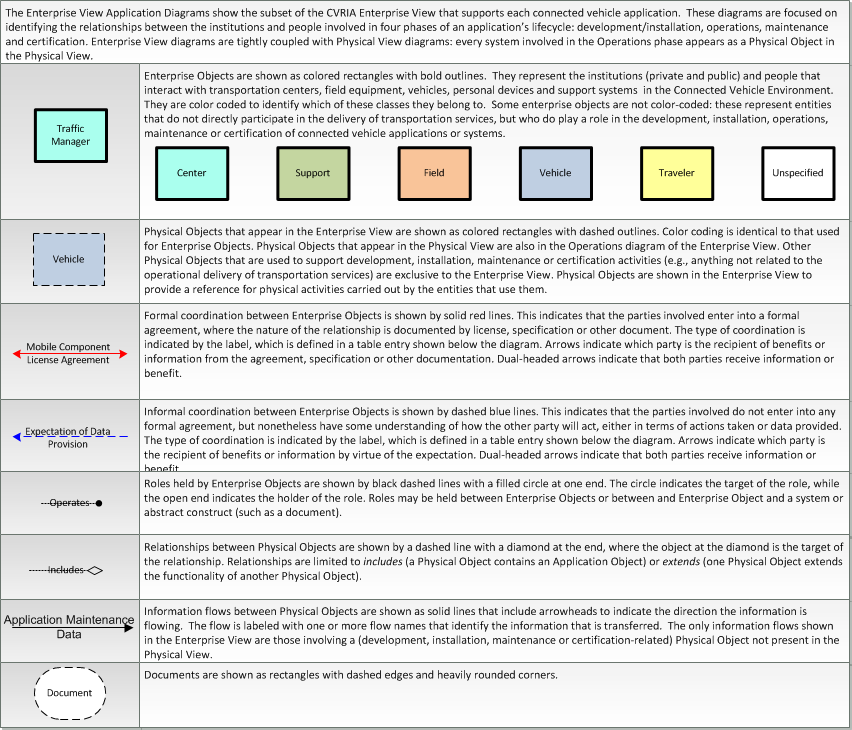
Type: Support
Groups:- Core Services
Data Distribution
Data Distribution is a support application that manages the distribution of data from data providers to data consumers and protects those data from unauthorized access. The application informs data providers of how to provide data, manages data subscriptions, and provides data forwarding capabilities. The application also maintains a directory of System Users that want data and supports multiple distribution mechanisms including publish-subscribe and directly from data provider to data consumer. The application allows data consumers to specify (and change the specification of) data they wish to receive.
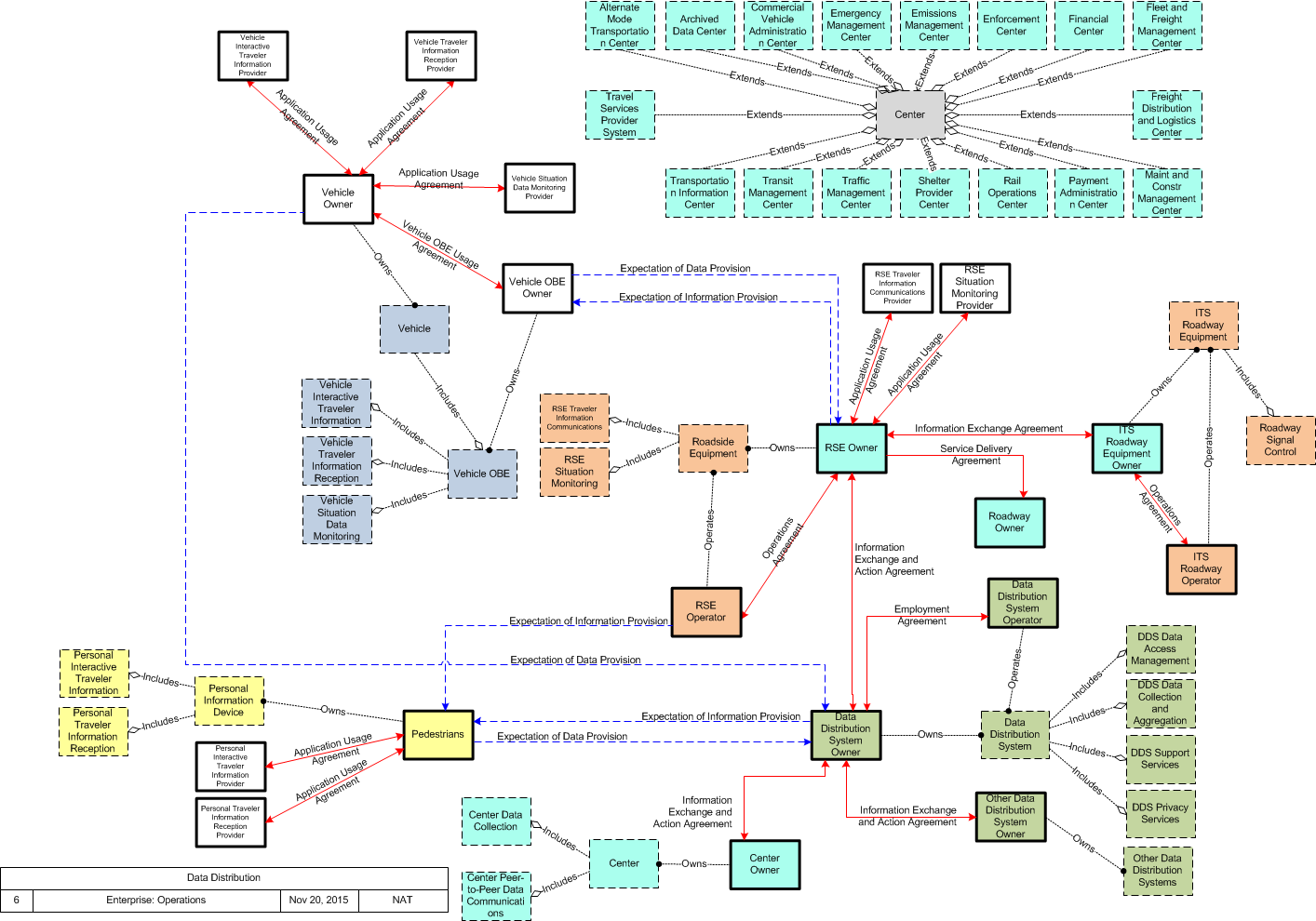
Enterprise
SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
Business Interaction Matrix:
| Data Distribution Operations Stage | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Owner | Vehicle OBE Owner | Roadway Owner | RSE Owner | RSE Operator | ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Operator | Pedestrians | Vehicle Interactive Traveler Information Provider | Personal Interactive Traveler Information Provider | Personal Traveler Information Reception Provider | Center Owner | Data Distribution System Owner | Other Data Distribution System Owner | Data Distribution System Operator | Vehicle Traveler Information Reception Provider | RSE Traveler Information Communications Provider | Vehicle Situation Data Monitoring Provider | RSE Situation Monitoring Provider | |
| Vehicle Owner | Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Expectation of Data Provision | Application Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||
| Vehicle OBE Owner | Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | |||||||||||||||||
| Roadway Owner | Service Delivery Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||
| RSE Owner | Expectation of Information Provision | Service Delivery Agreement | Operations Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||
| RSE Operator | Operations Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | |||||||||||||||||
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Information Exchange Agreement | Operations Agreement | |||||||||||||||||
| ITS Roadway Operator | Operations Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pedestrians | Expectation of Information Provision | Application Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | |||||||||||||||
| Vehicle Interactive Traveler Information Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||
| Personal Interactive Traveler Information Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||
| Personal Traveler Information Reception Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||
| Center Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||
| Data Distribution System Owner | Expectation of Data Provision | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Employment Agreement | |||||||||||||
| Other Data Distribution System Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||
| Data Distribution System Operator | Employment Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vehicle Traveler Information Reception Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||
| RSE Traveler Information Communications Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vehicle Situation Data Monitoring Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||
| RSE Situation Monitoring Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||
Includes Enterprise Objects:
| Enterprise Object | Description |
|---|---|
| Center Owner | General representation of the owner of the general "Center" physical object. |
| Data Distribution System Operator | The 'Data Distribution System Operator' represents the person or people that monitor and manage the data services provided by the Data Distribution System (DDS). These personnel manage and monitor the systems that support the publish/subscribe services of the DDS. |
| Data Distribution System Owner | The enterprise charged with providing data distribution services in the connected vehicle environment. This enterprise serves as broker between information and data providers and consumers. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | The entity that owns the Roadway ITS equipment. |
| ITS Roadway Operator | The entity that operates the Roadway ITS equipment. |
