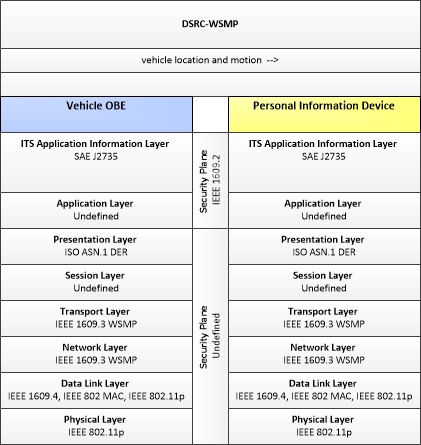
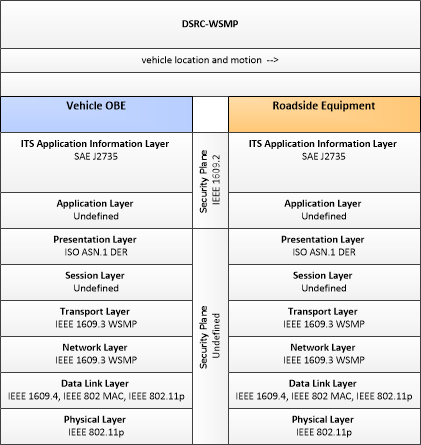
Type: Safety
Groups:- V2I Safety
Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning
The Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning application provides to the connected vehicle information from the infrastructure that indicates the possible presence of pedestrians in a crosswalk at a signalized intersection. The infrastructure based indication could include the outputs of pedestrian sensors or simply an indication that the pedestrian call button has been activated. This application has been defined for transit vehicles, but can be applicable to any class of vehicle. The application could also provide warning information to the pedestrian regarding crossing status or potential vehicle infringement into the crosswalk.
Enterprise
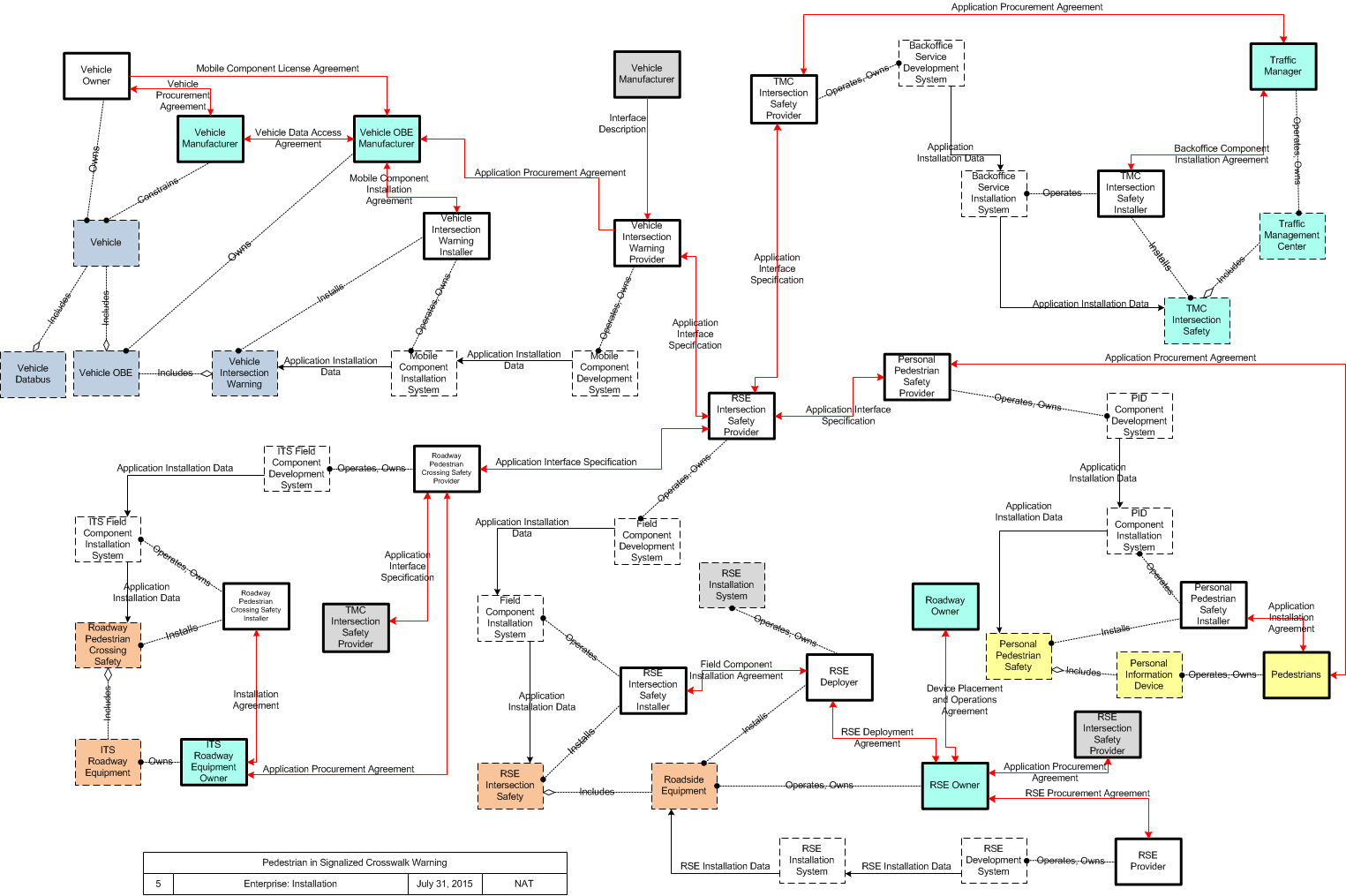
SVG Diagrams: Installation Operations Maintenance Certification
PNG Diagrams: Installation Operations Maintenance Certification
Business Interaction Matrix:
| Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning Operations Stage | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Owner | Driver | Vehicle OBE Owner | Roadway Owner | RSE Owner | RSE Operator | ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Operator | Traffic Manager | Pedestrians | Vehicle Intersection Warning Provider | RSE Intersection Safety Provider | |
| Vehicle Owner | Vehicle Usage Agreement | Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | |||||||||
| Driver | Vehicle Usage Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation of Information Provision | |||||||||
| Vehicle OBE Owner | Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation of Information Provision | Presumption of Correct Operation | ||||||||
| Roadway Owner | Service Delivery Agreement | |||||||||||
| RSE Owner | Expectation of Information Provision | Service Delivery Agreement | Operations Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | |||||||
| RSE Operator | Operations Agreement | |||||||||||
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Information Exchange Agreement | Operations Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | |||||||||
| ITS Roadway Operator | Expectation of Information Provision | Operations Agreement | Expectation of Safety Provision | |||||||||
| Traffic Manager | Information Exchange Agreement | |||||||||||
| Pedestrians | Presumption of Correct Operation | Expectation of Safety Provision | ||||||||||
| Vehicle Intersection Warning Provider | Application Usage Agreement | |||||||||||
| RSE Intersection Safety Provider | Application Usage Agreement | |||||||||||
Includes Enterprise Objects:
| Enterprise Object | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Certification Entity | The body that determines whether an application may be deployed and operated in the Connected Vehicle Environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with application type. For example, applications with human safety component (crash avoidance, movement assistance etc.) may have stringent requirements and extensive testing in a variety of conditions, while applications that provide strictly mobility functionality may have far less testing requirements; possibly as little as just making sure the application doesn't interfere with any other applications. |
| Device Certification Entity | The body that determines whether a device may be deployed and operated in the Connected Vehicle Environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with device type. |
| Driver | The 'Driver' represents the person that operates a vehicle on the roadway. Included are operators of private, transit, commercial, and emergency vehicles where the interactions are not particular to the type of vehicle (e.g., interactions supporting vehicle safety applications). The Driver originates driver requests and receives driver information that reflects the interactions which might be useful to all drivers, regardless of vehicle classification. Information and interactions which are unique to drivers of a specific vehicle type (e.g., fleet interactions with transit, commercial, or emergency vehicle drivers) are covered by separate objects. |
| Federal Regulatory | Federal regulatory bodies that have legal authority to control and/or provide input to policies regulating transportation infrastructure and operations. This includes entities such as the Federal Communications Commission and US Department of Transportation. |
| ITS Certification Entity | The body that determines whether an ITS device or application may be deployed and operated in the transportation environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with device and application type. Typically not a formal body, assigned on a project-by-project basis depending on the type of infrastructure involved. Since ITS projects are locally-focused (typically state or smaller), the entities that are part of this body are typically those with operational jurisdiction where the ITS is installed (e.g., state or local DOTs, state or local maintenance managers etc.) |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | The entity that owns the Roadway ITS equipment. |
| ITS Roadway Operator | The entity that operates the Roadway ITS equipment. |
| Pedestrians | 'Pedestrians' participate in connected vehicle applications that support safe, shared use of the transportation network by motorized and non-motorized transportation modes. Representing those using non-motorized travel modes, pedestrians provide input (e.g. a call signal requesting right of way at an intersection) and may be detected by connected vehicle applications to improve safety. Note that pedestrians represent all non-motorized users, including bicyclists. |
| Personal Pedestrian Safety Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Personal Pedestrian Safety Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Personal Pedestrian Safety Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| PID Provider | The entity that designs, manufacturers and provides (either to the end user or to a reseller) the personal information device, including its hardware and base operating software. |
| Roadway Owner | The owner of the roadway proximate to which roadside equipment will be/is installed. |
| Roadway Pedestrian Crossing Safety Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Pedestrian Crossing Safety Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Pedestrian Crossing Safety Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Deployer | The entity responsible for the deployment, operations and maintenance of roadside equipment. |
| RSE Intersection Safety Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Intersection Safety Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Intersection Safety Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Maintainer | The entity that maintains the roadside equipment, including its hardware and operating system software, but not applications software. |
| RSE Operator | The entity that operates roadside equipment in the transportation environment. |
| RSE Owner | The owner of roadside equipment. |
| RSE Provider | The "RSE Provider" is the entity that develops and (presumably) sells roadside equipment to other entities for deployment and research. |
| State Regulatory | State regulatory bodies that have legal authority to control and/or provide input to policies regulating vehicles, transportation infrastructure and operations. This includes entities like Departments of Motor Vehicles, property tax authorities and tolling agencies. |
| TMC Intersection Safety Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Intersection Safety Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Traffic Manager | The entity responsible for the management of traffic, both freeway and arterial. |
| Vehicle Intersection Warning Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Intersection Warning Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Intersection Warning Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Vehicle Manufacturer | The entity that builds, assembles, verifies and validates the Vehicle in which the Vehicle OBE will eventually operate. |
