| Transit Center Paratransit Operations |
"Transit Center Paratransit Operations" manages demand responsive transit services, including paratransit services. It supports planning and scheduling of these services, allowing paratransit and other demand response transit services to plan efficient routes and better estimate arrival times. It also supports automated dispatch of paratransit vehicles and tracks passenger pick-ups and drop-offs. Customer service operator systems are updated with the most current schedule information. |
| Transit Management Center |
The 'Transit Management Center' manages transit vehicle fleets and coordinates with other modes and transportation services. It provides operations, maintenance, customer information, planning and management functions for the transit property. It spans distinct central dispatch and garage management systems and supports the spectrum of fixed route, flexible route, paratransit services, transit rail, and bus rapid transit (BRT) service. The physical object's interfaces allow for communication between transit departments and with other operating entities such as emergency response services and traffic management systems. |
| Transit Vehicle |
The vehicle that provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support safe and efficient movement of passengers. This includes buses, paratransit vehicles, light rail vehicles, other vehicles designed to carry passengers, and supervisory vehicles. |
| Transit Vehicle Databus |
The 'Transit Vehicle Databus' represents the vehicle databus that interfaces with on-board equipment on a transit vehicle. It is a specialized and extended form of the Vehicle Databus that is subject to different vehicle databus standards and hosts a broad range of components that are unique to a transit vehicle including the farebox and associated electronics, passenger counters, and transit security systems. As a specialized form of the Vehicle Databus, it also provides access to the general-purpose sensors (e.g., radars, cameras), GPS, drive train monitoring and control systems, and vehicle safety features that support connected vehicle applications. The Transit Vehicle may represent a bus, paratransit vehicle, light rail vehicle, or other vehicle designed to carry passengers. In CVRIA, the 'Transit Vehicle Databus' is used to represent the onboard interactions between the Transit Vehicle OBE and the other systems included in a host transit vehicle. |
| Transit Vehicle OBE |
The Transit Vehicle On-Board equipment (OBE) resides in a transit vehicle and provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support safe and efficient movement of passengers. The types of transit vehicles containing this physical object include buses, paratransit vehicles, light rail vehicles, other vehicles designed to carry passengers, and supervisory vehicles. It collects ridership levels and supports electronic fare collection. It supports a traffic signal prioritization function that communicates with the roadside physical object to improve on-schedule performance. Automated vehicle location enhances the information available to the transit operator enabling more efficient operations. On-board sensors support transit vehicle maintenance. The physical object supports on-board security and safety monitoring. This monitoring includes transit user or vehicle operator activated alarms (silent or audible), as well as surveillance and sensor equipment. The surveillance equipment includes video (e.g. CCTV cameras), audio systems and/or event recorder systems. It also furnishes travelers with real-time travel information, continuously updated schedules, transfer options, routes, and fares. In CVRIA, a separate 'Vehicle OBE' physical object supports the general V2V and V2I safety applications and other applications that apply to all vehicles, including transit vehicles. The Transit Vehicle OBE supplements these general capabilities with capabilities that are specific to transit vehicles. |
| Transit Vehicle On-Board Paratransit Operations |
"Transit Vehicle On-board Paratransit Operations" forwards paratransit and flexible-route dispatch requests to the operator and forwards acknowledgements to the center. It coordinates with, and assists the operator in managing multi-stop runs associated with demand responsive transit services including paratransit. It collects transit vehicle passenger data and makes it available to the center. |
| Transit Vehicle On-Board Trip Monitoring |
"Transit Vehicle On-Board Trip Monitoring" tracks vehicle location, monitors fuel usage, collects operational status (doors opened/closed, running times, etc.) and sends the collected, time stamped data to the Transit Management Center. |
| Transportation Information Center |
The 'Transportation Information Center' collects, processes, stores, and disseminates transportation information to system operators and the traveling public. The physical object can play several different roles in an integrated ITS. In one role, the TIC provides a data collection, fusing, and repackaging function, collecting information from transportation system operators and redistributing this information to other system operators in the region and other TICs. In this information redistribution role, the TIC provides a bridge between the various transportation systems that produce the information and the other TICs and their subscribers that use the information. The second role of a TIC is focused on delivery of traveler information to subscribers and the public at large. Information provided includes basic advisories, traffic and road conditions, transit schedule information, yellow pages information, ride matching information, and parking information. The TIC is commonly implemented as a website or a web-based application service, but it represents any traveler information distribution service. |
| Role |
