Type: Mobility
Groups:- Traffic Signals
Freight Signal Priority
The Freight Signal Priority application (FSP) provides traffic signal priority for freight and commercial vehicles traveling in a signalized network. The goal of the freight signal priority application is to reduce stops, delays, to increase travel time reliability for freight traffic, and to enhance safety at intersections.
Enterprise
This is one way this application may be realized, but not the only way. There are other ways to build a given application and accomplish a stated objective.
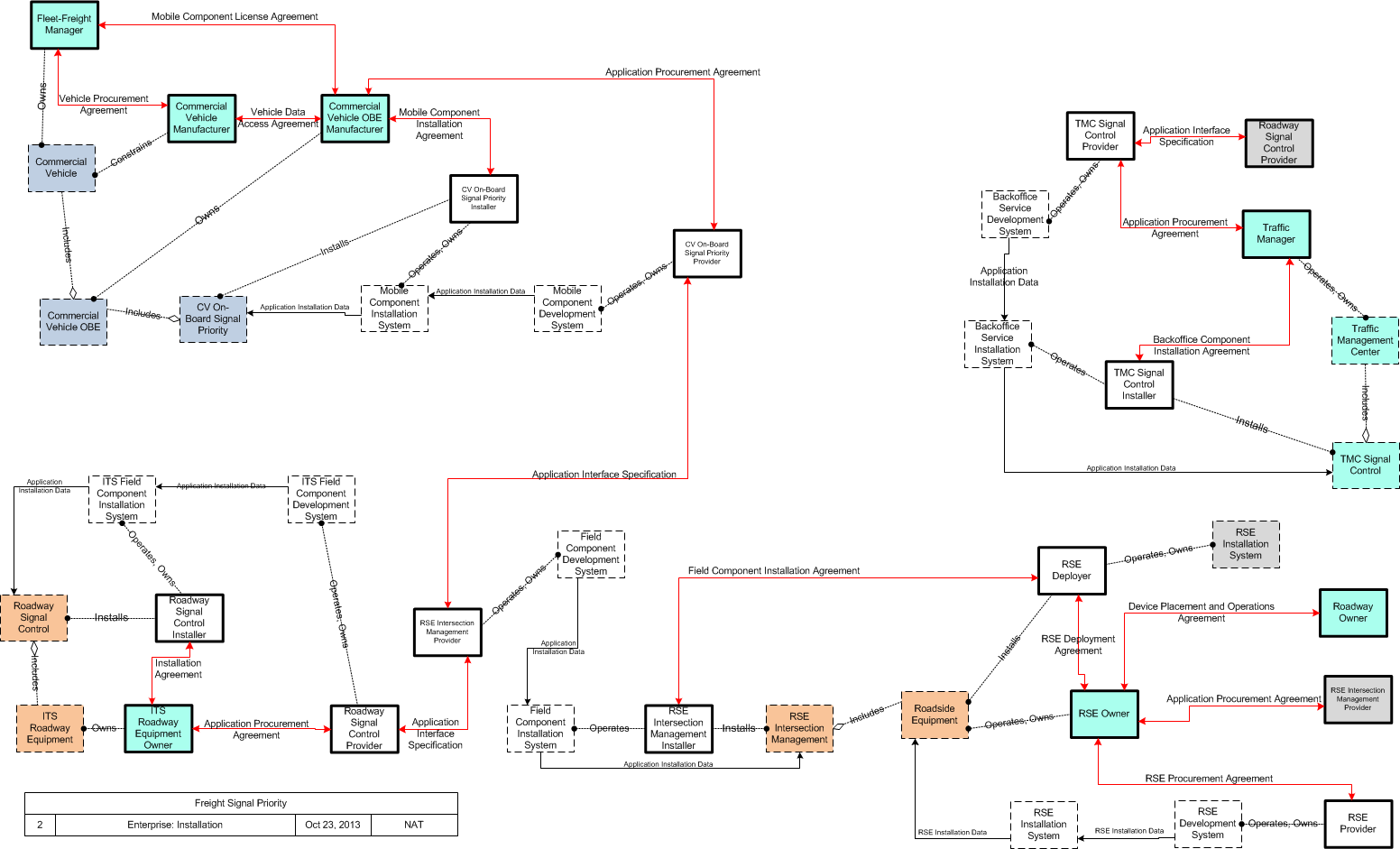
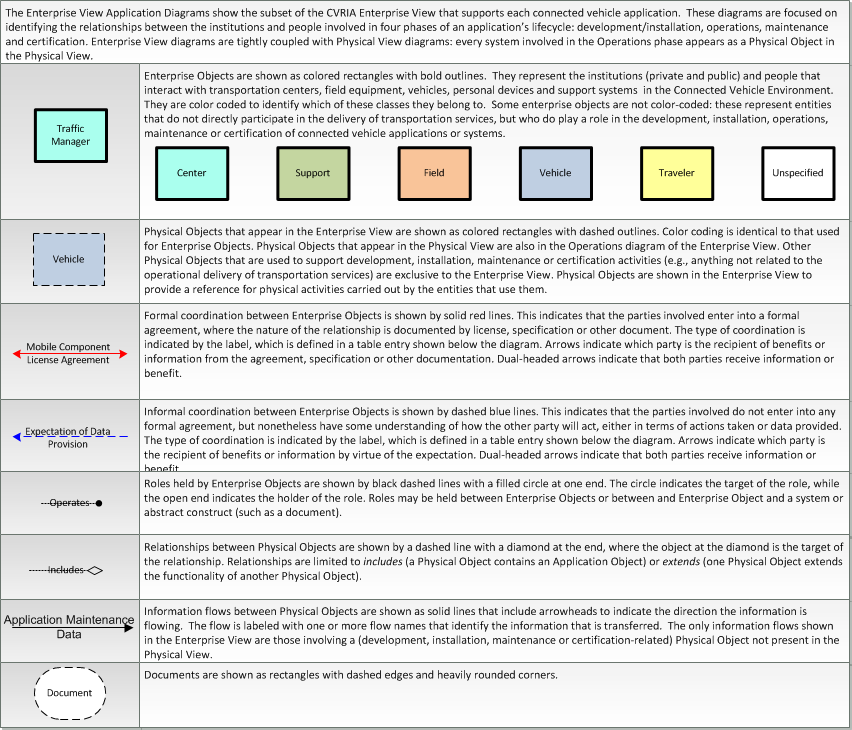
The enterprise diagram can be viewed in SVG or PNG format and the current format is SVG. SVG Diagrams: Installation Operations Maintenance Certification
PNG Diagrams: Installation Operations Maintenance Certification
Business Interaction Matrix:
| Freight Signal Priority Operations Stage | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roadway Owner | RSE Owner | RSE Operator | ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Operator | Fleet-Freight Manager | Intermodal Terminal Operator | Commercial Vehicle Owner | Commercial Vehicle Driver | Traffic Manager | RSE Intersection Management Provider | CV On-Board Signal Priority Provider | |
| Roadway Owner | Service Delivery Agreement | |||||||||||
| RSE Owner | Service Delivery Agreement | Operations Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||
| RSE Operator | Operations Agreement | |||||||||||
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Operations Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | |||||||||
| ITS Roadway Operator | Operations Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | ||||||||||
| Fleet-Freight Manager | Information Exchange Agreement | Expectation of Data Provision | ||||||||||
| Intermodal Terminal Operator | Information Exchange Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | ||||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle Owner | Expectation of Data Provision | Vehicle Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | |||||||||
| Commercial Vehicle Driver | Expectation of Information Provision | Vehicle Usage Agreement | ||||||||||
| Traffic Manager | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | ||||||||||
| RSE Intersection Management Provider | Application Usage Agreement | |||||||||||
| CV On-Board Signal Priority Provider | Application Usage Agreement | |||||||||||
Includes Enterprise Objects:
| Enterprise Object | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Certification Entity | The body that determines whether an application may be deployed and operated in the Connected Vehicle Environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with application type. For example, applications with human safety component (crash avoidance, movement assistance etc.) may have stringent requirements and extensive testing in a variety of conditions, while applications that provide strictly mobility functionality may have far less testing requirements; possibly as little as just making sure the application doesn't interfere with any other applications. |
| Commercial Vehicle Driver | The 'Commercial Vehicle Driver' represents the people that operate vehicles transporting goods, including both long haul trucks and local pick-up and delivery vans. This physical object is complementary to the Driver physical object in that it represents those interactions which are unique to Commercial Vehicle Operations. Information flowing from the Commercial Vehicle Driver includes those system inputs specific to Commercial Vehicle Operations. |
| Commercial Vehicle Manufacturer | The entity which builds commercial vehicles, including long haul trucks and local pick up and delivery vehicles. This entity is complementary to the Vehicle Manufacturer entity in that it represents those aspects of vehicle manufacture which are unique to commercial vehicles. |
| Commercial Vehicle OBE Manufacturer | The Commercial Vehicle OBE Manufacturer is the provider of the commercial vehicle on-board equipment. This entity may design and build the OBE, or may integrate other components to form the OBE, or may use some combination of approaches to provide the on-board equipment. Since the OBE could be aftermarket, retrofit, built-in or nomadic, this entity is the one that builds whatever that-is. In some cases it may be a smart phone manufacturer, or in others a top tier parts supplier, or any other entity in the production chain, depending on the device and commercial vehicle in question. |
| Commercial Vehicle Owner | The entity that owns the commercial vehicle. This entity is complementary to the Vehicle Owner in that it represents those aspects of ownership which are unique to commercial vehicles. |
| CV On-Board Signal Priority Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| CV On-Board Signal Priority Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| CV On-Board Signal Priority Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Device Certification Entity | The body that determines whether a device may be deployed and operated in the Connected Vehicle Environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with device type. |