| Vehicle OBE Manufacturer | The entity that builds, assembles, verifies and validates the Vehicle OBE. This can be an OEM-equipped OBE, retrofit or aftermarket equipment. |
| Vehicle OBE Owner | The entity, individual, group or corporation that owns the Vehicle On-Board equipment. This could be the same as the Vehicle Owner, but it could be a third part that licenses the use of the OBE to the Owner. |
| Vehicle Owner | The individual, group of individuals or corporate entity that is identified as the registered owner of the Vehicle under state law. |
Includes Resources:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Component Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of an application component. Certification Requirements must be met in order for an application to be installed in the CVE. |
| Backoffice Service Development System | The systems used to develop backoffice (center) hardware and software components of applications. |
| Backoffice Service Installation System | The systems used to install and configure backoffice (center) hardware and software components. |
| Device Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of a connected vehicle device. Certification Requirements must be met in order for the device to be granted the credentials necessary to operate in the Connected Vehicle Environment. |
| Field Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the field component of the application. |
| Field Component Installation System | The system used to install a field component of a connected vehicle application. |
| Field Component Maintenance System | The system used to install and configure changes and updates to the field component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| ITS Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of an ITS device or ITS application. Applicability varies with jurisdictions, but typically devices and applications must meet pre-defined acceptance criteria prior to usage in the transportation environment. |
| ITS Field Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the ITS field component of the application. |
| ITS Field Component Installation System | The system used to install a field component of a connected vehicle application. |
| ITS Field Component Maintenance System | The system used to install and configure changes and updates to the ITS field component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway itself. In CVRIA, this physical object represents all of the other ITS field equipment that interfaces with and supports the Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE). This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| Mobile Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the mobile component of the application. |
| Mobile Component Installation System | The system that interacts with the Vehicle OBE other mobile device and installs the mobile component of the application. |
| Personal Information Device | The 'Personal Information Device' provides the capability for travelers to receive formatted traveler information wherever they are. Capabilities include traveler information, trip planning, and route guidance. Frequently a smart phone, the Personal Information Device provides travelers with the capability to receive route planning and other personally focused transportation services from the infrastructure in the field, at home, at work, or while en-route. Personal Information Devices may operate independently or may be linked with connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| Personal Pedestrian Safety | The "Personal Pedestrian Safety" application improves pedestrian safety by providing pedestrian location information to the infrastructure that can be used to avoid collisions involving pedestrians. The application may also alert the pedestrian of unsafe conditions, augmenting or extending information provided by signals and signs. The information provided and the user interface delivery mechanism (visual, audible, or haptic) can also be tailored to the needs of the user that is carrying or wearing the device that hosts the application. |
| PID Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the PID component of the application. |
| PID Component Installation System | The system used to install the PID component of a connected vehicle application. |
| PID Component Maintenance System | The system used to configure changes and updates to the PID component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| Roadside Equipment | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Roadway Pedestrian Crossing Safety | "Roadway Pedestrian Crossing Safety" is an advanced infrastructure application that detects pedestrians and provides active safety warnings to drivers when cross walks are occupied. |
| RSE Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the roadside equipment. |
| RSE Installation System | The system used to install and configure the roadside equipment. |
| RSE Intersection Safety | "RSE Intersection Safety" uses short range communications to support connected vehicle applications that improve intersection safety. It communicates with approaching vehicles and ITS infrastructure to alert and warn drivers of potential stop sign, red light, and pedestrian crossing conflicts or violations. |
| RSE Maintenance System | The system used to configure changes and updates to the roadside equipment. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the RSE's configuration and performance. |
| TMC Intersection Safety | "TMC Intersection Safety" controls and monitors RSEs that support stop sign, red light, and pedestrian crossing violations. It configures the RSEs for the current intersection geometry and traffic signal control equipment at the intersection. Information that is currently being communicated to passing vehicles and the operational status of the field equipment is monitored by this application. The operational status of the field equipment is reported to operations personnel. |
| Traffic Management Center | The 'Traffic Management Center' monitors and controls traffic and the road network. It represents centers that manage a broad range of transportation facilities including freeway systems, rural and suburban highway systems, and urban and suburban traffic control systems. It communicates with ITS Roadway Equipment and Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE) to monitor and manage traffic flow and monitor the condition of the roadway, surrounding environmental conditions, and field equipment status. It manages traffic and transportation resources to support allied agencies in responding to, and recovering from, incidents ranging from minor traffic incidents through major disasters. |
| Vehicle | The conveyance that provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support efficient, safe, and convenient travel. These functions reside in general vehicles including personal automobiles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, or other vehicle types. |
| Vehicle Databus | The 'Vehicle Databus' represents the interface to the vehicle databus (e.g., CAN, LIN, Ethernet/IP, FlexRay, and MOST) that may enable communication between the Vehicle OBE and other vehicle systems to support connected vehicle applications. The vehicle system statuses and/or sensor outputs available on the databus will vary based on the equipment installed on the vehicle and availability on databus. System statuses and sensor outputs may include select vehicle systems and sensors such as accelerometers, yaw rate sensors, and GPS derived location and timing information. In CVRIA, this physical object is used to represent the onboard interactions between the Vehicle OBE and the other systems included in a host vehicle. Note that the vehicle databus interface is not standardized across all vehicle classes. Also, some Vehicle OBE implementations will not have access to the vehicle databus. See 'Vehicle OBE' for more information. |