Description |
| Certifies |
An Enterprise verifies that a target Resource meets relevant performance, functional, environmental and quality requirements. |
| Constrains |
A Resource or Enterprise applies requirements, constraints and associated tests to another Resource. |
| Installs |
An Enterprise performs the initial delivery, integration and configuration of the target Resource. |
| Maintains |
An Enterprise administers the hardware and software that comprise the target Resource. |
| Member |
An Enterprise is part of another larger, target Enterprise. |
| Operates |
An Enterprise controls the functionality and state of the target Resource. An Enterprise that Operates a resource is considered Responsible. |
| Owns |
An Enterprise has financial ownership and control over the Resource. An Enterprise that Owns a resource is considered Accountable. |
| Coordination |
Type |
Description |
| Application Installation Agreement |
Agreement |
An agreement that grants one party permission to install an application component on a device controlled by the other party. |
| Application Installation Data |
Information Sharing |
Data needed to install the application, including the application executable code and any configuration data. Unidirectional flow. |
| Application Interface Specification |
Agreement |
The definition of an interface between two application components that operate on two distinct pieces of hardware. The Application Interface Specification is specific to the application in question. |
| Application Maintenance Data |
Information Sharing |
Data used to facilitate the upgrade, patching and general health maintenance of an application component. |
| Application Performance Data |
Information Sharing |
Data used to characterize application performance, including such measures as availability, known errors and known uses. |
| Application Procurement Agreement |
Agreement |
An agreement whereupon one entity provides a copy of an application component to another entity. This component is capable of being installed and functioning, according to its requirements that passed through the application's certification process. |
| Application Usage Agreement |
Agreement |
An agreement in which one entity that controls an application component's use gives the other entity the necessary tools and permission to operate that application or application component. |
| Backoffice Component Installation Agreement |
Agreement |
An agreement that grants one party permission to install a backoffice application component on a center-based device controlled by the other party. |
| Backoffice Component Maintenance Agreement |
Agreement |
An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the backoffice component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Expectation of Information Provision |
Expectation |
An expectation where one party believes another party will provide it information whenever such information is likely relevant to the recipient. |
| Includes |
Includes |
Indicates that one component is entirely contained within another component. |
| Information Exchange Agreement |
Agreement |
An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. |
| Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
Agreement |
An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. This also includes a specification for action that shall, should or may be taken by one party in response to this information. |
| Information Provision Agreement |
Agreement |
An agreement where one party agrees to provide information to another party. This is a unidirectional agreement. |
| Interface Description |
Agreement |
Documentation of the interface between two systems, where one system does not have an application component that is part of the application, but does provide and/or receive data and/or information that is used by or sourced from the application. In many cases this is an existing interface used by the application, so the description of the interface already exists and is imposed by the terminator. |
| Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
Agreement |
An agreement that states one entity will provide data related to maintenance of an application component to the other entity. |
| Mobile Component Installation Agreement |
Agreement |
An agreement whereupon the controller of OBE gives another party permission to install, configure and make operational a component that enables the mobile portion of an application. |
| Mobile Component License Agreement |
Agreement |
An end-user license agreement allowing the operator of the mobile device to use the mobile application component that is part of the application in question. |
| Mobile Component Maintenance Agreement |
Agreement |
An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the mobile component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Vehicle Data Access Agreement |
Agreement |
An agreement whereby the party that controls access to on-board vehicle data grants another party the right and ability to access that data. Includes the conditions under which data may be accessed, and specifies the mechanisms, including physical and functional access methods, data formats and any other considerations necessary for the accessing party to acquire data. May also include caveats regarding responsibility for data quality and responsibility for use of the data. |
| Vehicle Procurement Agreement |
Agreement |
The exchange of a vehicle for compensation. One entity purchases the vehicle from the other. |
| Vehicle Usage Agreement |
Agreement |
An agreement between the owner of a vehicle and a prospective operator, whereupon the owner allows the operator to use the vehicle. |
| Warranty |
Agreement |
A guarantee or promise made by one entity to another, that provides assurance of the functionality and performance over time of an application component. |