| Federal Regulatory | Federal regulatory bodies that have legal authority to control and/or provide input to policies regulating transportation infrastructure and operations. This includes entities such as the Federal Communications Commission and US Department of Transportation. |
| Fleet-Freight Manager | The 'Fleet-Freight Manager' represents the people that are responsible for the dispatching and management of Commercial Vehicle fleets (e.g. traditional Fleet Managers) and Freight Equipment assets. It may be many people in a large tracking organization or a single person (owner driver) in the case of single vehicle fleets. The Fleet-Freight Manager provides instructions and coordination for Commercial Vehicles and Freight Equipment and receives the status of the vehicles and freight equipment in the fleet that they manage. |
| Intermodal Terminal Operator | The entity that operates the intermodal terminal, the point of exchange where freight is moved from one mode to another. |
| ITS Certification Entity | The body that determines whether an ITS device or application may be deployed and operated in the transportation environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with device and application type. Typically not a formal body, assigned on a project-by-project basis depending on the type of infrastructure involved. Since ITS projects are locally-focused (typically state or smaller), the entities that are part of this body are typically those with operational jurisdiction where the ITS is installed (e.g., state or local DOTs, state or local maintenance managers etc.) |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | The entity that owns the Roadway ITS equipment. |
| ITS Roadway Operator | The entity that operates the Roadway ITS equipment. |
| Roadway Owner | The owner of the roadway proximate to which roadside equipment will be/is installed. |
| Roadway Signal Control Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Signal Control Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Signal Control Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Deployer | The entity responsible for the deployment, operations and maintenance of roadside equipment. |
| RSE Intersection Management Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Intersection Management Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Intersection Management Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Operator | The entity that operates roadside equipment in the transportation environment. |
| RSE Owner | The owner of roadside equipment. |
| RSE Provider | The "RSE Provider" is the entity that develops and (presumably) sells roadside equipment to other entities for deployment and research. |
| State Regulatory | State regulatory bodies that have legal authority to control and/or provide input to policies regulating vehicles, transportation infrastructure and operations. This includes entities like Departments of Motor Vehicles, property tax authorities and tolling agencies. |
| TMC Signal Control Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Signal Control Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Signal Control Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Traffic Manager | The entity responsible for the management of traffic, both freeway and arterial. |
Includes Resources:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Component Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of an application component. Certification Requirements must be met in order for an application to be installed in the CVE. |
| Backoffice Service Development System | The systems used to develop backoffice (center) hardware and software components of applications. |
| Backoffice Service Installation System | The systems used to install and configure backoffice (center) hardware and software components. |
| Backoffice Service Maintenance System | The systems used to maintain and upgrade backoffice (center) hardware and software components. |
| Commercial Vehicle | The commercial vehicle includes the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support safe and efficient commercial vehicle operations. It includes two-way communications between the commercial vehicle drivers, their fleet managers, attached freight equipment, and roadside officials, and provides HAZMAT response teams with timely and accurate cargo contents information after a vehicle incident. It can collect and process vehicle, cargo information from the attached freight equipment, and driver safety data and status and alert the driver whenever there is a potential safety or security problem. Basic identification, security and safety status data are supplied to inspection facilities at mainline speeds. In addition, it can automatically collect and record mileage, fuel usage, and border crossings. |