| Other Data Distribution System Owner | Representing the owner of another Data Distribution System, for environments where DDS exchange information and data. |
| Pedestrians | 'Pedestrians' participate in connected vehicle applications that support safe, shared use of the transportation network by motorized and non-motorized transportation modes. Representing those using non-motorized travel modes, pedestrians provide input (e.g. a call signal requesting right of way at an intersection) and may be detected by connected vehicle applications to improve safety. Note that pedestrians represent all non-motorized users, including bicyclists. |
| Personal Interactive Traveler Information Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Personal Traveler Information Reception Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Roadway Owner | The owner of the roadway proximate to which roadside equipment will be/is installed. |
| RSE Operator | The entity that operates roadside equipment in the transportation environment. |
| RSE Owner | The owner of roadside equipment. |
| RSE Situation Monitoring Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Traveler Information Communications Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Vehicle Interactive Traveler Information Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Vehicle OBE Owner | The entity, individual, group or corporation that owns the Vehicle On-Board equipment. This could be the same as the Vehicle Owner, but it could be a third part that licenses the use of the OBE to the Owner. |
| Vehicle Owner | The individual, group of individuals or corporate entity that is identified as the registered owner of the Vehicle under state law. |
| Vehicle Situation Data Monitoring Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Vehicle Traveler Information Reception Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
Includes Resources:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Alternate Mode Transportation Center | The 'Alternate Mode Transportation Center' provides the interface through which non-ITS transportation systems (e.g., airlines, ferry services, passenger-carrying heavy rail) can exchange data with ITS.. This two-way interface enables coordination for efficient movement of people across multiple transportation modes. It also enables the traveler to efficiently plan itineraries which include segments using other modes. |
| Archived Data Center | The 'Archived Data Center' collects, archives, manages, and distributes data generated from ITS sources for use in transportation administration, policy evaluation, safety, planning, performance monitoring, program assessment, operations, and research applications. The data received is formatted and tagged with attributes that define the data source, conditions under which it was collected, data transformations, and other information (i.e. meta data) necessary to interpret the data. The archive can fuse ITS generated data with data from non-ITS sources and other archives to generate information products utilizing data from multiple functional areas, modes, and jurisdictions. The archive prepares data products that can serve as inputs to federal, state, and local data reporting systems. The 'Archived Data Center' may reside within an operational center and provide focused access to a particular agency's data archives. Alternatively, it may operate as a distinct center that collects data from multiple agencies and sources and provides a general data warehouse service. |
| Center | This general physical object is used to model core capabilities that are common to any center. |
| Center Data Collection | "Center Data Collection" collects and stores information that is created in the course of center operations. This data can be used directly by operations personnel or it can be made available to other data users and archives in the region. |
| Center Peer-to-Peer Data Communications | "Center Peer-to-Peer Data Communications" supports general back office communications services. It supports peer-to-peer communications with other regional centers supporting operational data sharing. It also supports general communications with vehicles, supporting the transfer of non-specified (proprietary) data using connected vehicle standards-based communications. |
