Type: Environmental
Groups:- AERIS/ Sustainable Travel
Electric Charging Stations Management
The Electric Charging Station Management application provides an exchange of information between vehicle and charging station to manage the charging operation. The agency or company operating the charging station can use vehicle information such as the capability of the vehicle (e.g. operational status of the electrical system, how many amps can the vehicle handle, and % charge complete) to determine that the charge is being properly applied and determine an estimated time to complete charging.
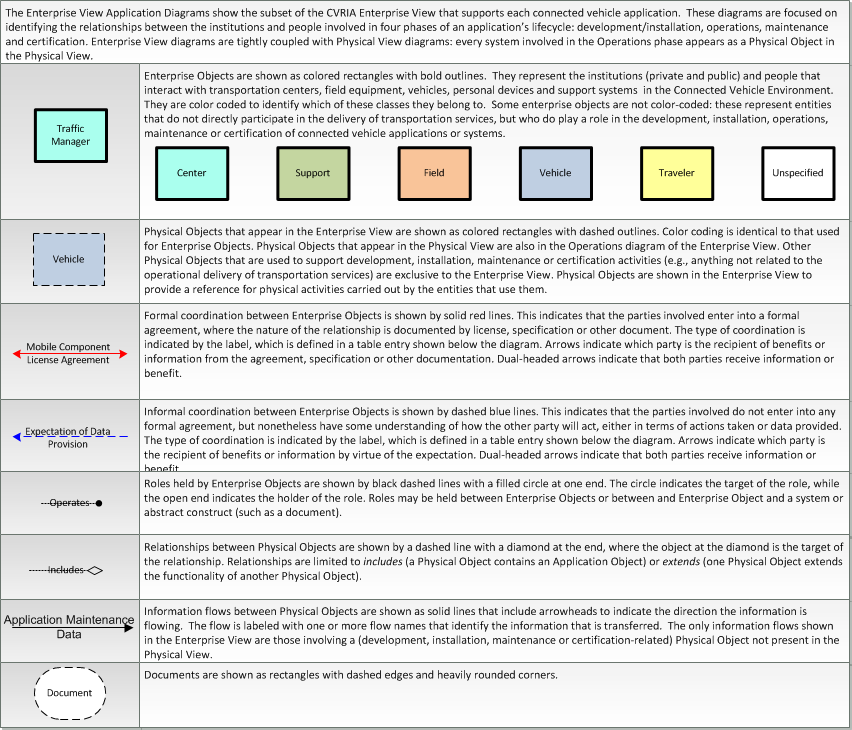
Enterprise
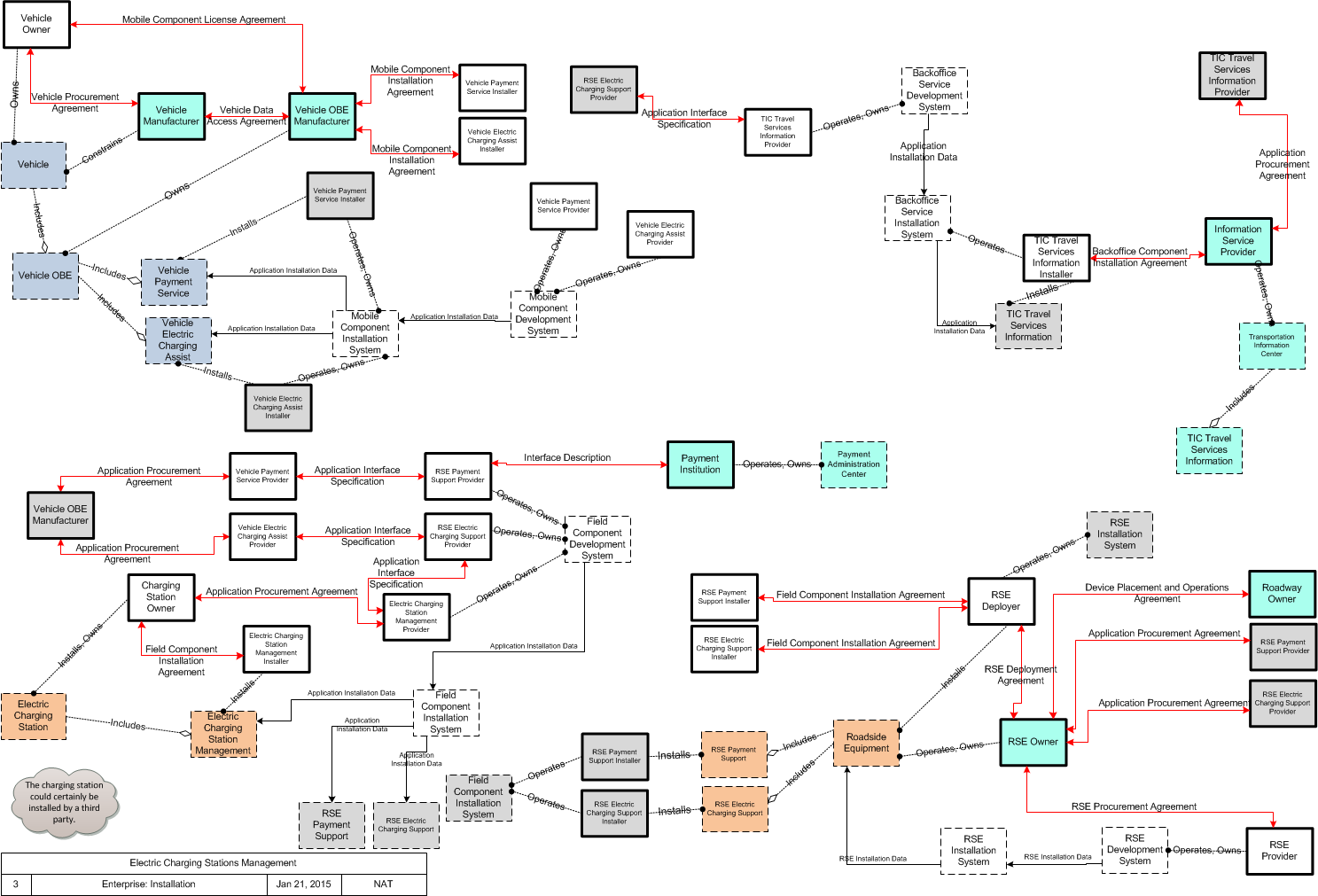
SVG Diagrams: Installation Operations Maintenance Certification
PNG Diagrams: Installation Operations Maintenance Certification
Business Interaction Matrix:
| Electric Charging Stations Management Operations Stage | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Owner | Driver | Vehicle OBE Owner | Roadway Owner | RSE Owner | RSE Operator | Information Service Provider | Payment Institution | RSE Payment Support Provider | RSE Electric Charging Support Provider | Charging Station Owner | Vehicle Payment Service Provider | Vehicle Electric Charging Assist Provider | |
| Vehicle Owner | Vehicle Usage Agreement | Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | |||||||||
| Driver | Vehicle Usage Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation of Information Provision | ||||||||||
| Vehicle OBE Owner | Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation of Data Provision | ||||||||||
| Roadway Owner | Service Delivery Agreement | ||||||||||||
| RSE Owner | Service Delivery Agreement | Operations Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | ||||||
| RSE Operator | Operations Agreement | ||||||||||||
| Information Service Provider | Expectation of Data Provision | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | |||||||||||
| Payment Institution | Information Exchange Agreement | ||||||||||||
| RSE Payment Support Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||
| RSE Electric Charging Support Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||
| Charging Station Owner | Expectation of Information Provision | Information Exchange Agreement | |||||||||||
| Vehicle Payment Service Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||
| Vehicle Electric Charging Assist Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||
Includes Enterprise Objects:
| Enterprise Object | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Certification Entity | The body that determines whether an application may be deployed and operated in the Connected Vehicle Environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with application type. For example, applications with human safety component (crash avoidance, movement assistance etc.) may have stringent requirements and extensive testing in a variety of conditions, while applications that provide strictly mobility functionality may have far less testing requirements; possibly as little as just making sure the application doesn't interfere with any other applications. |
| Charging Station Owner | The entity that owns the charging station. |
| Device Certification Entity | The body that determines whether a device may be deployed and operated in the Connected Vehicle Environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with device type. |
| Driver | The 'Driver' represents the person that operates a vehicle on the roadway. Included are operators of private, transit, commercial, and emergency vehicles where the interactions are not particular to the type of vehicle (e.g., interactions supporting vehicle safety applications). The Driver originates driver requests and receives driver information that reflects the interactions which might be useful to all drivers, regardless of vehicle classification. Information and interactions which are unique to drivers of a specific vehicle type (e.g., fleet interactions with transit, commercial, or emergency vehicle drivers) are covered by separate objects. |
| Electric Charging Station Management Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Electric Charging Station Management Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Electric Charging Station Management Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Federal Regulatory | Federal regulatory bodies that have legal authority to control and/or provide input to policies regulating transportation infrastructure and operations. This includes entities such as the Federal Communications Commission and US Department of Transportation. |
| Information Service Provider | The "Information Service Provider" represents the owner of the Transportation Information Center. The Information Service Provider is responsible for collecting and disseminating information relevant to the traveling public. |