| Vehicle Intersection Warning | "Vehicle Intersection Warning" uses V2V and V2I communications to monitor other connected vehicles at intersections and support the safe movement of the vehicle through the intersection. Driver warnings are provided and the application may also optionally take control of the vehicle to avoid collisions. The application will also notify the infrastructure and other vehicles if it detects an unsafe infringement on the intersection. |
| Vehicle OBE | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
Includes Roles:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Certifies | An Enterprise verifies that a target Resource meets relevant performance, functional, environmental and quality requirements. |
| Constrains | A Resource or Enterprise applies requirements, constraints and associated tests to another Resource. |
| Installs | An Enterprise performs the initial delivery, integration and configuration of the target Resource. |
| Maintains | An Enterprise administers the hardware and software that comprise the target Resource. |
| Member | An Enterprise is part of another larger, target Enterprise. |
| Operates | An Enterprise controls the functionality and state of the target Resource. An Enterprise that Operates a resource is considered Responsible. |
| Owns | An Enterprise has financial ownership and control over the Resource. An Enterprise that Owns a resource is considered Accountable. |
Includes Coordination:
| Coordination | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Application Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one party permission to install an application component on a device controlled by the other party. |
| Application Installation Data | Information Sharing | Data needed to install the application, including the application executable code and any configuration data. Unidirectional flow. |
| Application Interface Specification | Agreement | The definition of an interface between two application components that operate on two distinct pieces of hardware. The Application Interface Specification is specific to the application in question. |
| Application Maintenance Data | Information Sharing | Data used to facilitate the upgrade, patching and general health maintenance of an application component. |
| Application Performance Data | Information Sharing | Data used to characterize application performance, including such measures as availability, known errors and known uses. |
| Application Procurement Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity provides a copy of an application component to another entity. This component is capable of being installed and functioning, according to its requirements that passed through the application's certification process. |
| Application Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity that controls an application component's use gives the other entity the necessary tools and permission to operate that application or application component. |
| Backoffice Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one party permission to install a backoffice application component on a center-based device controlled by the other party. |
| Device Placement and Operations Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that enables the controller of a physical device to install it (so as to make it operational) at a fixed location controlled by another entity. |
| Expectation of Data Provision | Expectation | An expectation where one party believes another party will provide data on a regular and recurring basis, and that that data will be useful to the receiver in the context of the receiver's application. This thus includes some expectation of data fields, timeliness, quality, precision and similar qualities of data. |
| Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation | An expectation where one party believes another party will provide it information whenever such information is likely relevant to the recipient. |
| Expectation of Safety Provision | Expectation | Users of the transportation environment expect that the entities that operate the environment do so in such a way as to preserve and enhance users' safety. This is inherent to current operations, and is an underlying assumption of drivers and pedestrians when accepting information from ITS. This expectation is explicitly noted for connected vehicle applications where this is a new relationship, whereupon the transportation system user expects a transportation service provider to do something (i.e., actuate a system or deliver information) that will protect and/or enhance the user's safety. |
| Field Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one party permission to install a field application component on a roadside device controlled by the other party. |
| Field Component Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the field component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Includes | Includes | Indicates that one component is entirely contained within another component. |
| Information Exchange Agreement | Agreement | An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. |
| Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity installs an application component on a device controlled by another entity. |
| Interface Description | Agreement | Documentation of the interface between two systems, where one system does not have an application component that is part of the application, but does provide and/or receive data and/or information that is used by or sourced from the application. In many cases this is an existing interface used by the application, so the description of the interface already exists and is imposed by the terminator. |
| Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of a system under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that states one entity will provide data related to maintenance of an application component to the other entity. |
| Mobile Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon the controller of OBE gives another party permission to install, configure and make operational a component that enables the mobile portion of an application. |
| Mobile Component License Agreement | Agreement | An end-user license agreement allowing the operator of the mobile device to use the mobile application component that is part of the application in question. |
| Mobile Component Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the mobile component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Operations Agreement | Agreement | An agreement where one entity agrees to operate a device or application on behalf of another, device/application controlling entity. |
| Presumption of Correct Operation | Expectation | The assumption made by one party that another party operates their device in a similar and correct fashion. Specific to devices in the transportation environment, this assumption is relevant when devices interact, where one party's device receives information from another's. The operator of the device implicitly trusts that the other device is operating according to a similar set of governing rules as its device. |
| RSE Deployment Agreement | Agreement | Agreement to install, configure and make operational roadside equipment, between the provider of that equipment and the entity that controls access to the roadside. May define locations, expectation of power provision, backhaul responsibility and installation restrictions. |
| RSE Installation Data | Information Sharing | Data necessary to configure and make RSE operational. Uni-directional. |
| RSE Maintenance Data | Information Sharing | Data necessary to modify the operational configuration of RSE; assumes RSE is already configured. Uni-directional. |
| RSE Performance Data | Information Sharing | Data that includes metrics of RSE performance. Could include fields such as uptime, packets received/transmitted, distance vector from which packets received, as well as application-specific performance measures. |