| Commercial Vehicle Administration Center | The 'Commercial Vehicle Administration Center' performs administrative functions supporting credentials, tax, and safety regulations associated with commercial vehicles. It issues credentials, collects fees and taxes, and supports enforcement of credential requirements. It communicates with motor carriers to process credentials applications and collect fuel taxes, weight/distance taxes, and other taxes and fees associated with commercial vehicle operations. It also receives applications for, and issues special Oversize/Overweight and HAZMAT permits in coordination with cognizant authorities. It coordinates with other Commercial Vehicle Administration Centers (in other states/regions) to support nationwide access to credentials and safety information for administration and enforcement functions. It communicates with field equipment to enable credential checking and safety information collection at the roadside. It makes safety information available to qualified stakeholders to identify carriers and drivers that operate unsafely. |
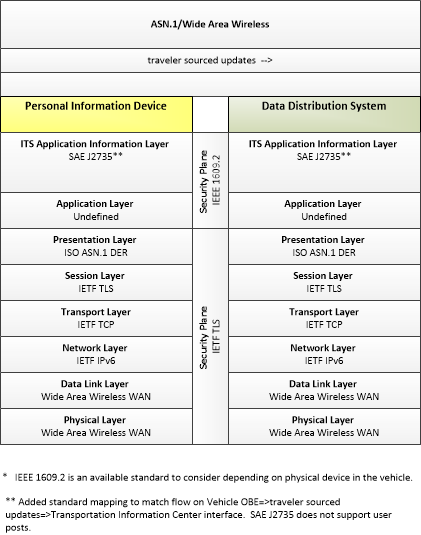
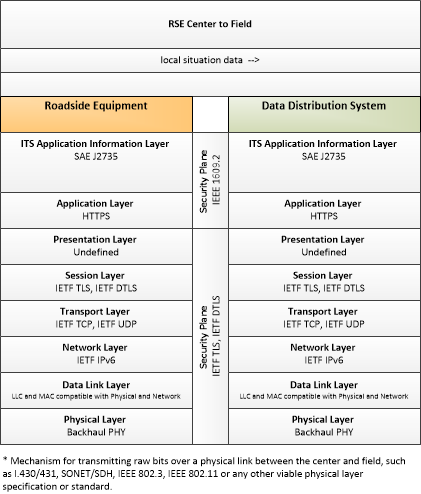
| Data Distribution System | The 'Data Distribution System' collects, processes, and distributes connected vehicle data, connecting data producers with data consumers and facilitating data exchange in the Connected Vehicle Environment. |
| DDS Data Access Management | "DDS Data Access Management" defines the access mechanisms, structures and restrictions for inbound (from providers) and outbound (to consumers) data. |
| DDS Data Collection and Aggregation | "DDS Data Collection and Aggregation" collects data "deposits" from producers including meta data such as the generation location and time. It authenticates and validates the data deposits and logs all associated meta data. Authenticated, valid data is bundled based on information type and location and made available as data products to consumers who are interested in the data. It establishes delivery parameters for data consumers that subscribe based on parameters including content type and geographic region of interest and delivers data to consumers based on these parameters. |
| DDS Privacy Services | "DDS Privacy Services" operates as a proxy, replacing the mobile device's network address with the DDS's, and tagging the message so that it can return replies to the mobile device. |
| DDS Support Services | "DDS Support Services" provides foundational functions that support data collection, management, and distribution. It coordinates with Object Registration and Discovery to maintain its registration with respect to location/geographic scope and credentialing information. It maintains the necessary security credentials, authorizations, and associated keys to support communications in the connected vehicle environment. It also provides an overall service monitoring function. |
| Emergency Management Center | The 'Emergency Management Center' represents systems that support incident management, disaster response and evacuation, security monitoring, and other security and public safety-oriented ITS applications. It includes the functions associated with fixed and mobile public safety communications centers including public safety call taker and dispatch centers operated by police (including transit police), fire, and emergency medical services. It includes the functions associated with Emergency Operations Centers that are activated at local, regional, state, and federal levels for emergencies and the portable and transportable systems that support Incident Command System operations at an incident. This Center also represents systems associated with towing and recovery, freeway service patrols, HAZMAT response teams, and mayday service providers. It manages sensor and surveillance equipment used to enhance transportation security of the roadway infrastructure (including bridges, tunnels, interchanges, and other key roadway segments) and the public transportation system (including transit vehicles, public areas such as transit stops and stations, facilities such as transit yards, and transit infrastructure such as rail, bridges, tunnels, or bus guideways). It provides security/surveillance services to improve traveler security in public areas not a part of the public transportation system. It monitors alerts, advisories, and other threat information and prepares for and responds to identified emergencies. It coordinates emergency response