Type: Resource
Traffic Management Center
Overview
The 'Traffic Management Center' monitors and controls traffic and the road network. It represents centers that manage a broad range of transportation facilities including freeway systems, rural and suburban highway systems, and urban and suburban traffic control systems. It communicates with ITS Roadway Equipment and Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE) to monitor and manage traffic flow and monitor the condition of the roadway, surrounding environmental conditions, and field equipment status. It manages traffic and transportation resources to support allied agencies in responding to, and recovering from, incidents ranging from minor traffic incidents through major disasters.
This resource is related to the "Traffic Management Center" physical object.
This resource is included in the following applications:
- Advanced Traveler Information Systems
- Border Management Systems
- Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control
- Curve Speed Warning
- Data Distribution
- Dynamic Eco-Routing
- Dynamic Transit Operations
- Eco-Approach and Departure at Signalized Intersections
- Eco-Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control
- Eco-Integrated Corridor Management Decision Support System
- Eco-Lanes Management
- Eco-Ramp Metering
- Eco-Speed Harmonization
- Eco-Traffic Signal Timing
- Eco-Transit Signal Priority
- Emergency Communications and Evacuation
- Emergency Vehicle Preemption
- Enhanced Maintenance Decision Support System
- Freight Signal Priority
- Freight-Specific Dynamic Travel Planning
- Incident Scene Pre-Arrival Staging Guidance for Emergency Responders
- Incident Scene Work Zone Alerts for Drivers and Workers
- Infrastructure Management