| Commercial Vehicle OBE | The Commercial Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) resides in a commercial vehicle and provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support safe and efficient commercial vehicle operations. It provides two-way communications between the commercial vehicle drivers, their fleet managers, attached freight equipment, and roadside officials. In CVRIA, a separate 'Vehicle OBE' physical object supports the general V2V and V2I safety applications and other applications that apply to all vehicles, including commercial vehicles. The Commercial Vehicle OBE supplements these general capabilities with capabilities that are specific to commercial vehicles. |
| CV On-Board Signal Priority | "CV On-board Signal Priority" provides the capability for commercial vehicles to determine eligibility for priority and request signal priority at signalized intersections, ramps, and interchanges through short range communication with traffic control equipment at the roadside. |
| Device Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of a connected vehicle device. Certification Requirements must be met in order for the device to be granted the credentials necessary to operate in the Connected Vehicle Environment. |
| Field Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the field component of the application. |
| Field Component Installation System | The system used to install a field component of a connected vehicle application. |
| Field Component Maintenance System | The system used to install and configure changes and updates to the field component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| Fleet and Freight Management Center | The 'Fleet and Freight Management Center' provides the capability for commercial drivers and fleet-freight managers to receive real-time routing information and access databases containing vehicle and/or freight equipment locations as well as carrier, vehicle, freight equipment and driver information. The 'Fleet and Freight Management Center' also provides the capability for fleet managers to monitor the safety and security of their commercial vehicle drivers and fleet. |
| Intermodal Terminal | The 'Intermodal Terminal' represents the terminal areas corresponding to modal change points. This includes interfaces between roadway freight transportation and air, rail, and/or water shipping modes. The basic unit of cargo handled by the Intermodal Terminal physical object is the container; less-than-container load handling is typically handled at a different facility (i.e., Freight Consolidation Station). The Intermodal Terminal can include electronic gate control for entrance and exit from the facility, automated guidance of vehicles within the facility, alerting appropriate parties of container arrivals and departures, and inventory and location of temporarily stored containers. |
| ITS Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of an ITS device or ITS application. Applicability varies with jurisdictions, but typically devices and applications must meet pre-defined acceptance criteria prior to usage in the transportation environment. |
| ITS Field Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the ITS field component of the application. |
| ITS Field Component Installation System | The system used to install a field component of a connected vehicle application. |
| ITS Field Component Maintenance System | The system used to install and configure changes and updates to the ITS field component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway itself. In CVRIA, this physical object represents all of the other ITS field equipment that interfaces with and supports the Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE). This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| Mobile Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the mobile component of the application. |
| Mobile Component Installation System | The system that interacts with the Vehicle OBE other mobile device and installs the mobile component of the application. |
| Mobile Component Maintenance System | The system used to configure changes and updates to the mobile component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| Roadside Equipment | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Roadway Signal Control | "Roadway Signal Control" includes the field elements that monitor and control signalized intersections. It includes the traffic signal controllers, detectors, conflict monitors, signal heads, and other ancillary equipment that supports traffic signal control. It also includes field masters, and equipment that supports communications with a central monitoring and/or control system, as applicable. The communications link supports upload and download of signal timings and other parameters and reporting of current intersection status. It represents the field equipment used in all levels of traffic signal control from basic actuated systems that operate on fixed timing plans through adaptive systems. It also supports all signalized intersection configurations, including those that accommodate pedestrians. In advanced, future implementations, environmental data may be monitored and used to support dilemma zone processing and other aspects of signal control that are sensitive to local environmental conditions. |
| RSE Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the roadside equipment. |
| RSE Installation System | The system used to install and configure the roadside equipment. |