| RSE Procurement Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity provides roadside equipment to another entity. The RSE is capable of being installed and functioning, according to its requirements that passed through the device's certification process. |
| Service Delivery Agreement | Agreement | A relationship where one party agrees to provide a service to the other party. This agreement may specify the expected performance of this service in terms of availability and/or actions/time-type performance specifications. |
| Vehicle Data Access Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereby the party that controls access to on-board vehicle data grants another party the right and ability to access that data. Includes the conditions under which data may be accessed, and specifies the mechanisms, including physical and functional access methods, data formats and any other considerations necessary for the accessing party to acquire data. May also include caveats regarding responsibility for data quality and responsibility for use of the data. |
| Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one entity permission to use a Vehicle OBE that the other party controls. |
| Vehicle Procurement Agreement | Agreement | The exchange of a vehicle for compensation. One entity purchases the vehicle from the other. |
| Vehicle Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement between the owner of a vehicle and a prospective operator, whereupon the owner allows the operator to use the vehicle. |
| Warranty | Agreement | A guarantee or promise made by one entity to another, that provides assurance of the functionality and performance over time of an application component. |
Functional
Includes Processes:
Includes Data Flows:
Physical
SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
Includes Physical Objects:
| Physical Object | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Driver | Vehicle | The 'Driver' represents the person that operates a vehicle on the roadway. Included are operators of private, transit, commercial, and emergency vehicles where the interactions are not particular to the type of vehicle (e.g., interactions supporting vehicle safety applications). The Driver originates driver requests and receives driver information that reflects the interactions which might be useful to all drivers, regardless of vehicle classification. Information and interactions which are unique to drivers of a specific vehicle type (e.g., fleet interactions with transit, commercial, or emergency vehicle drivers) are covered by separate objects. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Field | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway itself. In CVRIA, this physical object represents all of the other ITS field equipment that interfaces with and supports the Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE). This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| Pedestrians | Traveler | 'Pedestrians' participate in connected vehicle applications that support safe, shared use of the transportation network by motorized and non-motorized transportation modes. Representing those using non-motorized travel modes, pedestrians provide input (e.g. a call signal requesting right of way at an intersection) and may be detected by connected vehicle applications to improve safety. Note that pedestrians represent all non-motorized users, including bicyclists. |
| Personal Information Device | Traveler | The 'Personal Information Device' provides the capability for travelers to receive formatted traveler information wherever they are. Capabilities include traveler information, trip planning, and route guidance. Frequently a smart phone, the Personal Information Device provides travelers with the capability to receive route planning and other personally focused transportation services from the infrastructure in the field, at home, at work, or while en-route. Personal Information Devices may operate independently or may be linked with connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| Roadside Equipment | Field | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Traffic Management Center | Center | The 'Traffic Management Center' monitors and controls traffic and the road network. It represents centers that manage a broad range of transportation facilities including freeway systems, rural and suburban highway systems, and urban and suburban traffic control systems. It communicates with ITS Roadway Equipment and Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE) to monitor and manage traffic flow and monitor the condition of the roadway, surrounding environmental conditions, and field equipment status. It manages traffic and transportation resources to support allied agencies in responding to, and recovering from, incidents ranging from minor traffic incidents through major disasters. |
| Vehicle Databus | Vehicle | The 'Vehicle Databus' represents the interface to the vehicle databus (e.g., CAN, LIN, Ethernet/IP, FlexRay, and MOST) that may enable communication between the Vehicle OBE and other vehicle systems to support connected vehicle applications. The vehicle system statuses and/or sensor outputs available on the databus will vary based on the equipment installed on the vehicle and availability on databus. System statuses and sensor outputs may include select vehicle systems and sensors such as accelerometers, yaw rate sensors, and GPS derived location and timing information. In CVRIA, this physical object is used to represent the onboard interactions between the Vehicle OBE and the other systems included in a host vehicle. Note that the vehicle databus interface is not standardized across all vehicle classes. Also, some Vehicle OBE implementations will not have access to the vehicle databus. See 'Vehicle OBE' for more information. |
| Vehicle OBE | Vehicle | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
Includes Application Objects:
| Application Object | Description | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Pedestrian Safety | The "Personal Pedestrian Safety" application improves pedestrian safety by providing pedestrian location information to the infrastructure that can be used to avoid collisions involving pedestrians. The application may also alert the pedestrian of unsafe conditions, augmenting or extending information provided by signals and signs. The information provided and the user interface delivery mechanism (visual, audible, or haptic) can also be tailored to the needs of the user that is carrying or wearing the device that hosts the application. | Personal Information Device |
| Roadway Pedestrian Crossing Safety | "Roadway Pedestrian Crossing Safety" is an advanced infrastructure application that detects pedestrians and provides active safety warnings to drivers when cross walks are occupied. | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| RSE Intersection Safety | "RSE Intersection Safety" uses short range communications to support connected vehicle applications that improve intersection safety. It communicates with approaching vehicles and ITS infrastructure to alert and warn drivers of potential stop sign, red light, and pedestrian crossing conflicts or violations. | Roadside Equipment |
| TMC Intersection Safety | "TMC Intersection Safety" controls and monitors RSEs that support stop sign, red light, and pedestrian crossing violations. It configures the RSEs for the current intersection geometry and traffic signal control equipment at the intersection. Information that is currently being communicated to passing vehicles and the operational status of the field equipment is monitored by this application. The operational status of the field equipment is reported to operations personnel. | Traffic Management Center |
| Vehicle Intersection Warning | "Vehicle Intersection Warning" uses V2V and V2I communications to monitor other connected vehicles at intersections and support the safe movement of the vehicle through the intersection. Driver warnings are provided and the application may also optionally take control of the vehicle to avoid collisions. The application will also notify the infrastructure and other vehicles if it detects an unsafe infringement on the intersection. | Vehicle OBE |