| ITS Certification Entity | The body that determines whether an ITS device or application may be deployed and operated in the transportation environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with device and application type. Typically not a formal body, assigned on a project-by-project basis depending on the type of infrastructure involved. Since ITS projects are locally-focused (typically state or smaller), the entities that are part of this body are typically those with operational jurisdiction where the ITS is installed (e.g., state or local DOTs, state or local maintenance managers etc.) |
| Payment Institution | The 'Payment Administrator' represents the person(s) that manage the back office payment administration systems for electronic toll, VMT road use payment, and other services paid for from a vehicle. It monitors the systems that support the electronic transfer of funds from the customer to the system operator. It monitors customer enrollment and supports the establishment of escrow accounts depending on the clearinghouse scheme and the type of payments involved. It also establishes and administers the pricing structures and policies. |
| Roadway Owner | The owner of the roadway proximate to which roadside equipment will be/is installed. |
| RSE Deployer | The entity responsible for the deployment, operations and maintenance of roadside equipment. |
| RSE Electric Charging Support Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Electric Charging Support Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Electric Charging Support Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Operator | The entity that operates roadside equipment in the transportation environment. |
| RSE Owner | The owner of roadside equipment. |
| RSE Payment Support Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Payment Support Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Payment Support Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Provider | The "RSE Provider" is the entity that develops and (presumably) sells roadside equipment to other entities for deployment and research. |
| State Regulatory | State regulatory bodies that have legal authority to control and/or provide input to policies regulating vehicles, transportation infrastructure and operations. This includes entities like Departments of Motor Vehicles, property tax authorities and tolling agencies. |
| TIC Travel Services Information Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TIC Travel Services Information Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TIC Travel Services Information Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Vehicle Electric Charging Assist Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Electric Charging Assist Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Electric Charging Assist Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Vehicle Manufacturer | The entity that builds, assembles, verifies and validates the Vehicle in which the Vehicle OBE will eventually operate. |
| Vehicle OBE Manufacturer | The entity that builds, assembles, verifies and validates the Vehicle OBE. This can be an OEM-equipped OBE, retrofit or aftermarket equipment. |
| Vehicle OBE Owner | The entity, individual, group or corporation that owns the Vehicle On-Board equipment. This could be the same as the Vehicle Owner, but it could be a third part that licenses the use of the OBE to the Owner. |
| Vehicle Owner | The individual, group of individuals or corporate entity that is identified as the registered owner of the Vehicle under state law. |
| Vehicle Payment Service Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Payment Service Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Payment Service Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
Includes Resources:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Component Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of an application component. Certification Requirements must be met in order for an application to be installed in the CVE. |
| Backoffice Service Development System | The systems used to develop backoffice (center) hardware and software components of applications. |
| Backoffice Service Installation System | The systems used to install and configure backoffice (center) hardware and software components. |
| Backoffice Service Maintenance System | The systems used to maintain and upgrade backoffice (center) hardware and software components. |
| Device Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of a connected vehicle device. Certification Requirements must be met in order for the device to be granted the credentials necessary to operate in the Connected Vehicle Environment. |
| Electric Charging Station | The 'Electric Charging Station' provides access to electric vehicle supply equipment that is used to charge hybrid and all-electric vehicles. This includes public charging stations that support consumers, workplace charging stations, and fleet charging stations. |