| RSE Intersection Management | "RSE Intersection Management" uses short range communications to support connected vehicle applications that manage signalized intersections. It communicates with approaching vehicles and ITS infrastructure (e.g., the traffic signal controller) to enhance traffic signal operations. Coordination with the ITS infrastructure also supports conflict monitoring to ensure the RSE output and traffic signal control output are consistent and degrade in a fail safe manner. |
| RSE Maintenance System | The system used to configure changes and updates to the roadside equipment. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the RSE's configuration and performance. |
| TMC Signal Control | "TMC Signal Control" provides the capability for traffic managers to monitor and manage the traffic flow at signalized intersections. This capability includes analyzing and reducing the collected data from traffic surveillance equipment and developing and implementing control plans for signalized intersections. Control plans may be developed and implemented that coordinate signals at many intersections under the domain of a single traffic management center and are responsive to traffic conditions and adapt to support incidents, preemption and priority requests, pedestrian crossing calls, etc. |
| Traffic Management Center | The 'Traffic Management Center' monitors and controls traffic and the road network. It represents centers that manage a broad range of transportation facilities including freeway systems, rural and suburban highway systems, and urban and suburban traffic control systems. It communicates with ITS Roadway Equipment and Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE) to monitor and manage traffic flow and monitor the condition of the roadway, surrounding environmental conditions, and field equipment status. It manages traffic and transportation resources to support allied agencies in responding to, and recovering from, incidents ranging from minor traffic incidents through major disasters. |
| Vehicle OBE | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
Includes Roles:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Certifies | An Enterprise verifies that a target Resource meets relevant performance, functional, environmental and quality requirements. |
| Constrains | A Resource or Enterprise applies requirements, constraints and associated tests to another Resource. |
| Installs | An Enterprise performs the initial delivery, integration and configuration of the target Resource. |
| Maintains | An Enterprise administers the hardware and software that comprise the target Resource. |
| Member | An Enterprise is part of another larger, target Enterprise. |
| Operates | An Enterprise controls the functionality and state of the target Resource. An Enterprise that Operates a resource is considered Responsible. |
| Owns | An Enterprise has financial ownership and control over the Resource. An Enterprise that Owns a resource is considered Accountable. |
Includes Coordination:
| Coordination | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Application Installation Data | Information Sharing | Data needed to install the application, including the application executable code and any configuration data. Unidirectional flow. |
| Application Interface Specification | Agreement | The definition of an interface between two application components that operate on two distinct pieces of hardware. The Application Interface Specification is specific to the application in question. |
| Application Maintenance Data | Information Sharing | Data used to facilitate the upgrade, patching and general health maintenance of an application component. |
| Application Performance Data | Information Sharing | Data used to characterize application performance, including such measures as availability, known errors and known uses. |
| Application Procurement Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity provides a copy of an application component to another entity. This component is capable of being installed and functioning, according to its requirements that passed through the application's certification process. |
| Application Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity that controls an application component's use gives the other entity the necessary tools and permission to operate that application or application component. |
| Backoffice Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one party permission to install a backoffice application component on a center-based device controlled by the other party. |
| Device Placement and Operations Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that enables the controller of a physical device to install it (so as to make it operational) at a fixed location controlled by another entity. |
| Expectation of Data Provision | Expectation | An expectation where one party believes another party will provide data on a regular and recurring basis, and that that data will be useful to the receiver in the context of the receiver's application. This thus includes some expectation of data fields, timeliness, quality, precision and similar qualities of data. |
| Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation | An expectation where one party believes another party will provide it information whenever such information is likely relevant to the recipient. |
| Field Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one party permission to install a field application component on a roadside device controlled by the other party. |
| Includes | Includes | Indicates that one component is entirely contained within another component. |
| Information Exchange Agreement | Agreement | An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. |
| Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Agreement | An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. This also includes a specification for action that shall, should or may be taken by one party in response to this information. |
| Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity installs an application component on a device controlled by another entity. |
| Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of a system under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that states one entity will provide data related to maintenance of an application component to the other entity. |
| Mobile Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon the controller of OBE gives another party permission to install, configure and make operational a component that enables the mobile portion of an application. |
| Mobile Component License Agreement | Agreement | An end-user license agreement allowing the operator of the mobile device to use the mobile application component that is part of the application in question. |
| Operations Agreement | Agreement | An agreement where one entity agrees to operate a device or application on behalf of another, device/application controlling entity. |
| RSE Deployment Agreement | Agreement | Agreement to install, configure and make operational roadside equipment, between the provider of that equipment and the entity that controls access to the roadside. May define locations, expectation of power provision, backhaul responsibility and installation restrictions. |
| RSE Installation Data | Information Sharing | Data necessary to configure and make RSE operational. Uni-directional. |
| RSE Maintenance Data | Information Sharing | Data necessary to modify the operational configuration of RSE; assumes RSE is already configured. Uni-directional. |
| RSE Performance Data | Information Sharing | Data that includes metrics of RSE performance. Could include fields such as uptime, packets received/transmitted, distance vector from which packets received, as well as application-specific performance measures. |
| RSE Procurement Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity provides roadside equipment to another entity. The RSE is capable of being installed and functioning, according to its requirements that passed through the device's certification process. |
| Service Delivery Agreement | Agreement | A relationship where one party agrees to provide a service to the other party. This agreement may specify the expected performance of this service in terms of availability and/or actions/time-type performance specifications. |
| Vehicle Data Access Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereby the party that controls access to on-board vehicle data grants another party the right and ability to access that data. Includes the conditions under which data may be accessed, and specifies the mechanisms, including physical and functional access methods, data formats and any other considerations necessary for the accessing party to acquire data. May also include caveats regarding responsibility for data quality and responsibility for use of the data. |
| Vehicle Procurement Agreement | Agreement | The exchange of a vehicle for compensation. One entity purchases the vehicle from the other. |
| Vehicle Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement between the owner of a vehicle and a prospective operator, whereupon the owner allows the operator to use the vehicle. |
| Warranty | Agreement | A guarantee or promise made by one entity to another, that provides assurance of the functionality and performance over time of an application component. |
Functional
Includes Processes:
Includes Data Flows:
Physical
This is one way this application may be realized, but not the only way. There are other ways to build a given application and accomplish a stated objective.
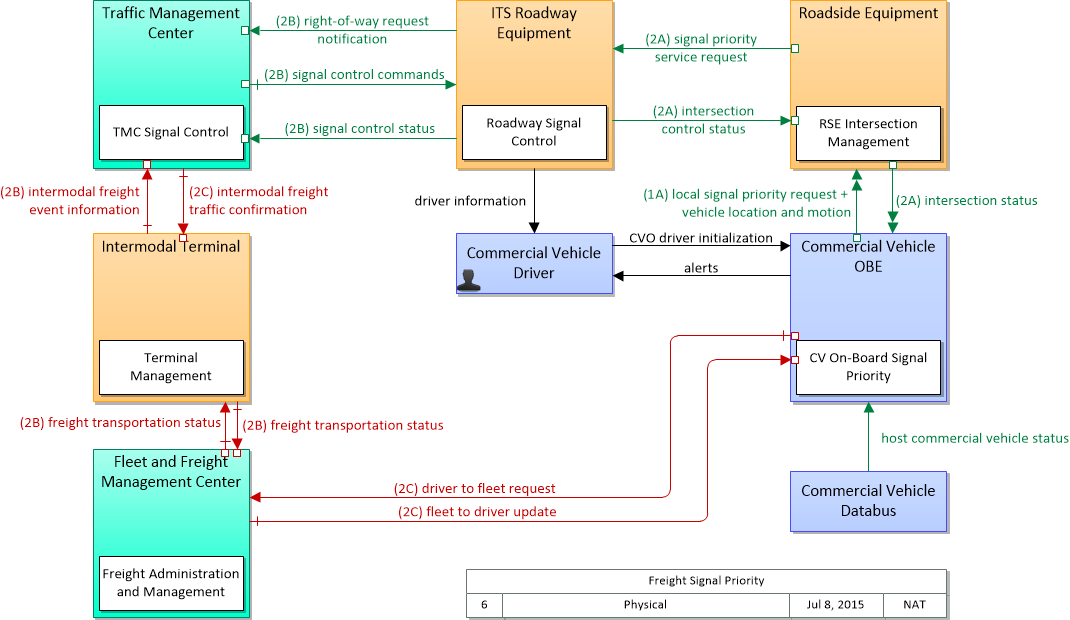
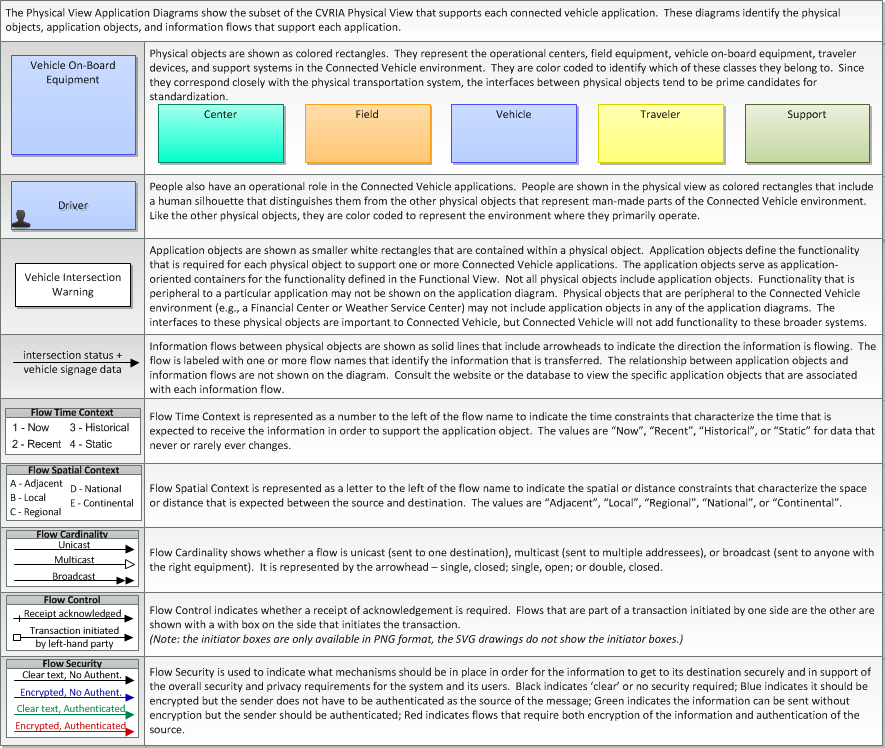
The physical diagram can be viewed in SVG or PNG format and the current format is SVG. SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
Includes Physical Objects:
| Physical Object | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
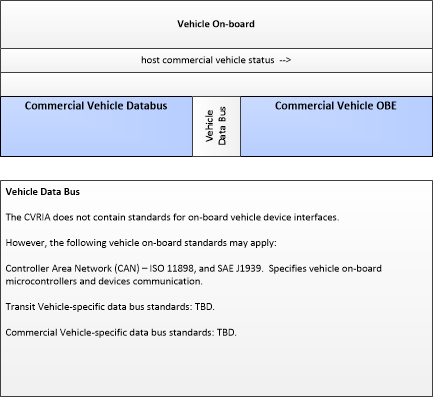