Includes Information Flows:
| Information Flow | Description |
|---|---|
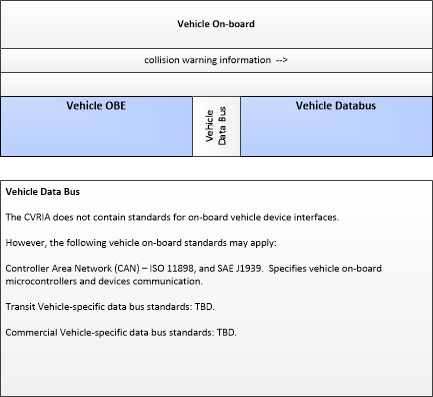
| collision warning information | Information provided to support computer-based intervention of vehicle controls. Analogous to driver warnings, these are warnings issued to on-board control systems of an impending collision or other situation detected by the Vehicle OBE that may require control intervention. |
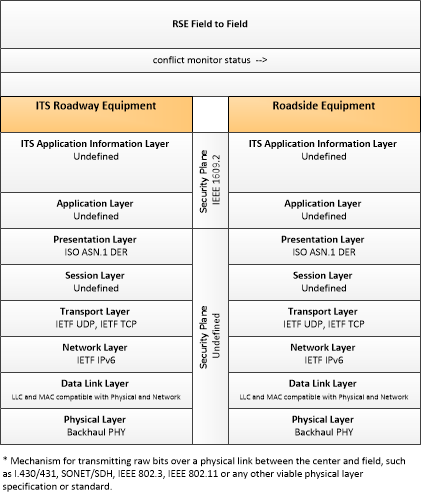
| conflict monitor status | A control flow that supports failsafe operation in the event that a conflict is detected that requires the RSE to enter a failsafe operating mode. |
| crossing permission | Information provided to guide and warn pedestrians at crossings including crossing permission, crossing time remaining, and real-time warnings of safety threats. |
| driver information | Regulatory, warning, and guidance information provided to the driver while en route to support safe and efficient vehicle operation. |
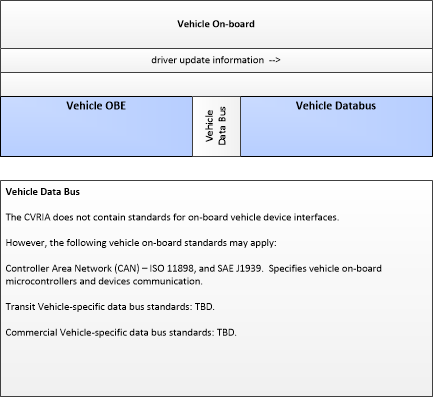
| driver update information | Information provided to the driver-vehicle interface to inform the driver about current conditions, potential hazards, and the current status of vehicle on-board equipment. The flow includes the information to be presented to the driver and associated metadata that supports processing, prioritization, and presentation by the DVI as visual displays, audible information and warnings, and/or haptic feedback. |
| driver updates | Information provided to the driver including visual displays, audible information and warnings, and haptic feedback. The updates inform the driver about current conditions, potential hazards, and the current status of vehicle on-board equipment. |
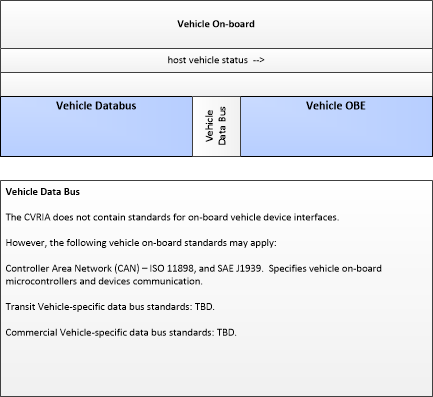
| host vehicle status | Information provided to the connected vehicle on-board equipment from other systems on the vehicle platform. This includes data from on-board sensors, the current status of the powertrain, steering, and braking systems, and status of safety and convenience systems. In implementations where GPS is not integrated into the Vehicle On-Board Equipment, the host vehicle is also the source for data describing the vehicle's location in three dimensions (latitude, longitude, elevation) and accurate time that can be used for time synchronization across the Connected Vehicle environment. |
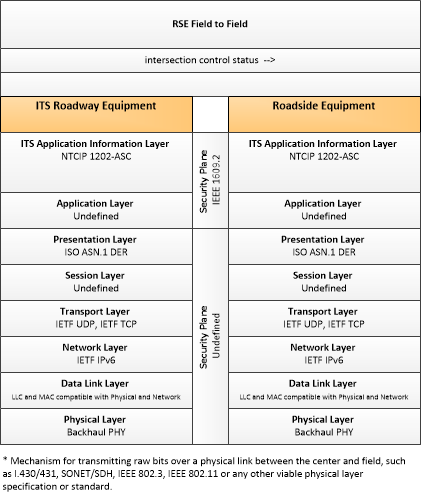
| intersection control status | Status data provided by the traffic signal controller including phase information, alarm status, and priority/preempt status. |
| intersection infringement info | Vehicle path information sent by a vehicle that is performing an unpermitted movement at an intersection such as a stop sign violation or running a red light. |
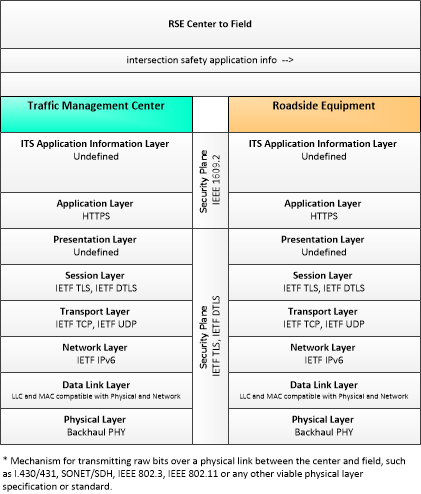
| intersection safety application info | Intersection and device configuration data and warning parameters and thresholds. This flow also supports remote control of the application so the application can be taken offline, reset, or restarted. |
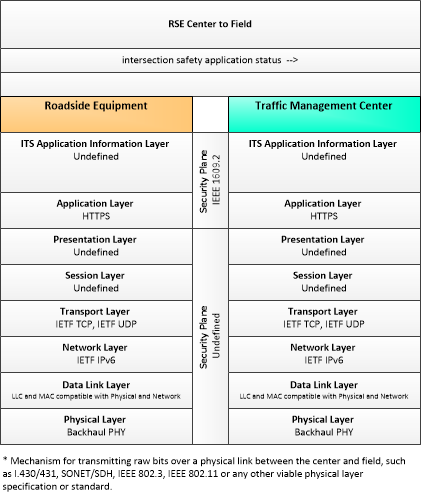
| intersection safety application status | Infrastructure safety application status reported by the RSE. This includes current operational state and status of the RSE and a record of intersection safety issues identified and alerts and warnings issued. |
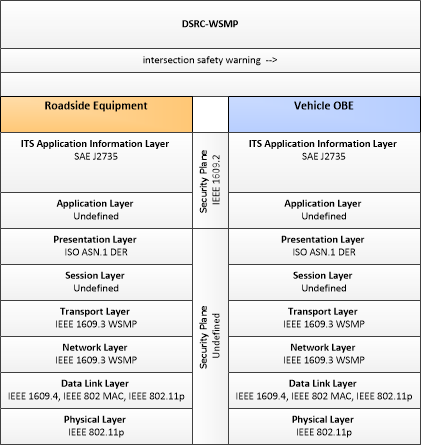
| intersection safety warning | A warning of an imminent unsafe vehicle infringement at an intersection that may endanger other vehicles or pedestrians. This allows vehicles approaching the intersection to be warned in the event of an imminent red light or stop sign violation or potential infringement on an occupied crosswalk. All connected vehicles at the intersection receive the warning, including both the infringing vehicle and other vehicles at or near the intersection. |
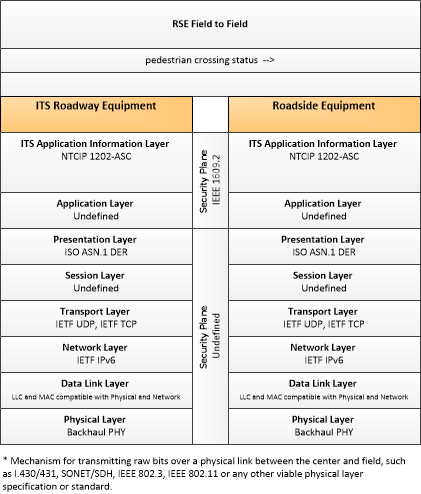
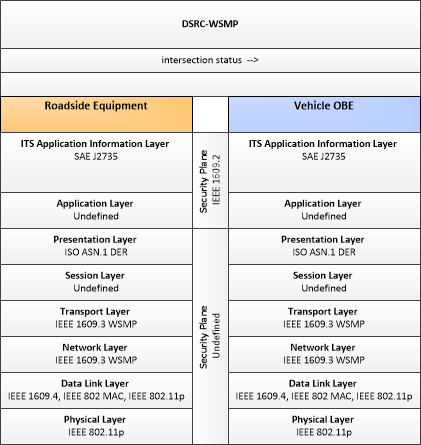
| intersection status | Current signal phase and timing information for all lanes at a signalized intersection. This flow identifies active lanes and lanes that are being stopped and specifies the length of time that the current state will persist for each lane. It also identifies signal priority and preemption status and pedestrian crossing status information where applicable. |
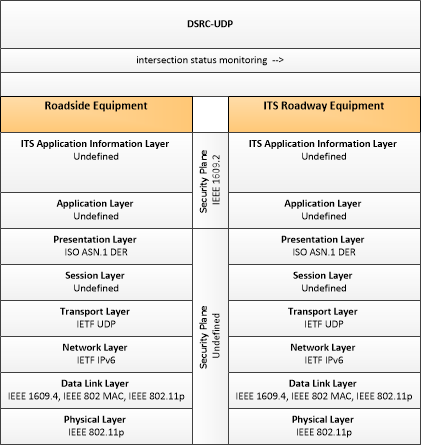
| intersection status monitoring | Current signal phase and timing information for all lanes at a signalized intersection. This flow represents monitoring of communications by a receiver at the intersection to support monitoring for conflicts between actual signal states and RSE communications about those states. |
| pedestrian crossing status | Current pedestrian information including an indication of whether the pedestrian call button has been activated, the current state of the pedestrian signal, and information indicating whether pedestrians are currently occupying the cross walk. |
| pedestrian detection | Pedestrian request to cross the roadway. This may be an overt (e.g., push button) request from a pedestrian or the physical presence of a pedestrian that can be detected by sensors or surveillance systems. |
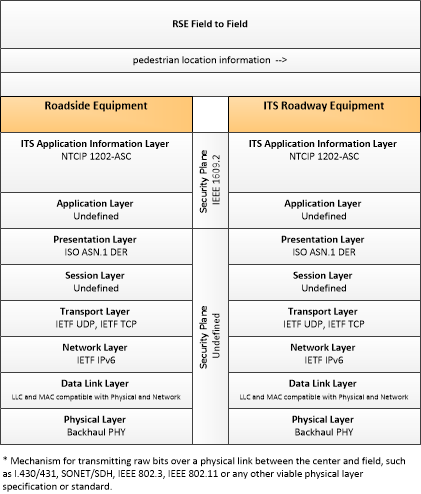
| pedestrian location information | Pedestrian locations at an intersection as detected and reported by an RSE. |
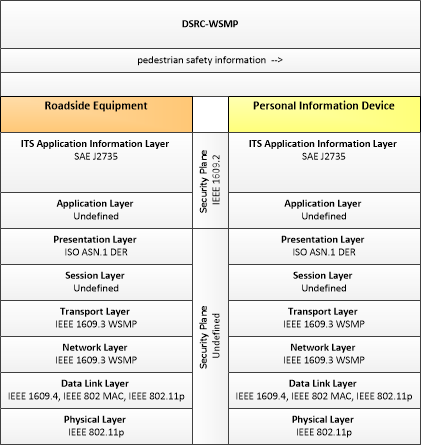
| pedestrian safety information | Current pedestrian crossing status including permission to cross, crossing time remaining, and warnings in the event that a vehicle reports an imminent intersection infringement that may impact pedestrians. |
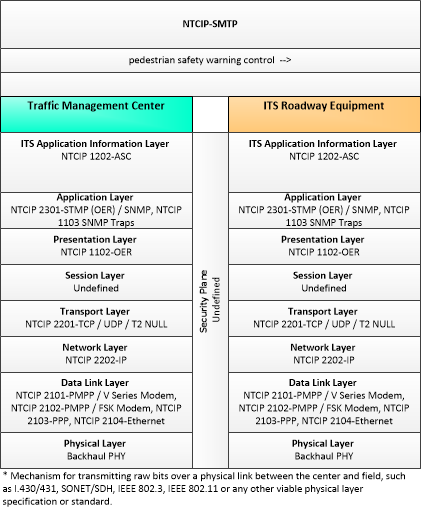
| pedestrian safety warning control | Configuration and control of equipment that monitors and manages pedestrian crossings and provides visual displays and warnings to drivers when pedestrians are occupying a cross walk. |
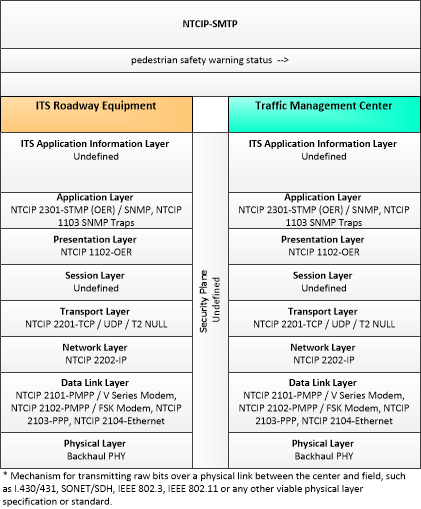
| pedestrian safety warning status | Current operational status and state of pedestrian crossing warning systems. |
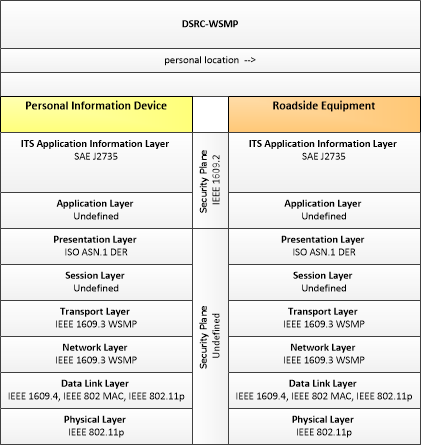
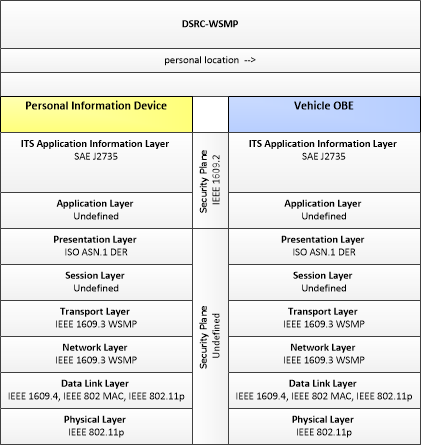
| personal location | The current location (latitude, longitude, and elevation) reported by the personal information device |
| personal updates | Personal information, alerts, and warnings provided to pedestrians, work crew members, and other individuals in a mixed use area. This includes visual, audio, and haptic outputs that may be customized to support individual needs. |
| vehicle location and motion | Data describing the vehicle's location in three dimensions, heading, speed, acceleration, braking status, and size. |
Application Interconnect Diagram
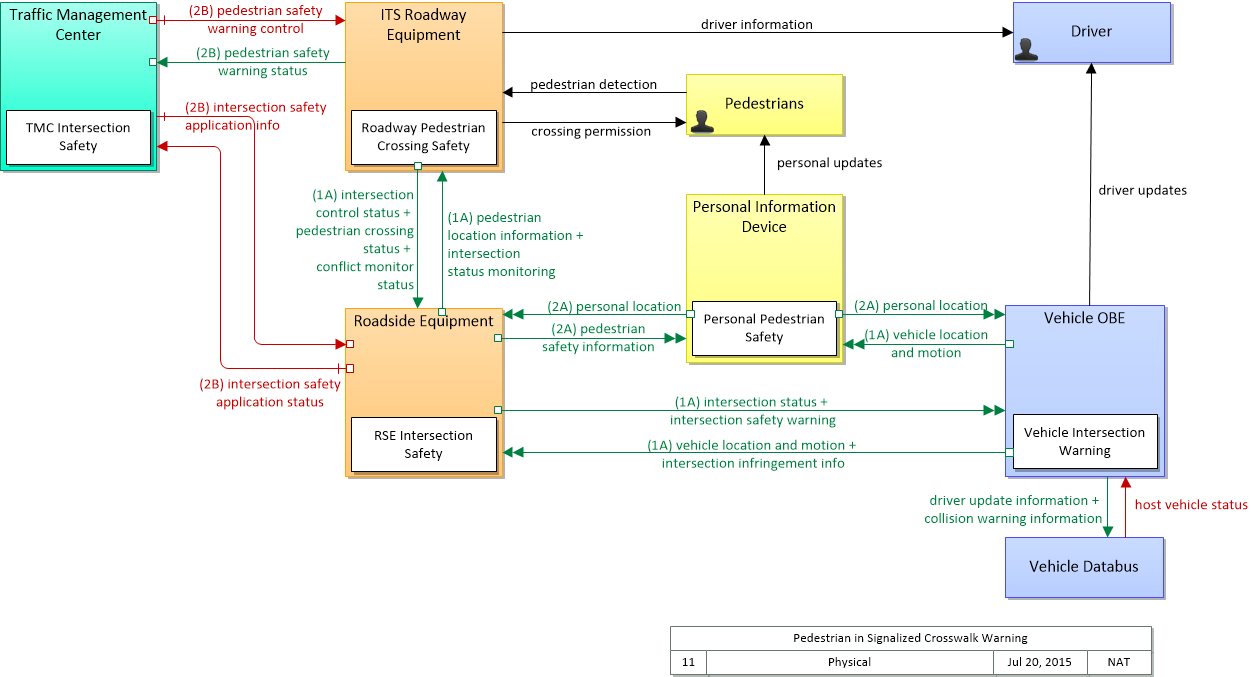
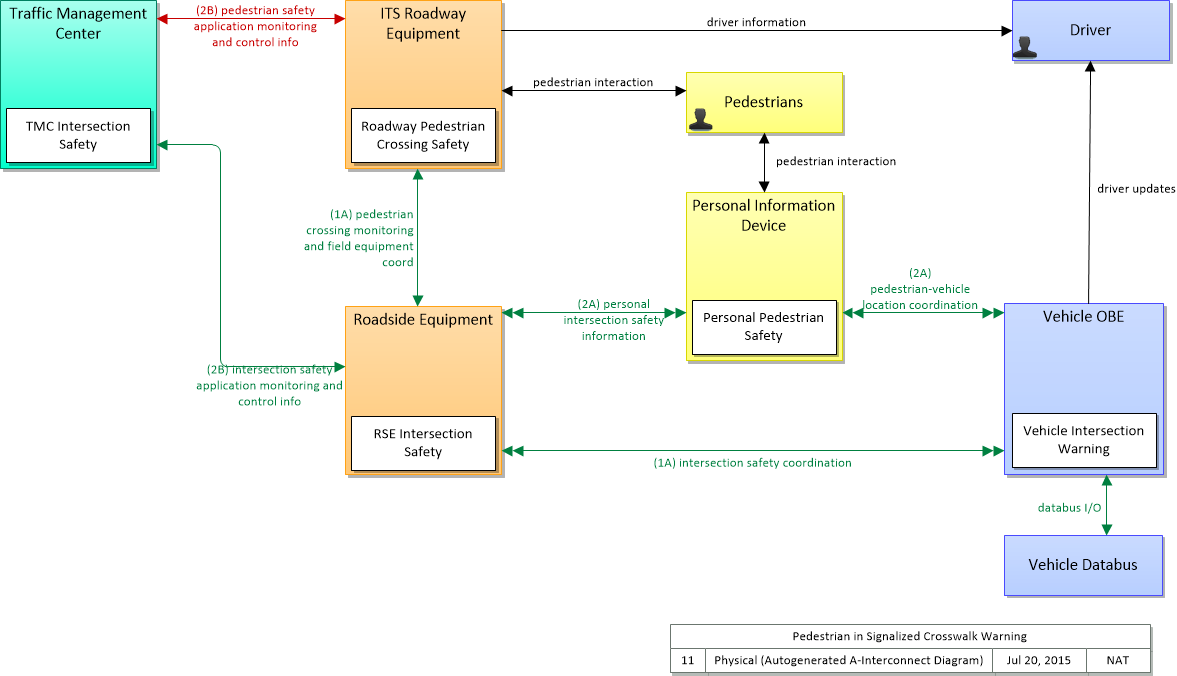
SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
Application Triples
Requirements
| Need | Requirement | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N3.034 | Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning needs to detect pedestrians in the crosswalk so that the vehicle's driver may be informed and thereby avoid a crash. | 3.079 | Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning shall be able to receive location information describing the positions of pedestrians. |
| 3.080 | Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning shall determine the location of crosswalks over which the vehicle will cross. | ||
| 3.081 | Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning shall calculate whether pedestrians that are present in the crosswalk the vehicle is approaching or turning into. | ||
| N3.035 | Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning needs to determine if a vehicle is making a turn, so it can warn the vehicle about pedestrians in the crosswalk in the direction the vehicle is turning. | 3.082 | Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning shall determine if a vehicle is making a turn. |