| Electric Charging Station Management | 'Electric Charging Station Management' manages vehicle charging. It communicates with the vehicle during charging and provides charge status information to the driver. A connection with Roadside Equipment provides the capability to integrate charging station coordination and communication into the broader Connected Vehicle Environment. |
| Field Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the field component of the application. |
| Field Component Installation System | The system used to install a field component of a connected vehicle application. |
| Field Component Maintenance System | The system used to install and configure changes and updates to the field component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| ITS Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of an ITS device or ITS application. Applicability varies with jurisdictions, but typically devices and applications must meet pre-defined acceptance criteria prior to usage in the transportation environment. |
| Mobile Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the mobile component of the application. |
| Mobile Component Installation System | The system that interacts with the Vehicle OBE other mobile device and installs the mobile component of the application. |
| Mobile Component Maintenance System | The system used to configure changes and updates to the mobile component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| Payment Administration Center | The 'Payment Administration Center' provides general payment administration capabilities and supports the electronic transfer of funds from the customer to the transportation system operator or other service provider. Charges can be recorded for tolls, vehicle-mileage charging, congestion charging, or other goods and services. It supports traveler enrollment and collection of both pre-payment and post-payment transportation fees in coordination with the financial infrastructure supporting electronic payment transactions. The system may establish and administer escrow accounts depending on the clearinghouse scheme and the type of payments involved. It may post a transaction to the customer account, generate a bill (for post-payment accounts), debit an escrow account, or interface to a financial infrastructure to debit a customer designated account. It supports communications with the ITS Roadway Payment Equipment to support fee collection operations. As an alternative, a wide-area wireless interface can be used to communicate directly with vehicle equipment. It also sets and administers the pricing structures and may implement road pricing policies in coordination with the Traffic Management Center. |
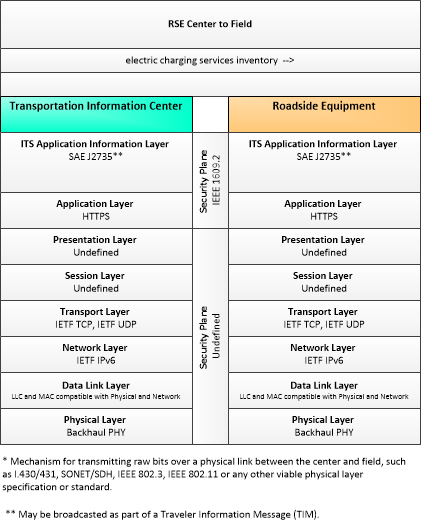
| Roadside Equipment | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| RSE Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the roadside equipment. |
| RSE Electric Charging Support | "RSE Electric Charging Support" uses short range communications to coordinate with a vehicle that is being charged, receiving information about the operational state of the electrical system, the maximum charge rate, and the percentage-complete of the charge from the vehicle. |
| RSE Installation System | The system used to install and configure the roadside equipment. |
| RSE Maintenance System | The system used to configure changes and updates to the roadside equipment. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the RSE's configuration and performance. |
| RSE Payment Support | "RSE Payment Support" manages vehicle payments for road use based on fee structures and payment strategies based on vehicle-reported data including VMT, emissions, vehicle class or type. Fees may vary by time or location and may include incentives or credits to reward desirable driving behavior. To support payment, it receives vehicle data (e.g., time stamped roadways used by the vehicle since the last transmission) and forwards this to the Payment Administration Center. It also receives equipment status from the vehicle and vehicle characteristics sensed from the vehicle (number of axles, weight, vehicle tag image/ID). Faults are identified and forwarded to the Payment Administration Center. Finally, it requests, receives, processes, and reports vehicle payment information. |
| TIC Travel Services Information | "TIC Travel Services Information" disseminates information about traveler services such as lodging, restaurants, and service stations. Tailored traveler service information is provided on request that meets the constraints and preferences specified by the traveler. This application also supports reservations and advanced payment for traveler services. |