| Commercial Vehicle Databus | Vehicle | The 'Commercial Vehicle Databus' represents the interface to the heavy vehicle databus that connects on-board systems included in the commercial vehicle. This vehicle is used to transport goods, is operated by a professional driver and typically administered as part of a larger fleet. Commercial Vehicle classification applies to all goods transport vehicles ranging from small panel vans used in local pick-up and delivery services to large, multi-axle tractor-trailer rigs operating on long haul routes. It is a specialized and extended form of the Vehicle Databus that may be subject to different vehicle databus standards and connect with a broad range of components that are specific to commercial vehicles including the systems that are used to monitor, secure, and maintain freight while enroute. As a specialized form of the Vehicle Databus, it also provides access to the general-purpose sensors (e.g., radars, cameras), GPS, drive train monitoring and control systems, and vehicle safety features that support connected vehicle applications. |
| Commercial Vehicle Driver | Vehicle | The 'Commercial Vehicle Driver' represents the people that operate vehicles transporting goods, including both long haul trucks and local pick-up and delivery vans. This physical object is complementary to the Driver physical object in that it represents those interactions which are unique to Commercial Vehicle Operations. Information flowing from the Commercial Vehicle Driver includes those system inputs specific to Commercial Vehicle Operations. |
| Commercial Vehicle OBE | Vehicle | The Commercial Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) resides in a commercial vehicle and provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support safe and efficient commercial vehicle operations. It provides two-way communications between the commercial vehicle drivers, their fleet managers, attached freight equipment, and roadside officials. In CVRIA, a separate 'Vehicle OBE' physical object supports the general V2V and V2I safety applications and other applications that apply to all vehicles, including commercial vehicles. The Commercial Vehicle OBE supplements these general capabilities with capabilities that are specific to commercial vehicles. |
| Fleet and Freight Management Center | Center | The 'Fleet and Freight Management Center' provides the capability for commercial drivers and fleet-freight managers to receive real-time routing information and access databases containing vehicle and/or freight equipment locations as well as carrier, vehicle, freight equipment and driver information. The 'Fleet and Freight Management Center' also provides the capability for fleet managers to monitor the safety and security of their commercial vehicle drivers and fleet. |
| Intermodal Terminal | Field | The 'Intermodal Terminal' represents the terminal areas corresponding to modal change points. This includes interfaces between roadway freight transportation and air, rail, and/or water shipping modes. The basic unit of cargo handled by the Intermodal Terminal physical object is the container; less-than-container load handling is typically handled at a different facility (i.e., Freight Consolidation Station). The Intermodal Terminal can include electronic gate control for entrance and exit from the facility, automated guidance of vehicles within the facility, alerting appropriate parties of container arrivals and departures, and inventory and location of temporarily stored containers. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Field | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway itself. In CVRIA, this physical object represents all of the other ITS field equipment that interfaces with and supports the Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE). This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| Roadside Equipment | Field | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Traffic Management Center | Center | The 'Traffic Management Center' monitors and controls traffic and the road network. It represents centers that manage a broad range of transportation facilities including freeway systems, rural and suburban highway systems, and urban and suburban traffic control systems. It communicates with ITS Roadway Equipment and Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE) to monitor and manage traffic flow and monitor the condition of the roadway, surrounding environmental conditions, and field equipment status. It manages traffic and transportation resources to support allied agencies in responding to, and recovering from, incidents ranging from minor traffic incidents through major disasters. |
Includes Application Objects:
| Application Object | Description | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| CV On-Board Signal Priority | "CV On-board Signal Priority" provides the capability for commercial vehicles to determine eligibility for priority and request signal priority at signalized intersections, ramps, and interchanges through short range communication with traffic control equipment at the roadside. | Commercial Vehicle OBE |
| Freight Administration and Management | "Freight Administration and Management" manages the movement of freight from source to destination. It interfaces to intermodal customers to setup and schedule transportation and coordinates with intermodal terminals and freight consolidation stations to coordinate the shipment. It coordinates with the appropriate government agencies to expedite the movement of trucks, their drivers, and their cargo across international borders. The application monitors the status of the freight and freight equipment (container, trailer, or chassis) and monitors freight location and compares it against the planned route. | Fleet and Freight Management Center |