- Intelligent Traffic Signal System
- Intermittent Bus Lanes
- In-Vehicle Signage
- Low Emissions Zone Management
- Oversize Vehicle Warning
- Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning
- Pedestrian Mobility
- Queue Warning
- Railroad Crossing Violation Warning
- Red Light Violation Warning
- Reduced Speed Zone Warning / Lane Closure
- Restricted Lane Warnings
- Road Weather Information and Routing Support for Emergency Responders
- Road Weather Information for Freight Carriers
- Roadside Lighting
- Speed Harmonization
- Spot Weather Impact Warning
- Stop Sign Gap Assist
- Stop Sign Violation Warning
- Transit Connection Protection
- Transit Signal Priority
- Variable Speed Limits for Weather-Responsive Traffic Management
- Vehicle Data for Traffic Operations
- Warnings about Upcoming Work Zone
Coordination
Security
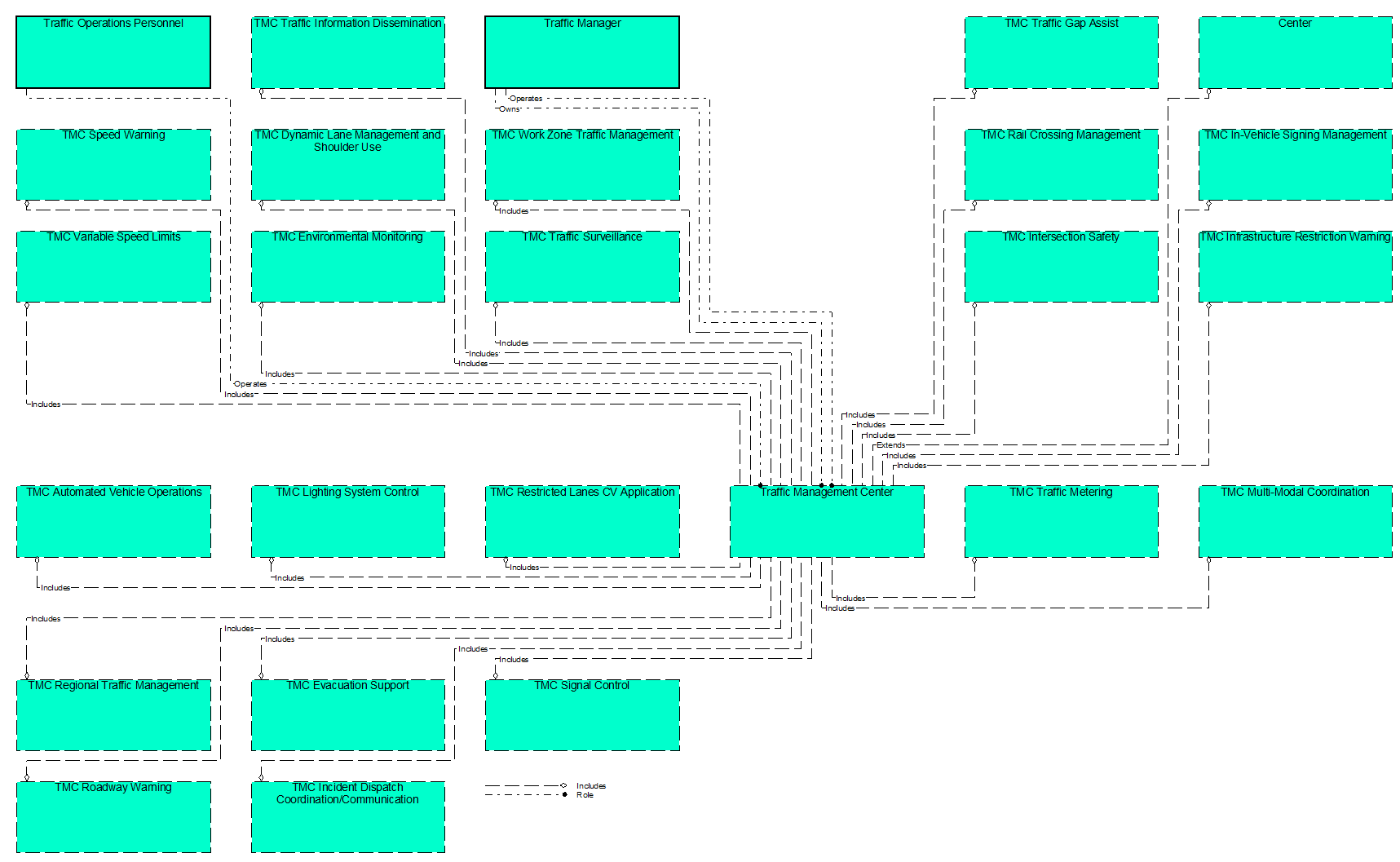
Interfaces Diagram
Alternative Configurations
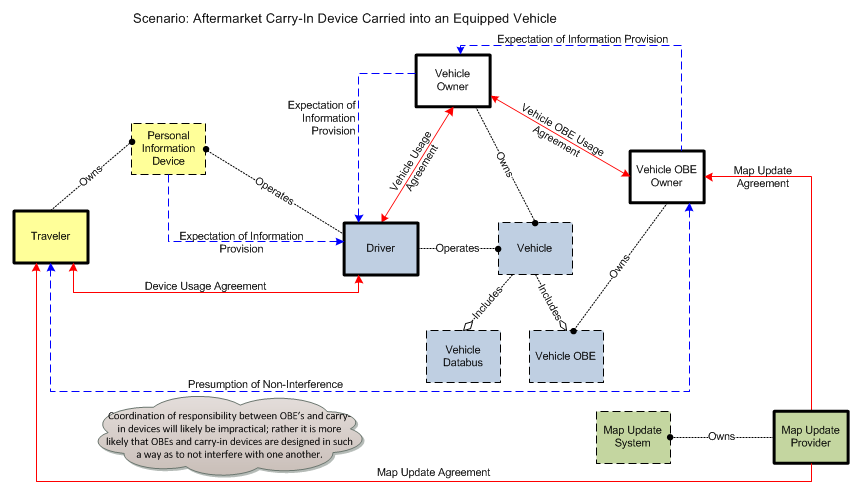
Four diagrams below illustrate four different implementations that may be represented by the Vehicle On-Board Equipment: 1) Vehicle Awareness Device, 2) Aftermarket Device, 3) Retrofit Device, or 4) Integrated System. Each diagram shows the subset of interfaces from CVRIA that are relevant to that particular implementation. Note that a V2V safety application is shown, but the four implementation options also provide varied support for other connected vehicle applications. Map provider shown as it is a likely interface for many safety applications, and the different points at which the map hooks in are illustrative of changes in necessary relationships. A fifth diagram covers a scenario where an aftermarket carry-in device is carried in to a vehicle that is already equipped with one of the Vehicle OBE implementations.