| Transportation Information Center | The 'Transportation Information Center' collects, processes, stores, and disseminates transportation information to system operators and the traveling public. The physical object can play several different roles in an integrated ITS. In one role, the TIC provides a data collection, fusing, and repackaging function, collecting information from transportation system operators and redistributing this information to other system operators in the region and other TICs. In this information redistribution role, the TIC provides a bridge between the various transportation systems that produce the information and the other TICs and their subscribers that use the information. The second role of a TIC is focused on delivery of traveler information to subscribers and the public at large. Information provided includes basic advisories, traffic and road conditions, transit schedule information, yellow pages information, ride matching information, and parking information. The TIC is commonly implemented as a website or a web-based application service, but it represents any traveler information distribution service. |
| Vehicle | The conveyance that provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support efficient, safe, and convenient travel. These functions reside in general vehicles including personal automobiles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, or other vehicle types. |
| Vehicle Electric Charging Assist | "Vehicle Electric Charging Assist" uses short range communications to coordinate with electric charging stations, providing information about the operational state of the electrical system, the maximum charge rate, and the percentage-complete of the charge. This application also receives current information about electric charging systems in the region and makes this information available to the driver on request. |
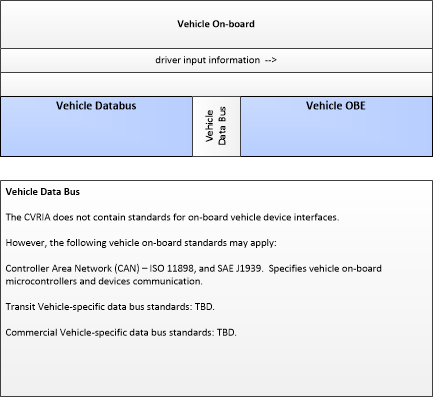
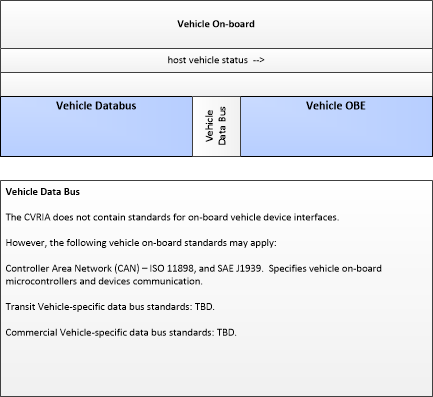
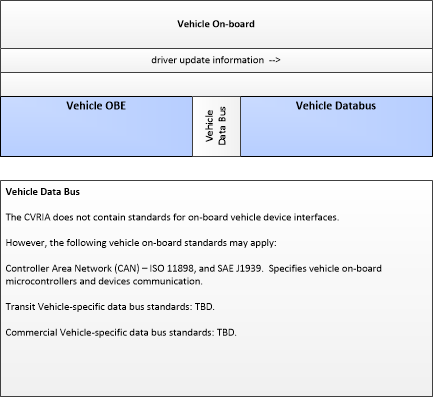
| Vehicle OBE | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
| Vehicle Payment Service | "Vehicle Payment Service" supports vehicle payments including VMT- and zone-based payments and payments for other services including fuel/charging services. To support VMT-based payment, this application tracks the location of the vehicle at specific times and reports this VMT data along with vehicle identification. A variety of pricing strategies are supported, including strategies that include credits or incentives that reward desired driving patterns and behavior. |
Includes Roles:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Certifies | An Enterprise verifies that a target Resource meets relevant performance, functional, environmental and quality requirements. |
| Constrains | A Resource or Enterprise applies requirements, constraints and associated tests to another Resource. |
| Installs | An Enterprise performs the initial delivery, integration and configuration of the target Resource. |
| Maintains | An Enterprise administers the hardware and software that comprise the target Resource. |
| Member | An Enterprise is part of another larger, target Enterprise. |
| Operates | An Enterprise controls the functionality and state of the target Resource. An Enterprise that Operates a resource is considered Responsible. |
| Owns | An Enterprise has financial ownership and control over the Resource. An Enterprise that Owns a resource is considered Accountable. |
Includes Coordination:
| Coordination | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Application Installation Data | Information Sharing | Data needed to install the application, including the application executable code and any configuration data. Unidirectional flow. |
| Application Interface Specification | Agreement | The definition of an interface between two application components that operate on two distinct pieces of hardware. The Application Interface Specification is specific to the application in question. |
| Application Maintenance Data | Information Sharing | Data used to facilitate the upgrade, patching and general health maintenance of an application component. |
| Application Performance Data | Information Sharing | Data used to characterize application performance, including such measures as availability, known errors and known uses. |
| Application Procurement Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity provides a copy of an application component to another entity. This component is capable of being installed and functioning, according to its requirements that passed through the application's certification process. |
| Application Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity that controls an application component's use gives the other entity the necessary tools and permission to operate that application or application component. |
| Backoffice Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one party permission to install a backoffice application component on a center-based device controlled by the other party. |
| Backoffice Component Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the backoffice component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Device Placement and Operations Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that enables the controller of a physical device to install it (so as to make it operational) at a fixed location controlled by another entity. |