| 3.083 | Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning shall determine the vehicle's trajectory. | ||
| 3.084 | Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning shall determine the geometry of the roadway (to distinguish between 'straight' and 'turning'. | ||
| N3.036 | Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning needs to warn the vehicle driver about pedestrians in the crosswalks at a signalized intersection. | 3.085 | Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning shall warn the driver that there are pedestrians in the crosswalk through which the vehicle is moving or turning. |
| N3.036a | Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning needs to warn the pedestrians about crossing status or potential vehicle infringement into the crosswalk. | 3.085a | Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning shall provide information to pedestrians about crossing status. |
| 3.085b | Pedestrian in Signalized Crosswalk Warning shall warn pedestrians about potential vehicle infringement into the crosswalk. | ||
| N3.104 | Vehicle to Infrastructure (V2I) Safety applications need to assess their own performance, to determine errors and avoid failures when critical components fail. | 3.207 | Vehicle to Infrastructure (V2I) Safety applications shall analyze their own performance and enter fail-safe mode (a mode such that the application cannot provide information or perform actions that affect its host) when critical components fail. |
| 3.208 | V2I Safety applications shall notify the driver when onboard components are offline | ||
| 3.209 | V2I Safety applications shall notify its owner/operator when onboard components are offline. | ||
| N3.105 | V2I Safety applications need to broadcast the performance of their host vehicle, to enable V2I applications that rely on knowing the location and/or trajectories of other vehicles. | 3.210 | V2I Safety applications shall broadcast the location, speed, acceleration, heading, steering wheel angle, brake system status, vehicle size and path history of host vehicles. |
| N3.106 | V2I Safety applications need to have a common time source so that location and projected positions may be synchronized. | 3.211 | V2I Safety applications shall have a common time source. |
| N3.107 | V2I Safety applications need to have positioning accurate enough to create alerts and/or warnings when warranted. | 3.212 | V2I Safety applications shall provide a means for any System component to determine its geographic position, in three dimensions. |
| N3.108 | V2I Safety applications need to have positioning accurate enough to avoid false positive alerts and/or warnings. | 3.213 | V2I Safety applications shall provide position data together with a measure of the accuracy of the geographic position. |
Related Sources
- Transit Safety Retrofit Package Development Applications Requirements Document, Final, 5/28/2014
- Transit Safety Retrofit Package Development Architecture and Design Specifications, Final, 5/19/2014
- Transit Safety Retrofit Package Development TRP Concept of Operations, Final, 5/28/2014
- SAE J3067- Candidate Improvements to Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) Message Set Dictionary (SAE J2735)Using Systems Engineering Methods, 8/15/2014
Security
In order to participate in this application, each physical object should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Physical Object Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Object | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability | Security Class |
| Driver | ||||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Moderate | High | Moderate | Class 3 |
| Pedestrians | ||||
| Personal Information Device | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Class 1 |
| Roadside Equipment | Moderate | High | Moderate | Class 3 |
| Traffic Management Center | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Class 2 |
| Vehicle Databus | ||||
| Vehicle OBE | Low | High | Moderate | Class 3 |
In order to participate in this application, each information flow triple should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Information Flow Security | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Destination | Information Flow | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability |
| Basis | Basis | Basis | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Driver | driver information | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. | This is the primary signal trusted by the driver to decide whether to go through the intersection and what speed to go through the intersection at; if it's wrong, accidents could happen. | If the lights are out you have to get a policeman to direct traffic – expensive and inefficient and may cause a cascading effect due to lack of coordination with other intersections. | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Pedestrians | crossing permission | Not Applicable | High | Low |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. | Although pedestrians have a responsibility to make sure the road is safe before they cross, they may react instinctively to incorrect information and be led to cross at unsafe times if they get incorrect information. Also, if the traffic signals are wrong and an accident happens, the pedestrian involved could sue, causing financial loss and other undesirable outcomes. | It is easy to tell whether this information flow is available and pedestrians are used to using crosswalks that do not provide this service. | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Roadside Equipment | conflict monitor status | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| This information could be ascertained by examining the signal states, and so is effectively broadcast. | If this is compromised, it could send incorrect data to the RSE. Since the data contained herein directly affects human safety, the RSE may react to modify its outputs, at the least disabling related outputs. Not 'High' because the signal state is also present. | A delay in reporting this may allow the RSE to distribute faulty information, but that information is contradicted by the signal state. Since there are multiple pathways for the information to be obtained, this is not 'High.' | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Roadside Equipment | intersection control status | Low | High | Moderate |
| This data is later intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. | If this is compromised, the Roadway Equipment and Roadside Equipment will be sending messages that are inconsistent with each other, leading to confusion and possible accidents and reducing the ability of the application to provide value. If this information is incorrect, it could lead to a collision between a vehicle and a pedestrian. | If this is down, the RSE doesn't get the information it needs to stay in synch with the actual signal state, reducing or eliminating the value add from having this application. The RSE must detect a lack of availability and choose not to send out-of-date information, so a failure of availability cannot have worse consequences than a failure of integrity which we have previously assessed at MEDIUM. | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Roadside Equipment | pedestrian crossing status | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is later intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. | If this is compromised, the ITS RE and RSE will be sending messages that are inconsistent with each other, leading to confusion and possible accidents and reducing the ability of the application to provide value. If this information is incorrect, it could lead to a collision between a vehicle and a pedestrian. | If this is down, the RSE doesn't get the information it needs to stay in synch with the actual signal state, reducing or eliminating the value add from having the RSE. We assume that the RSE will detect a lack of availability and choose not to send out-of-date information, so a failure of availability cannot have worse consequences than a failure of integrity which we have previously assessed at MEDIUM. | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Traffic Management Center | pedestrian safety warning status | Low | Moderate | Low |