1. Vehicle Awareness Device – This is an aftermarket electronic device, installed in a vehicle without connection to vehicle systems, that is only capable of sending the basic safety message over short range communications. Vehicle awareness devices do not issue audible or visual warnings, alerts, or guidance to the driver of the vehicle.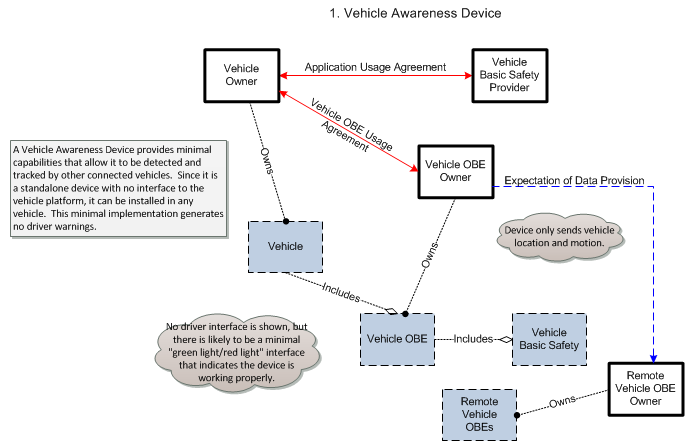
2. Aftermarket Device – This is an aftermarket electronic device, installed in a vehicle, and capable of sending and receiving messages over a wireless communications link. The self-contained device includes GPS, runs connected vehicle applications, and includes an integrated driver interface that issues audible or visual warnings, alerts, and guidance to the driver of the vehicle. The aftermarket device may or may not have access to some vehicle system status.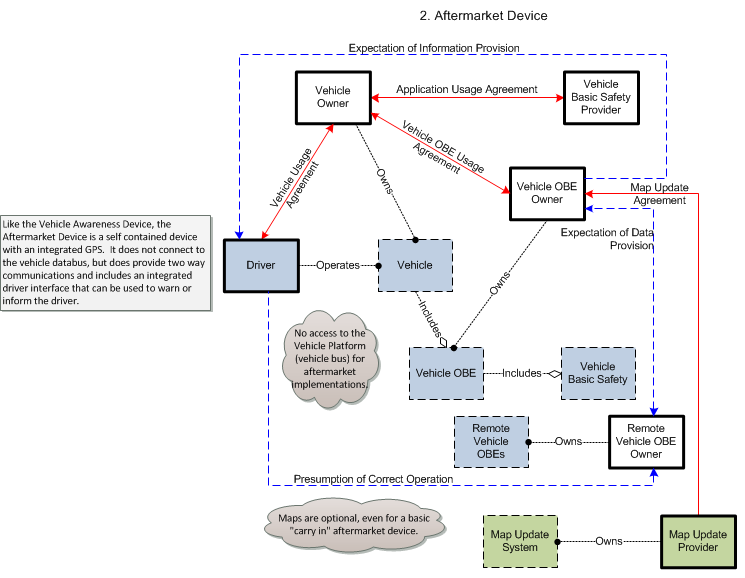
3. Retrofit Device – This is an OEM authorized electronic device installed in vehicles by an OEM authorized service provider, at a service facility after the vehicle has been built. This type of device provides two-way communications and is connected to a vehicle databus. Depending on implementation, the device may include an integrated driver interface and GPS or integrate with modules on the vehicle databus that provide these services. Depending on implementation, it may only support some of the connected vehicle applications identified in CVRIA and potentially support additional applications that are not identified in CVRIA.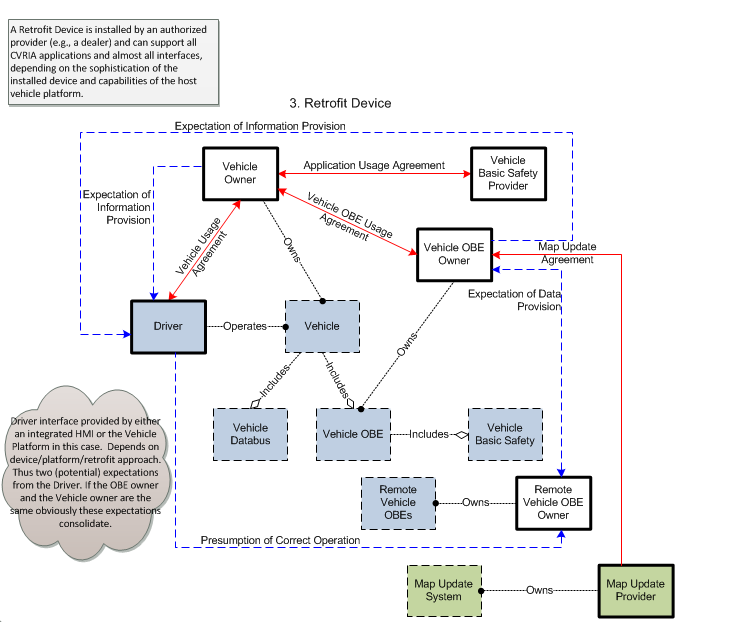