involving multiple agencies with peer centers. It stores, coordinates, and utilizes emergency response and evacuation plans to facilitate this coordinated response. Emergency situation information including damage assessments, response status, evacuation information, and resource information are shared The Emergency Management Center also provides a focal point for coordination of the emergency and evacuation information that is provided to the traveling public, including wide-area alerts when immediate public notification is warranted. It tracks and manages emergency vehicle fleets using real-time road network status and routing information from the other centers to aid in selecting the emergency vehicle(s) and routes, and works with other relevant centers to tailor traffic control to support emergency vehicle ingress and egress, implementation of special traffic restrictions and closures, evacuation traffic control plans, and other special strategies that adapt the transportation system to better meet the unique demands of an emergency. |
| Emissions Management Center | The 'Emissions Management Center' provides the capabilities for air quality managers to monitor and manage air quality. These capabilities include collecting emissions data from distributed emissions sensors (included in ITS Roadway Equipment in CVRIA) and directly from connected vehicles. The sensors monitor general air quality and also monitor the emissions of individual vehicles on the roadway. The measures are collected, processed, and used to support environmental monitoring applications. |
| Enforcement Center | The 'Enforcement Center' represents the systems that receive reports of violations detected by various ITS facilities including individual vehicle emissions, lane violations, toll violations, CVO violations, etc. |
| Financial Center | The 'Financial Center' represents the organization that handles electronic fund transfer requests to enable the transfer of funds from the user of the service to the provider of the service. The functions and activities of financial clearinghouses are subsumed by this entity. |
| Fleet and Freight Management Center | The 'Fleet and Freight Management Center' provides the capability for commercial drivers and fleet-freight managers to receive real-time routing information and access databases containing vehicle and/or freight equipment locations as well as carrier, vehicle, freight equipment and driver information. The 'Fleet and Freight Management Center' also provides the capability for fleet managers to monitor the safety and security of their commercial vehicle drivers and fleet. |
| Freight Distribution and Logistics Center | The 'Freight Distribution and Logistics Center' provides intermodal logistics support and support for the efficient distribution of freight across transport systems and modes. This can include consolidation arrangements, warehousing, and consignor-to-consignee intermodal shipping arrangements. These capabilities may be provided as part of intermodal fleet management activities or can be provided by an independent logistics specialist. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway itself. In CVRIA, this physical object represents all of the other ITS field equipment that interfaces with and supports the Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE). This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| Maint and Constr Management Center | The 'Maint and Constr Management Center' monitors and manages roadway infrastructure construction and maintenance activities. Representing both public agencies and private contractors that provide these functions, this physical object manages fleets of maintenance, construction, or special service vehicles (e.g., snow and ice control equipment). The physical object receives a wide range of status information from these vehicles and performs vehicle dispatch, routing, and resource management for the vehicle fleets and associated equipment. The physical object participates in incident response by deploying maintenance and construction resources to an incident scene, in coordination with other center physical objects. The physical object manages equipment at the roadside, including environmental sensors and automated systems that monitor and mitigate adverse road and surface weather conditions. It manages the repair and maintenance of both non-ITS and ITS