| Unless otherwise determined by the supplier (for example, because this flow contains proprietary or security-sensitive information about the device). | If this is compromised, the TMC might for example send maintenance teams to fix a traffic signal that isn't broken, incurring unnecessary expense. | A delay in reporting the state of the ITS RE may lead to a delay in providing necessary maintenance, but (a) this is not time-critical and (b) there are other channels for reporting malfunctioning ITS REs. | |||
| Pedestrians | ITS Roadway Equipment | pedestrian detection | Not Applicable | High | Low |
| The "Not Applicable" group includes information flows that do not actually carry information; for example, flows that represent the physical environment. | Although pedestrians have a responsibility to make sure the road is safe before they cross, and should ensure that they are detected by pedestrian detection systems, they may not always be detected and be led to cross at unsafe times if the ITS RE obtains incorrect information. | It is easy to tell whether this information flow is available and pedestrians are used to using crosswalks that do not provide this service. | |||
| Personal Information Device | Pedestrians | personal updates | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is informing the pedestrian about the safety of the intersections. It should not contain anything sensitive, and does not matter if another person can observe it. | This is the information that is presented to the individual. If they receive incorrect information, they may act in an unsafe manner. However, there are other indicators that would alert them to any hazards, such as an oncoming vehicle or crossing safety lights. | If this information is not made available to the pedestrian, then the system has not operated correctly. | |||
| Personal Information Device | Roadside Equipment | personal location | Low | Moderate | Low |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | If this information is incorrect it could cause the system to broadcast inaccurate messages, saying that a pedestrian is in an intersection that does not have anyone in it. It could also cause a failure to alert if the information was not accurately broadcast that the person was in the intersection. Too much inaccuracy in this information could lead to people ignoring valid warnings. | This information should not be required to determine if a pedestrian is in an intersection. Not all pedestrians will carry a personal information device, and the system should be able to operate without this information. | |||
| Personal Information Device | Vehicle OBE | personal location | Not Applicable | Moderate | Low |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | If this information is incorrect it could cause the system to broadcast inaccurate messages, saying that a pedestrian is in an intersection that does not have anyone in it. It could also cause a failure to alert if the information was not accurately broadcast that the person was in the intersection. Too much inaccuracy in this information could lead to people ignoring valid warnings. | This information should not be required to determine if a pedestrian is in an intersection. Not all pedestrians will carry a personal information device, and the system should be able to operate without this information. | |||
| Roadside Equipment | ITS Roadway Equipment | intersection status monitoring | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| This information could be ascertained by examining the signal states, and so is effectively broadcast. | If this is compromised, the RSE could send incorrect data to the Roadway Equipment. Since the data contained herein directly affects human safety, the Roadway Equipment may react to tell the RSE it is in conflict, which in turn may result in the RSE modifying or disabling its outputs. | A delay in reporting this may allow the RSE to distribute faulty information, but that information is contradicted by the signal state. Since there are multiple pathways for the information to be obtained, this is not 'High. | |||
| Roadside Equipment | ITS Roadway Equipment | pedestrian location information | Not Applicable | Moderate | Low |
| This is simply passing on received broadcast messages. It is intended to be received by everyone. | We assume that this information is not able to cause the ITS RE to behave in extreme ways, e.g. to keep all the lights red forever because it thinks there's a baby in the middle of the road. In other words, the ITS RE has maximum durations for the different phases of the cycle which it will not go beyond not matter what this information flow contains. Bad information can cause annoyances and disrupt traffic flow to a limited extent but will not have a large impact. | If this is down, the ITS RE goes back to default behavior, which we assume is set sensibly. | |||
| Roadside Equipment | Personal Information Device | pedestrian safety information | Not Applicable | Moderate | Low |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | People will use this information to determine if they can cross, so incorrect information increases the risk of accidents. | If this is down, the pedestrian still gets information from the RE and from the rest of the environment. | |||
| Roadside Equipment | Traffic Management Center | intersection safety application status | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
| This information could be of interest to a malicious individual who is attempting to determine the best way to accomplish a crime. As such it would be best to not make it easily accessible. | If this is compromised, it could send unnecessary maintenance workers, or cause the appearance of excessive traffic violations, leading to further unnecessary investigation. | A delay in reporting this may cause a delay in necessary maintenance, but (a) this is not time-critical and (b) there are other channels for reporting malfunctioning. Additionally, there is a message received notification, which means that RSE can ensure that all intersection safety issues are delivered. | |||
| Roadside Equipment | Vehicle OBE | intersection safety warning | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | This message is broadcast as a warning, allowing infringing drivers to avoid a collision with a pedestrian and all other drivers to avoid the infringing driver. If this message is falsely broadcast it could cause drivers who think they may be infringing to break suddenly, increasing the chance of a collisions from behind. If it were constantly broadcast incorrectly, it may lead to drivers ignoring this notifications. All of these cases have an impact on safety | This message has a very short window in which it is valid. If it is not delivered until after the driver has passed the point of no return before entering the crosswalk, they will not gain any information from it, rendering the application useless. | |||
| Roadside Equipment | Vehicle OBE | intersection status | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | If this is compromised, the Vehicle OBE will receive messages that are inconsistent with what the traffic signals are displaying. This could lead to confusion and reduce the ability of the application to provide value. | If this is down, the Vehicle OBE doesn't get the information it needs to stay in synch with the actual signal state, reducing or eliminating the value add from having this application. We assume that the Vehicle OBE will detect a lack of availability and choose not to send out-of-date information, so a failure of availability cannot have worse consequences than a failure of integrity which we have previously assessed at MEDIUM. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | ITS Roadway Equipment | pedestrian safety warning control | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