| Expectation of Data Provision | Expectation | An expectation where one party believes another party will provide data on a regular and recurring basis, and that that data will be useful to the receiver in the context of the receiver's application. This thus includes some expectation of data fields, timeliness, quality, precision and similar qualities of data. |
| Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation | An expectation where one party believes another party will provide it information whenever such information is likely relevant to the recipient. |
| Field Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one party permission to install a field application component on a roadside device controlled by the other party. |
| Field Component Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the field component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Includes | Includes | Indicates that one component is entirely contained within another component. |
| Information Exchange Agreement | Agreement | An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. |
| Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Agreement | An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. This also includes a specification for action that shall, should or may be taken by one party in response to this information. |
| Interface Description | Agreement | Documentation of the interface between two systems, where one system does not have an application component that is part of the application, but does provide and/or receive data and/or information that is used by or sourced from the application. In many cases this is an existing interface used by the application, so the description of the interface already exists and is imposed by the terminator. |
| Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of a system under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that states one entity will provide data related to maintenance of an application component to the other entity. |
| Mobile Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon the controller of OBE gives another party permission to install, configure and make operational a component that enables the mobile portion of an application. |
| Mobile Component License Agreement | Agreement | An end-user license agreement allowing the operator of the mobile device to use the mobile application component that is part of the application in question. |
| Mobile Component Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the mobile component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Operations Agreement | Agreement | An agreement where one entity agrees to operate a device or application on behalf of another, device/application controlling entity. |
| RSE Deployment Agreement | Agreement | Agreement to install, configure and make operational roadside equipment, between the provider of that equipment and the entity that controls access to the roadside. May define locations, expectation of power provision, backhaul responsibility and installation restrictions. |
| RSE Installation Data | Information Sharing | Data necessary to configure and make RSE operational. Uni-directional. |
| RSE Maintenance Data | Information Sharing | Data necessary to modify the operational configuration of RSE; assumes RSE is already configured. Uni-directional. |
| RSE Performance Data | Information Sharing | Data that includes metrics of RSE performance. Could include fields such as uptime, packets received/transmitted, distance vector from which packets received, as well as application-specific performance measures. |
| RSE Procurement Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity provides roadside equipment to another entity. The RSE is capable of being installed and functioning, according to its requirements that passed through the device's certification process. |
| Service Delivery Agreement | Agreement | A relationship where one party agrees to provide a service to the other party. This agreement may specify the expected performance of this service in terms of availability and/or actions/time-type performance specifications. |
| Vehicle Data Access Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereby the party that controls access to on-board vehicle data grants another party the right and ability to access that data. Includes the conditions under which data may be accessed, and specifies the mechanisms, including physical and functional access methods, data formats and any other considerations necessary for the accessing party to acquire data. May also include caveats regarding responsibility for data quality and responsibility for use of the data. |
| Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one entity permission to use a Vehicle OBE that the other party controls. |