equipment including the traffic controllers, detectors, dynamic message signs, signals, and other equipment associated with the roadway infrastructure. Weather information is collected and fused with other data sources and used to support advanced decision support systems. The physical object remotely monitors and manages ITS capabilities in work zones, gathering, storing, and disseminating work zone information to other systems. It manages traffic in the vicinity of the work zone and advises drivers of work zone status (either directly at the roadside or through an interface with the Transportation Information Center or Traffic Management Center physical objects.) Construction and maintenance activities are tracked and coordinated with other systems, improving the quality and accuracy of information available regarding closures and other roadway construction and maintenance activities. |
| Other Data Distribution Systems | Representing another Data Distribution System, 'Other Data Distribution Systems' is intended to provide a source and destination for information exchange between peer (e.g. inter-regional) data distribution systems. It supports modeling of projects or regions that include multiple interconnected data distribution systems that together manage data distribution in the connected vehicle environment. |
| Payment Administration Center | The 'Payment Administration Center' provides general payment administration capabilities and supports the electronic transfer of funds from the customer to the transportation system operator or other service provider. Charges can be recorded for tolls, vehicle-mileage charging, congestion charging, or other goods and services. It supports traveler enrollment and collection of both pre-payment and post-payment transportation fees in coordination with the financial infrastructure supporting electronic payment transactions. The system may establish and administer escrow accounts depending on the clearinghouse scheme and the type of payments involved. It may post a transaction to the customer account, generate a bill (for post-payment accounts), debit an escrow account, or interface to a financial infrastructure to debit a customer designated account. It supports communications with the ITS Roadway Payment Equipment to support fee collection operations. As an alternative, a wide-area wireless interface can be used to communicate directly with vehicle equipment. It also sets and administers the pricing structures and may implement road pricing policies in coordination with the Traffic Management Center. |
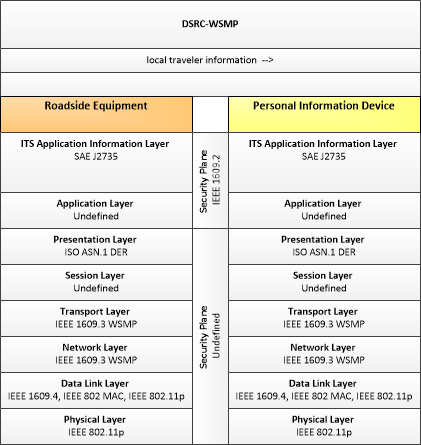
| Personal Information Device | The 'Personal Information Device' provides the capability for travelers to receive formatted traveler information wherever they are. Capabilities include traveler information, trip planning, and route guidance. Frequently a smart phone, the Personal Information Device provides travelers with the capability to receive route planning and other personally focused transportation services from the infrastructure in the field, at home, at work, or while en-route. Personal Information Devices may operate independently or may be linked with connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| Personal Interactive Traveler Information | "Personal Interactive Traveler Information" provides traffic information, road conditions, transit information, yellow pages (traveler services) information, special event information, and other traveler information that is specifically tailored based on the traveler's request and/or previously submitted traveler profile information. It also supports interactive services that support enrollment, account management, and payments for transportation services. The interactive traveler information capability is provided by personal devices including personal computers and personal portable devices such as smart phones. |
| Personal Traveler Information Reception | "Personal Traveler Information Reception" receives formatted traffic advisories, road conditions, transit information, broadcast alerts, and other general traveler information broadcasts and presents the information to the traveler. The traveler information broadcasts are received by personal devices including personal computers and personal portable devices such as smart phones. |