| Roadway Signal Control | "Roadway Signal Control" includes the field elements that monitor and control signalized intersections. It includes the traffic signal controllers, detectors, conflict monitors, signal heads, and other ancillary equipment that supports traffic signal control. It also includes field masters, and equipment that supports communications with a central monitoring and/or control system, as applicable. The communications link supports upload and download of signal timings and other parameters and reporting of current intersection status. It represents the field equipment used in all levels of traffic signal control from basic actuated systems that operate on fixed timing plans through adaptive systems. It also supports all signalized intersection configurations, including those that accommodate pedestrians. In advanced, future implementations, environmental data may be monitored and used to support dilemma zone processing and other aspects of signal control that are sensitive to local environmental conditions. | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| RSE Intersection Management | "RSE Intersection Management" uses short range communications to support connected vehicle applications that manage signalized intersections. It communicates with approaching vehicles and ITS infrastructure (e.g., the traffic signal controller) to enhance traffic signal operations. Coordination with the ITS infrastructure also supports conflict monitoring to ensure the RSE output and traffic signal control output are consistent and degrade in a fail safe manner. | Roadside Equipment |
| Terminal Management | "Terminal Management" supports the operation of the roadway aspects of an intermodal terminal. The key capabilities include the ability to identify and control vehicle traffic entering and departing the facility, guide vehicles to loading and unloading points, maintain site security and monitor container integrity, provide an interface to Customs as appropriate, and acknowledge container pickup and drop-off. Other capabilities include the ability to track container locations within the facility, manage any other required assets, like truck chassis, and provide reservation services to manage congestion at busy terminals. This application also provides information to support load matching services for drayage operators. | Intermodal Terminal |
| TMC Signal Control | "TMC Signal Control" provides the capability for traffic managers to monitor and manage the traffic flow at signalized intersections. This capability includes analyzing and reducing the collected data from traffic surveillance equipment and developing and implementing control plans for signalized intersections. Control plans may be developed and implemented that coordinate signals at many intersections under the domain of a single traffic management center and are responsive to traffic conditions and adapt to support incidents, preemption and priority requests, pedestrian crossing calls, etc. | Traffic Management Center |
Includes Information Flows:
| Information Flow | Description |
|---|---|
| alerts | This flow represents the visual or auditory interface with ITS equipment containing specific alerts and messages related to commercial vehicles (e.g. trucks not advised, trucks over 10 tons not allowed on bridge, route details). This also includes detected route deviations and warning indications detected by on-board sensors (e.g., safety) and freight equipment sensors (e.g., breach, cargo). |
| CVO driver initialization | This flow represents the tactile or auditory interface with ITS equipment containing the commercial vehicle driver and vehicle information. This flow contains inquiries to the commercial vehicle managing system, interaction with on-board equipment including setup, configuration, and initiation of self tests, and entry of carrier, driver, vehicle, and route information. |
| driver information | Regulatory, warning, and guidance information provided to the driver while en route to support safe and efficient vehicle operation. |
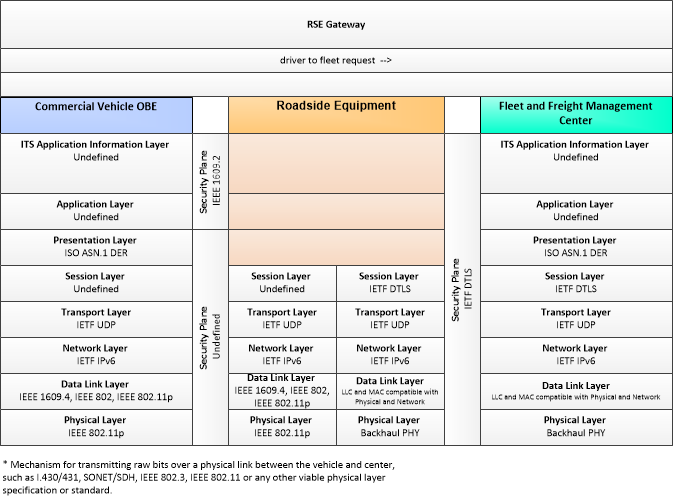
| driver to fleet request | Requests from the driver and vehicle for routing, payment, and enrollment information. |
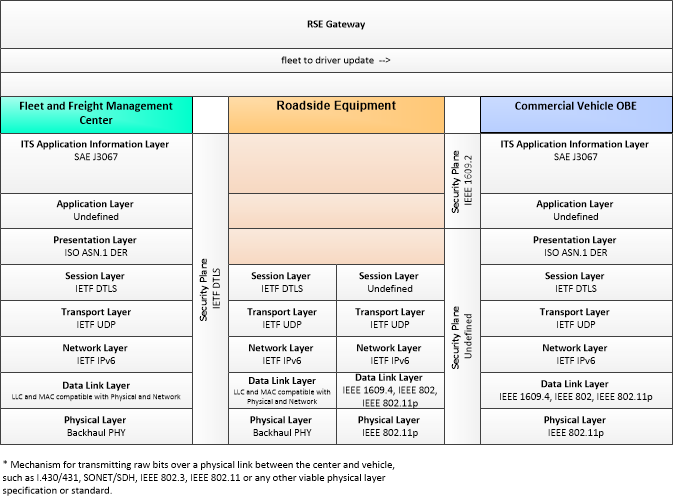
| fleet to driver update | Updated instructions to the driver including dispatch, routing, and special instructions. |
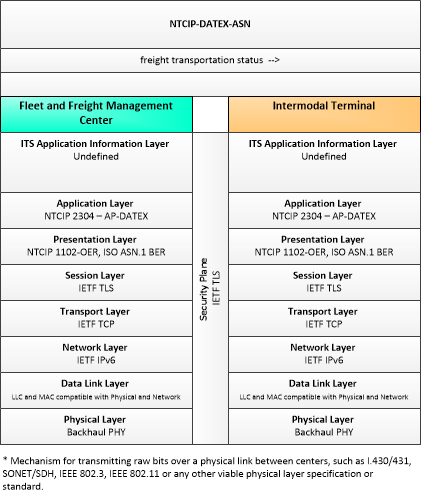
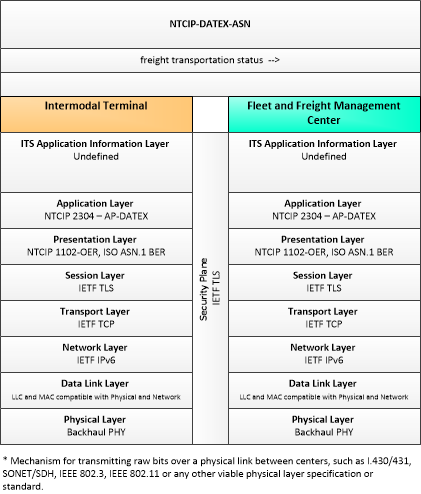
| freight transportation status | A time-stamped status of a freight shipment as it passes through the supply chain from manufacturer through arrival at its final destination; including cargo movement logs, routing information, and cargo ID's. |
| host commercial vehicle status | Information provided to the Connected Vehicle on-board equipment from other systems on the Commercial Vehicle Platform. |
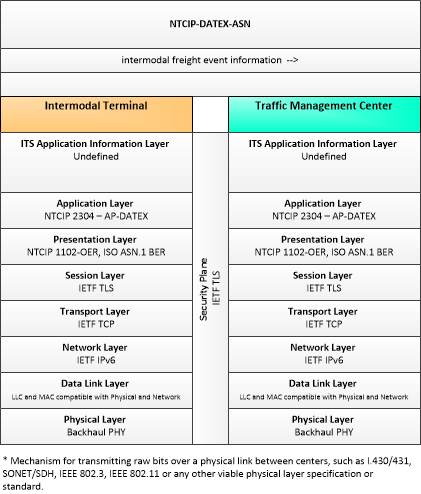
| intermodal freight event information | Plans for movement of intermodal freight from the depot area possibly impacting traffic. May also include requests for special treatment at traffic signals or dynamic lane management systems. |