4. Integrated System – This is a system of one or more electronic devices integrated into vehicles during vehicle production. The Integrated System is connected to proprietary data busses to share information with other on-board systems. The Integrated System may be distributed across multiple subsystems and may be configured to support some of the connected vehicle applications identified in CVRIA and potentially support additional applications that are not identified in CVRIA.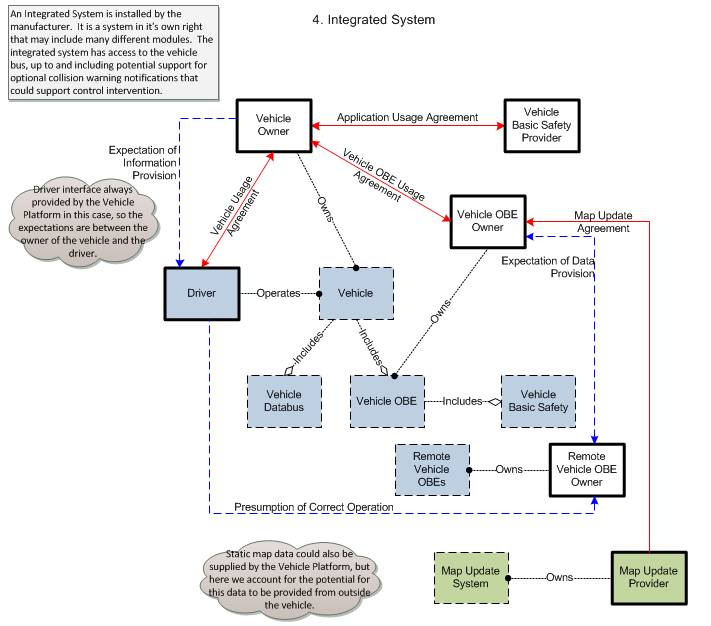
In retrofit and integrated implementations, the Vehicle OBE interfaces to other on-board systems through a vehicle databus (e.g., CAN). Represented in CVRIA as the Vehicle Databus, this interface provides access to on-board sensors, monitoring and control systems, and information systems that support connected vehicle applications. The vehicle databus may also be the source for GPS location and time, map data that supports connected vehicle applications, and the access point for the vehicle's driver-vehicle interface.
5. A fifth diagram covers a scenario where an aftermarket carry-in device is carried in to a vehicle that is already equipped with one of the Vehicle OBE implementations. In this scenario, we have two different devices with possibly two different radios and two different user interfaces that must be coordinated to avoid interference or conflicts.