| Rail Operations Center | 'Rail Operations Center' represents the (usually) centralized control point for a substantial segment of a freight railroad's operations and maintenance activities. It is roughly the railroad equivalent to a highway Traffic Management Center. It is the source and destination of information that can be used to coordinate rail and highway traffic management and maintenance operations. It is also the source and destination for incident, incident response, disaster, or evacuation information that is exchanged with an Emergency Management Center. The use of a single object for multiple sources and destination for information exchange with railroads implies the need for a single, consistent interface between a given railroad's operations and maintenance activities and ITS. |
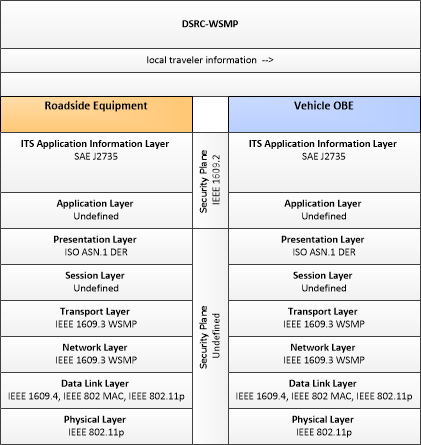
| Roadside Equipment | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Roadway Signal Control | "Roadway Signal Control" includes the field elements that monitor and control signalized intersections. It includes the traffic signal controllers, detectors, conflict monitors, signal heads, and other ancillary equipment that supports traffic signal control. It also includes field masters, and equipment that supports communications with a central monitoring and/or control system, as applicable. The communications link supports upload and download of signal timings and other parameters and reporting of current intersection status. It represents the field equipment used in all levels of traffic signal control from basic actuated systems that operate on fixed timing plans through adaptive systems. It also supports all signalized intersection configurations, including those that accommodate pedestrians. In advanced, future implementations, environmental data may be monitored and used to support dilemma zone processing and other aspects of signal control that are sensitive to local environmental conditions. |
| RSE Situation Monitoring | "RSE Situation Monitoring" is a general application object that supports collection of traffic, environmental, and emissions data from passing vehicles. The data is collected, filtered, and forwarded based on parameters provided by the back office. Parameters are provided to passing vehicles that are equipped to collect and send situation data to the infrastructure in snapshots. In addition, this object collects current status information from local field devices including intersection status, sensor data, and signage data, providing complete, configurable monitoring of the situation for the local transportation system in the vicinity of the RSE. |
| RSE Traveler Information Communications | "RSE Traveler Information Communications" includes field elements that distribute information to vehicles for in-vehicle display. The information may be provided by a center (e.g., variable information on traffic and road conditions in the vicinity of the field equipment) or it may be determined and output locally (e.g., static sign information and signal phase and timing information). This includes the interface to the center or field equipment that controls the information distribution and the short range communications equipment that provides information to passing vehicles. |
| Shelter Provider Center | The 'Shelter Provider Center' provides information about the shelters that open with the threat of a disaster and are operated and maintained until the threat has passed. It may represent individual shelters if they have the capability to provide current information directly to ITS or it may represent a center operated by a managing organization such as the American Red Cross that operates the shelters and collects and provides aggregate shelter information for a region. |
| Traffic Management Center | The 'Traffic Management Center' monitors and controls traffic and the road network. It represents centers that manage a broad range of transportation facilities including freeway systems, rural and suburban highway systems, and urban and suburban traffic control systems. It communicates with ITS Roadway Equipment and Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE) to monitor and manage traffic flow and monitor the condition of the roadway, surrounding environmental conditions, and field equipment status. It manages traffic and transportation resources to support allied agencies in responding to, and recovering from, incidents ranging from minor traffic incidents through major disasters. |