| Vehicle Procurement Agreement | Agreement | The exchange of a vehicle for compensation. One entity purchases the vehicle from the other. |
| Vehicle Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement between the owner of a vehicle and a prospective operator, whereupon the owner allows the operator to use the vehicle. |
| Warranty | Agreement | A guarantee or promise made by one entity to another, that provides assurance of the functionality and performance over time of an application component. |
Functional
Includes Processes:
Includes Data Flows:
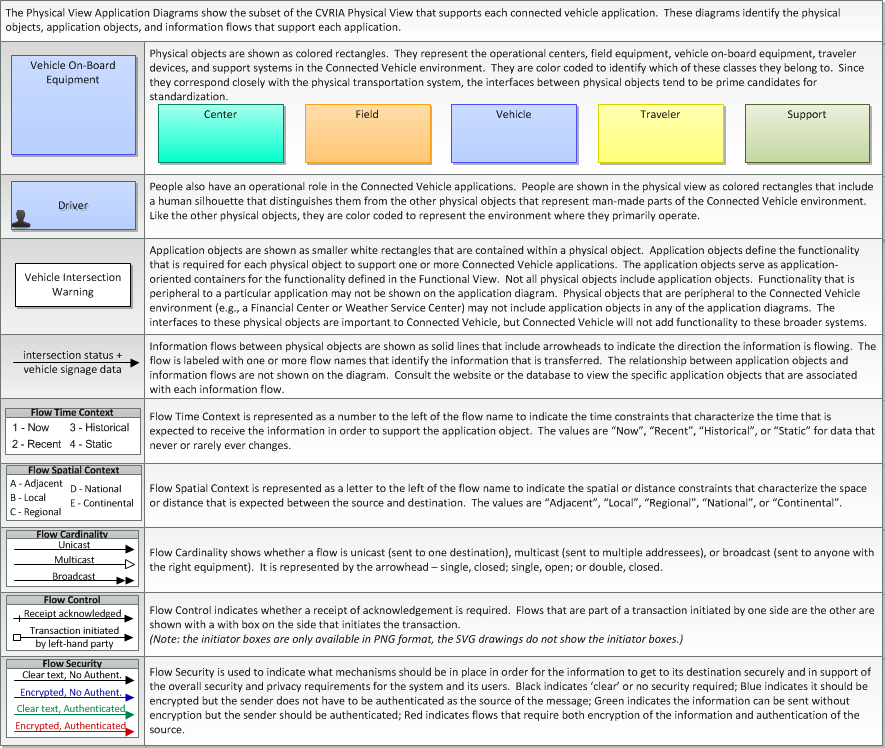
Physical
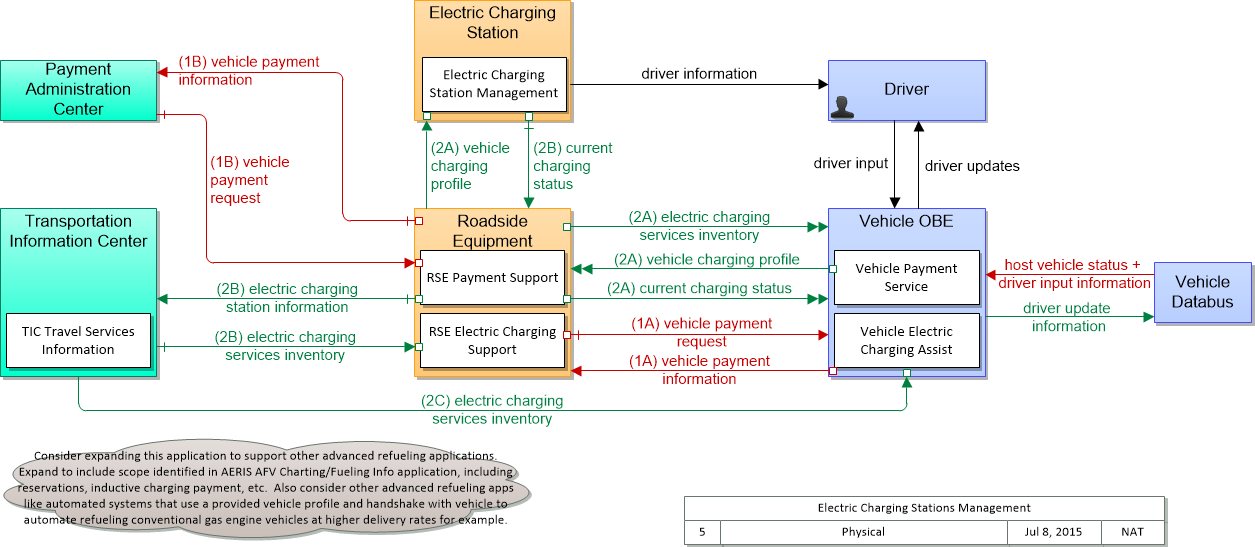
SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
Includes Physical Objects:
| Physical Object | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Driver | Vehicle | The 'Driver' represents the person that operates a vehicle on the roadway. Included are operators of private, transit, commercial, and emergency vehicles where the interactions are not particular to the type of vehicle (e.g., interactions supporting vehicle safety applications). The Driver originates driver requests and receives driver information that reflects the interactions which might be useful to all drivers, regardless of vehicle classification. Information and interactions which are unique to drivers of a specific vehicle type (e.g., fleet interactions with transit, commercial, or emergency vehicle drivers) are covered by separate objects. |
| Electric Charging Station | Field | The 'Electric Charging Station' provides access to electric vehicle supply equipment that is used to charge hybrid and all-electric vehicles. This includes public charging stations that support consumers, workplace charging stations, and fleet charging stations. |
| Payment Administration Center | Center | The 'Payment Administration Center' provides general payment administration capabilities and supports the electronic transfer of funds from the customer to the transportation system operator or other service provider. Charges can be recorded for tolls, vehicle-mileage charging, congestion charging, or other goods and services. It supports traveler enrollment and collection of both pre-payment and post-payment transportation fees in coordination with the financial infrastructure supporting electronic payment transactions. The system may establish and administer escrow accounts depending on the clearinghouse scheme and the type of payments involved. It may post a transaction to the customer account, generate a bill (for post-payment accounts), debit an escrow account, or interface to a financial infrastructure to debit a customer designated account. It supports communications with the ITS Roadway Payment Equipment to support fee collection operations. As an alternative, a wide-area wireless interface can be used to communicate directly with vehicle equipment. It also sets and administers the pricing structures and may implement road pricing policies in coordination with the Traffic Management Center. |
| Roadside Equipment | Field | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Transportation Information Center | Center | The 'Transportation Information Center' collects, processes, stores, and disseminates transportation information to system operators and the traveling public. The physical object can play several different roles in an integrated ITS. In one role, the TIC provides a data collection, fusing, and repackaging function, collecting information from transportation system operators and redistributing this information to other system operators in the region and other TICs. In this information redistribution role, the TIC provides a bridge between the various transportation systems that produce the information and the other TICs and their subscribers that use the information. The second role of a TIC is focused on delivery of traveler information to subscribers and the public at large. Information provided includes basic advisories, traffic and road conditions, transit schedule information, yellow pages information, ride matching information, and parking information. The TIC is commonly implemented as a website or a web-based application service, but it represents any traveler information distribution service. |
| Vehicle Databus | Vehicle | The 'Vehicle Databus' represents the interface to the vehicle databus (e.g., CAN, LIN, Ethernet/IP, FlexRay, and MOST) that may enable communication between the Vehicle OBE and other vehicle systems to support connected vehicle applications. The vehicle system statuses and/or sensor outputs available on the databus will vary based on the equipment installed on the vehicle and availability on databus. System statuses and sensor outputs may include select vehicle systems and sensors such as accelerometers, yaw rate sensors, and GPS derived location and timing information. In CVRIA, this physical object is used to represent the onboard interactions between the Vehicle OBE and the other systems included in a host vehicle. Note that the vehicle databus interface is not standardized across all vehicle classes. Also, some Vehicle OBE implementations will not have access to the vehicle databus. See 'Vehicle OBE' for more information. |