| o Application configuration: The displays and warnings on the controlled device are not confidential, so messages containing possible displays and warnings or setting the conditions under which they are displayed should not be confidential. O Device management: If this information flow includes device management as well as display and alert configuration, the device management may include proprietary information about the particular device being managed such as firmware details, memory size, processor limitations etc. The confidentiality requirement for the roadway equipment should be set by the supplier based on their understanding of the confidentiality requirements of the management messages. Note that the supplier can be assumed to provide devices that meet their own security requirements; however, the confidentiality requirements of this flow will also apply to the TMC. |
Fake instances of this information flow can cause drivers and pedestrians to get incorrect information. However, it would not be possible to put the traffic signal into an inconsistent | Assuming that the traffic signal is configured reasonably well to start off with, the system should be robust if it goes an arbitrary amount of time without reconfiguration. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Roadside Equipment | intersection safety application info | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
| o Application configuration: The messages sent from the RSE are public and the warning parameters can be assumed to follow widely-known industry best practices, so management messages to configure these do not have a significant confidentiality requirement. o Device management: As with TMC: Pedestrian Safety Warning Control, the device management may include proprietary information about the particular device being managed such as firmware details, memory size, processor limitations etc. The confidentiality requirement for the roadway equipment should be set by the supplier based on their understanding of the confidentiality requirements of the management messages. Note that the supplier can be assumed to provide devices that meet their own security requirements; however, the confidentiality requirements of this flow will also apply to the TMC. |
Fake instances of this information flow can cause drivers and pedestrians to get incorrect information (for example, swap the "safe to cross" and "not safe to cross" messages so pedestrians are told to cross when it isn't safe). In particular, visually impaired people may rely on the message content to cross safely and may be endangered by bad message content. However, the impact is limited to a single crossing area and drivers still have primary responsibility for the safety of vulnerable road users, so the integrity requirement is MEDIUM rather than HIGH. | Assuming that the traffic signal is configured reasonably well to start off with, the system should be robust if it goes an arbitrary amount of time without reconfiguration. | |||
| Vehicle Databus | Vehicle OBE | host vehicle status | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| In general this is information that will be broadcast but the information flow may include OEM-proprietary or sensitive information. | At least some data from this information flow is broadcast to other systems, and is then is used in the decision making process. All of the other stages that utilize this data flow have a MEDIUM integrity requirement, which leads to this one having a MEDIUM as well. | The Vehicle OBE relies on this data being available from the Vehicle Platform. If this data is not available, then the other systems cannot function. All of the other systems have a MEDIUM requirement, leading to a MEDIUM here. | |||
| Vehicle OBE | Driver | driver updates | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is informing the driver about the safety of the intersections. It should not contain anything sensitive, and does not matter if another person can observe it. | This is the information that is presented to the driver. If they receive incorrect information, they may act in an unsafe manner. However, there are other indicators that would alert them to any hazards, such as an oncoming vehicle or crossing safety lights. | If this information is not made available to the driver, then the system has not operated correctly. | |||
| Vehicle OBE | Personal Information Device | vehicle location and motion | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators | Incorrect information could lead to the system not operating properly. If the system does not properly know where the vehicle is, it cannot make an accurate decision about whether there is going to be a pedestrian in the crosswalk that the vehicle is approaching. This can have a safety impact. | This data is required for the system to operate properly. If this data is not available, the system cannot give accurate warning information. | |||
| Vehicle OBE | Roadside Equipment | intersection infringement info | Low | High | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | This message is an indication of a potential hazard and should not be easy to forge. False messages here may lead to confusion that causes a traffic accident. | This message is an indication of a potential hazard. If it isn't received it increases the risk to other road users. If a vehicle is infringing on an intersection, it must report this. | |||
| Vehicle OBE | Roadside Equipment | vehicle location and motion | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators | Incorrect information could lead to the system not operating properly. If the system does not properly know where the vehicle is, it cannot make an accurate decision about whether there is going to be a pedestrian in the crosswalk that the vehicle is approaching. This can have a safety impact. | This data is required for the system to operate properly. If this data is not available, the system cannot give accurate warning information. | |||
| Vehicle OBE | Vehicle Databus | collision warning information | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| The information described in this message is the result of an analysis on broadcast data. It would not be difficult for a third party to produce the same message by listening to the broadcast information. | This information is used by automated control systems on the vehicle platform to decide whether to react automatically, for example by braking. We assume that the vehicle platform uses this as only one input to the decision and will also take input from front-facing sensors (for pedestrian detection), rear-facing sensors (to detect possible rear-ending), etc. We strongly recommend that this message is not used as the sole basis for action; if it were to be so used, the integrity requirement might need to be HIGH, but we do not consider this case in detail here. | This information is just one of a number of inputs to the vehicle platform that may be used to determine whether or not to take evasive action. | |||
| Vehicle OBE | Vehicle Databus | driver update information | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| All of this information is information that will be sent via broadcast, received via broadcast, or could be derived by observing the vehicle. | In this instance, the data displayed to the driver is based on all of the previous inputs to the application. If the integrity of this information flow is not held to the same standard, it invalids the rest of the assessments. | As with integrity, the requirement here is based off of all of the previous information flows. This should be MEDIUM to ensure that the notification reaches the driver correctly. However, there are other indicators of pedestrians in the crosswalk, and the driver should not be 100% reliant on the notifications before proceeding. Additionally, there should some form of notification to the driver when messages are unable to be presented correctly, informing them to have their vehicle serviced | |||