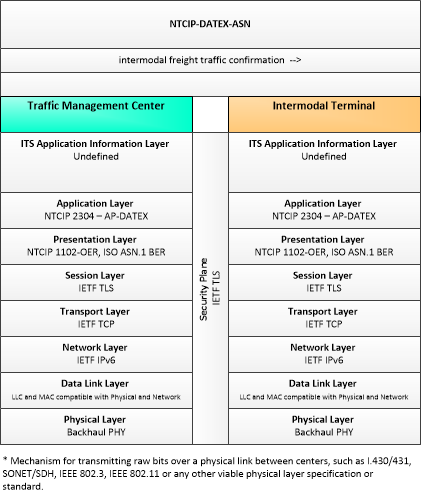
| intermodal freight traffic confirmation | Confirmation that details concerning the movement of intermodal freight on the roadway network have been received and processed. May also include information on traffic conditions affecting the depot including information concerning any special traffic control accommodations or restrictions for commercial vehicles. |
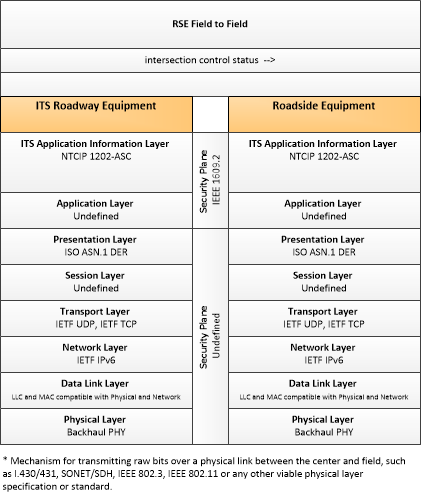
| intersection control status | Status data provided by the traffic signal controller including phase information, alarm status, and priority/preempt status. |
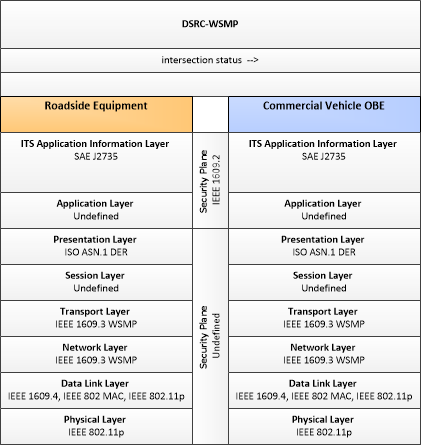
| intersection status | Current signal phase and timing information for all lanes at a signalized intersection. This flow identifies active lanes and lanes that are being stopped and specifies the length of time that the current state will persist for each lane. It also identifies signal priority and preemption status and pedestrian crossing status information where applicable. |
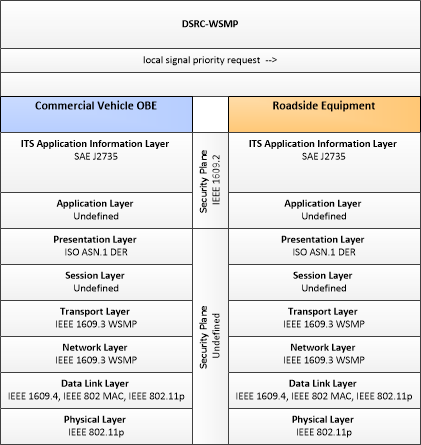
| local signal priority request | Request from a vehicle to a signalized intersection for priority at that intersection. This flow also allows the vehicle to cancel a priority request (for example, when the vehicle clears the intersection). |
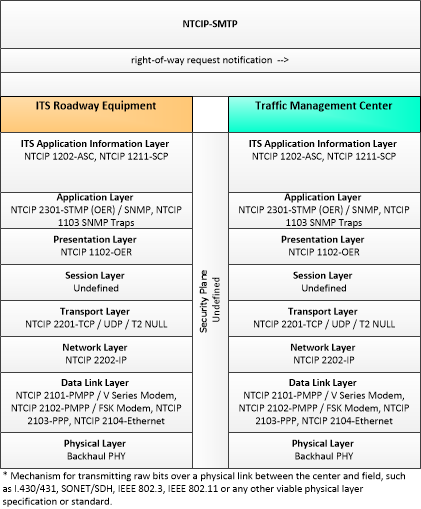
| right-of-way request notification | Notice that a request has occurred for signal prioritization, signal preemption, pedestrian call, multi-modal crossing activation, or other source for right-of-way. |
| signal control commands | Control of traffic signal controllers or field masters including clock synchronization. |
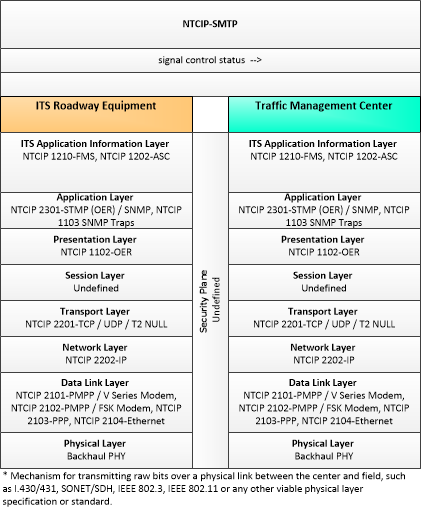
| signal control status | Operational and status data of traffic signal control equipment including operating condition and current indications. |
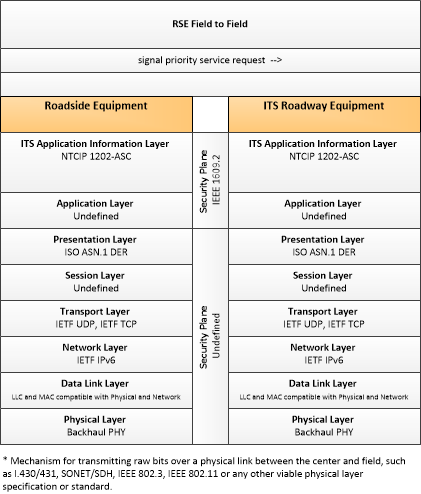
| signal priority service request | A service request for vehicle priority issued to a traffic signal controller that results in green extension or other accommodation for the priority vehicle, within the current signal timing plan. The request includes the priority level, the desired time and duration of service, and the intended travel path through the intersection. This flow also allows the RSE to cancel a previously issued request for priority. |
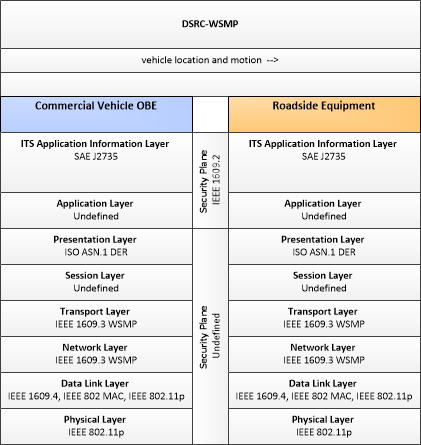
| vehicle location and motion | Data describing the vehicle's location in three dimensions, heading, speed, acceleration, braking status, and size. |
Application Interconnect Diagram
This is one way this application may be realized, but not the only way. There are other ways to build a given application and accomplish a stated objective.
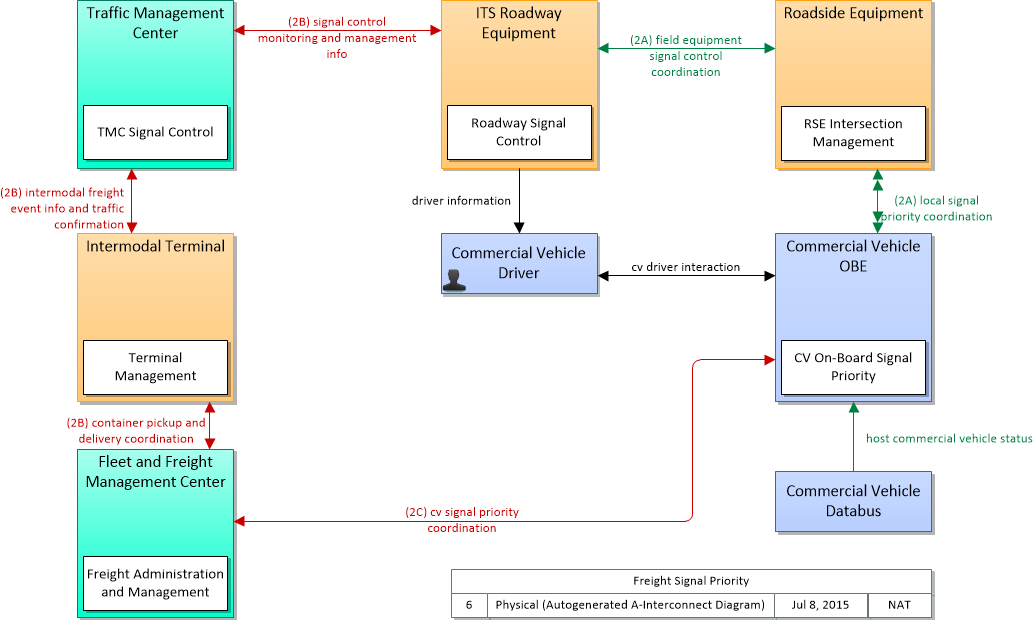
The application interconnect diagram can be viewed in SVG or PNG format and the current format is SVG. SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
Application Triples
Requirements
| Need | Requirement | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N2.082 | The Freight Signal Priority System needs to collect data for traffic signal system optimization for commercial vehicles. | 2.185 | The Freight Signal Priority System shall collect traffic data (e.g., volume, speed, occupancy, vehicle classification, incidents) for signalized intersections. |
| N2.083 | The Freight Signal Priority System needs to collect data from commercial vehicles. | 2.186 | The Freight Signal Priority System shall collect commercial vehicle data (e.g., characteristics, route, schedule). |
| N2.084 | The Freight Signal Priority System needs to process traffic and commercial vehicle data in order to provide commercial vehicle signal priority operations. | 2.187 | The Freight Signal Priority System shall process traffic data in support of commercial vehicle signal priority. |
| N2.085 | The Freight Signal Priority System needs to send commercial vehicle signal priority commands to the intersection. | 2.188 | The Freight Signal Priority System shall send weighted commercial vehicle signal priority commands to the intersection. |
Related Sources
- Multi-Modal Intelligent Traffic Signal System (MMITSS) ConOps, Draft v2.0, 9/14/2012
- Multi-Modal Intelligent Traffic Signal System Final System Requirements Document, Final, 3/7/2013
- Multi-Modal Intelligent Traffic Signal System- System Design, Fi nal, 6/26/2013
Security
In order to participate in this application, each physical object should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Physical Object Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Object | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability | Security Class |
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | ||||
In order to participate in this application, each information flow triple should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Information Flow Security | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Destination | Information Flow | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability |
| Basis | Basis | Basis | |||
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | |||||