| Vehicle OBE | Vehicle | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
Includes Application Objects:
| Application Object | Description | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Charging Station Management | 'Electric Charging Station Management' manages vehicle charging. It communicates with the vehicle during charging and provides charge status information to the driver. A connection with Roadside Equipment provides the capability to integrate charging station coordination and communication into the broader Connected Vehicle Environment. | Electric Charging Station |
| RSE Electric Charging Support | "RSE Electric Charging Support" uses short range communications to coordinate with a vehicle that is being charged, receiving information about the operational state of the electrical system, the maximum charge rate, and the percentage-complete of the charge from the vehicle. | Roadside Equipment |
| RSE Payment Support | "RSE Payment Support" manages vehicle payments for road use based on fee structures and payment strategies based on vehicle-reported data including VMT, emissions, vehicle class or type. Fees may vary by time or location and may include incentives or credits to reward desirable driving behavior. To support payment, it receives vehicle data (e.g., time stamped roadways used by the vehicle since the last transmission) and forwards this to the Payment Administration Center. It also receives equipment status from the vehicle and vehicle characteristics sensed from the vehicle (number of axles, weight, vehicle tag image/ID). Faults are identified and forwarded to the Payment Administration Center. Finally, it requests, receives, processes, and reports vehicle payment information. | Roadside Equipment |
| TIC Travel Services Information | "TIC Travel Services Information" disseminates information about traveler services such as lodging, restaurants, and service stations. Tailored traveler service information is provided on request that meets the constraints and preferences specified by the traveler. This application also supports reservations and advanced payment for traveler services. | Transportation Information Center |
| Vehicle Electric Charging Assist | "Vehicle Electric Charging Assist" uses short range communications to coordinate with electric charging stations, providing information about the operational state of the electrical system, the maximum charge rate, and the percentage-complete of the charge. This application also receives current information about electric charging systems in the region and makes this information available to the driver on request. | Vehicle OBE |
| Vehicle Payment Service | "Vehicle Payment Service" supports vehicle payments including VMT- and zone-based payments and payments for other services including fuel/charging services. To support VMT-based payment, this application tracks the location of the vehicle at specific times and reports this VMT data along with vehicle identification. A variety of pricing strategies are supported, including strategies that include credits or incentives that reward desired driving patterns and behavior. | Vehicle OBE |
Includes Information Flows:
| Information Flow | Description |
|---|---|
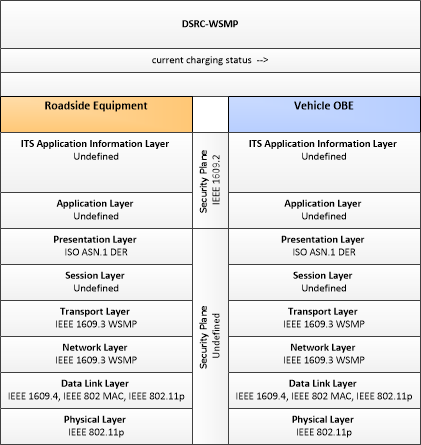
| current charging status | Current charging status including current charge rate, estimated time to completion, and cost associated with the charge. |
| driver information | Regulatory, warning, and guidance information provided to the driver while en route to support safe and efficient vehicle operation. |
| driver input | Driver input to the vehicle on-board equipment including configuration data, settings and preferences, interactive requests, and control commands. |
| driver input information | Driver input received from the driver-vehicle interface equipment via the vehicle bus. It includes configuration data, settings and preferences, interactive requests, and control commands for the connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| driver update information | Information provided to the driver-vehicle interface to inform the driver about current conditions, potential hazards, and the current status of vehicle on-board equipment. The flow includes the information to be presented to the driver and associated metadata that supports processing, prioritization, and presentation by the DVI as visual displays, audible information and warnings, and/or haptic feedback. |
| driver updates | Information provided to the driver including visual displays, audible information and warnings, and haptic feedback. The updates inform the driver about current conditions, potential hazards, and the current status of vehicle on-board equipment. |
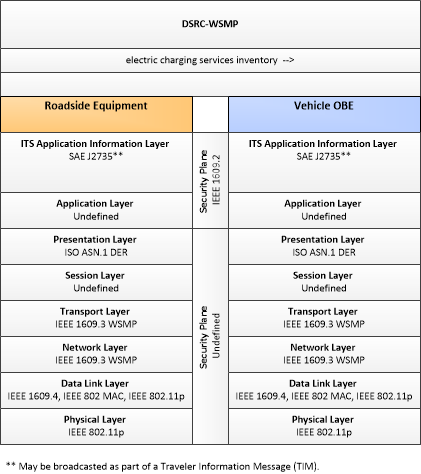
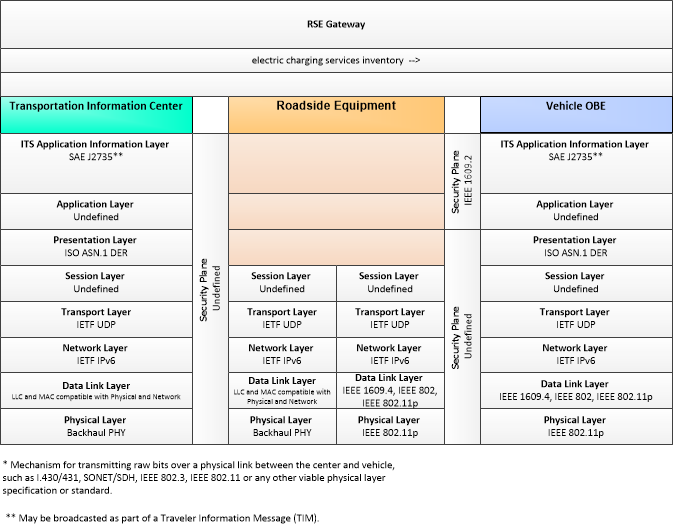
| electric charging services inventory | Aggregate information provided for electric charging stations identifying the location, operating hours, current availability, charging capacity and standards supported, access restrictions, and rates/fee structure for each station. |
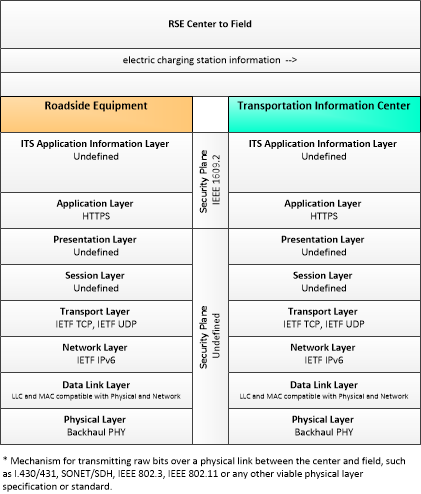
| electric charging station information | Information provided for electric charging stations identifying the location, operating hours, current availability, charging capacity and standards supported, access restrictions, and rates/fee structure. |
| host vehicle status | Information provided to the connected vehicle on-board equipment from other systems on the vehicle platform. This includes data from on-board sensors, the current status of the powertrain, steering, and braking systems, and status of safety and convenience systems. In implementations where GPS is not integrated into the Vehicle On-Board Equipment, the host vehicle is also the source for data describing the vehicle's location in three dimensions (latitude, longitude, elevation) and accurate time that can be used for time synchronization across the Connected Vehicle environment. |
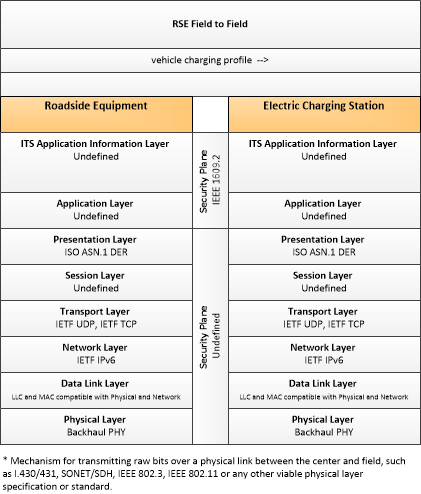
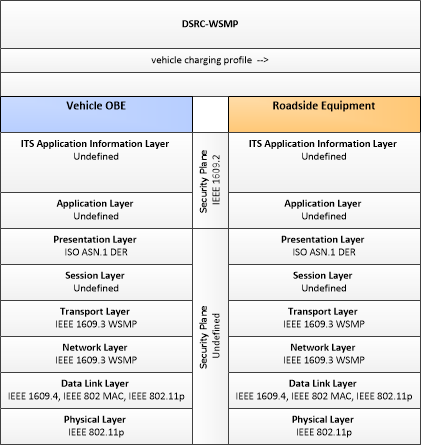
| vehicle charging profile | Vehicle information provided to an electric charging station including the operational status of the electrical system, the charging capacity and charging rate for the vehicle, and % charge complete. |
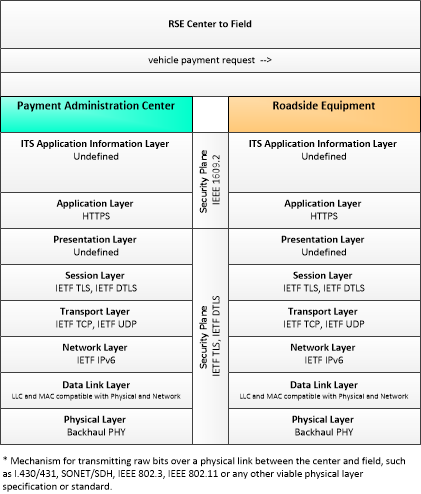
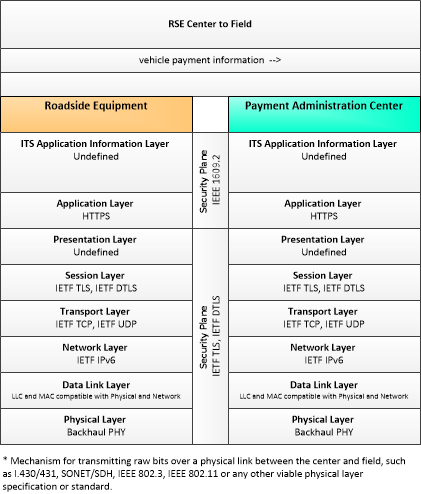
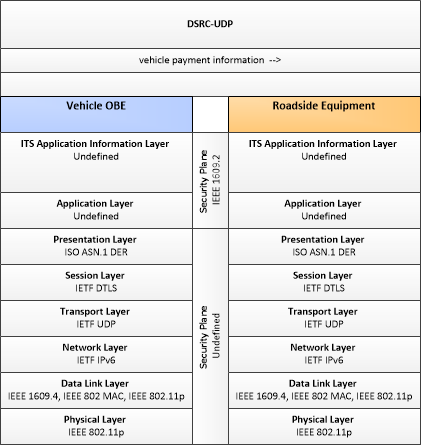
| vehicle payment information | Information provided for payment of tolls or parking fees including identification that can be used to identify the payment account or source and related vehicle and service information that are used to determine the type and price of service requested. The information exchange normally supports an account debit to pay fees, but an account credit may be initiated where pricing strategies include incentives. |
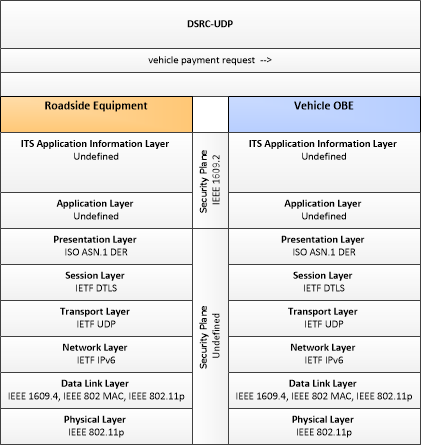
| vehicle payment request | Request for information supporting payments. For fee structures that include incentives, the request may support either an account debit or an account credit or reimbursement. |
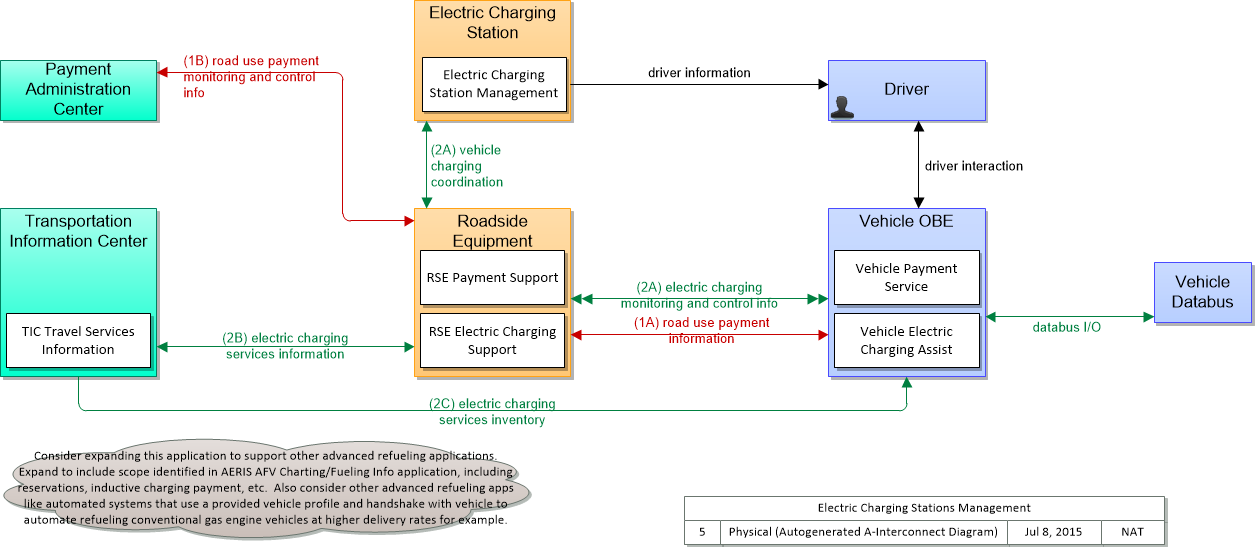
Application Interconnect Diagram
SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
Application Triples
Requirements
| Need | Requirement | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N1.001 | Transportation agencies need to gather data from vehicles or infrastructure to support environmental monitoring. | 1.001 | All environmental applications shall collect data from mobile devices to support environmental monitoring, including ambient air quality, emissions, temperature, precipitation, and other road weather information. |
| 1.002 | All environmental applications shall collect data from infrastructure devices to support environmental monitoring, including ambient air quality, emissions, temperature, precipitation, wind speed, and other road weather information. | ||
| N1.051 | Electric Charging Stations Management (ECSM) needs to collect the charging needs (duration, amount, interface) and location of electric vehicles. | 1.145 | ECSM shall collect the charging needs (duration, amount, interface) and location of electric vehicles. |
| N1.052 | ECSM needs to know the charging capacity (stations, amount) of charging stations. | 1.146 | ECSM shall collect the charging capacity (stations, amount) of charging stations. |
| N1.053 | ECSM needs to correlate electric vehicle needs to charging station capacities. | 1.147 | ECSM shall correlate electric vehicle needs to charging station capacities. |
| N1.054 | ECSM needs to provide charging station information to electric vehicles in order to balance the supply and demand of charging facilities. | 1.148 | ECSM shall provide charging station information to electric vehicles in order to balance the supply and demand of charging facilities. |
Related Sources
- SAE J3067- Candidate Improvements to Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) Message Set Dictionary (SAE J2735)Using Systems Engineering Methods, 8/15/2014
Security
In order to participate in this application, each physical object should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Physical Object Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Object | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability | Security Class |
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | ||||
In order to participate in this application, each information flow triple should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Information Flow Security | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Destination | Information Flow | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability |
| Basis | Basis | Basis | |||
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | |||||