| Transit Management Center | The 'Transit Management Center' manages transit vehicle fleets and coordinates with other modes and transportation services. It provides operations, maintenance, customer information, planning and management functions for the transit property. It spans distinct central dispatch and garage management systems and supports the spectrum of fixed route, flexible route, paratransit services, transit rail, and bus rapid transit (BRT) service. The physical object's interfaces allow for communication between transit departments and with other operating entities such as emergency response services and traffic management systems. |
| Transportation Information Center | The 'Transportation Information Center' collects, processes, stores, and disseminates transportation information to system operators and the traveling public. The physical object can play several different roles in an integrated ITS. In one role, the TIC provides a data collection, fusing, and repackaging function, collecting information from transportation system operators and redistributing this information to other system operators in the region and other TICs. In this information redistribution role, the TIC provides a bridge between the various transportation systems that produce the information and the other TICs and their subscribers that use the information. The second role of a TIC is focused on delivery of traveler information to subscribers and the public at large. Information provided includes basic advisories, traffic and road conditions, transit schedule information, yellow pages information, ride matching information, and parking information. The TIC is commonly implemented as a website or a web-based application service, but it represents any traveler information distribution service. |
| Travel Services Provider System | The 'Travel Services Provider System' represents the individual information systems operated by providers of traveler-oriented services. Example services that could be included are gas, food, lodging, vehicle repair, points of interest, and recreation areas. Also included are services specifically directed toward bicyclists and pedestrians such as bicycle shops and parking locations and bicycle and pedestrian rest areas. The interface with the Service Provider is necessary so that accurate, up-to-date service information can be provided to the traveler and to support electronic reservation capabilities. |
| Vehicle | The conveyance that provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support efficient, safe, and convenient travel. These functions reside in general vehicles including personal automobiles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, or other vehicle types. |
| Vehicle Interactive Traveler Information | "Vehicle Interactive Traveler Information" provides drivers with personalized traveler information including traffic and road conditions, transit information, maintenance and construction information, multimodal information, event information, and weather information. The provided information is tailored based on driver requests. Both one-time requests for information and on-going information streams based on a submitted traveler profile and preferences are supported. |
| Vehicle OBE | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
| Vehicle Situation Data Monitoring | "Vehicle Situation Data Monitoring" is the highest-level representation of the functionality required to collect traffic and environmental situation data by monitoring and storing the experience of the vehicle as it travels through the road network. Collected data is aggregated into snapshots that are reported when communications is available and with flow control based on parameters provided by the infrastructure. Note that this application object supports collection of data for areas remote from RSEs or other communications infrastructure. |
| Vehicle Traveler Information Reception | "Vehicle Traveler Information Reception" provides the capability for drivers to receive general transportation information including traffic and road conditions, incident information, maintenance and construction information, event information, transit information, parking information, weather information, and broadcast alerts. |
Includes Roles:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Operates | An Enterprise controls the functionality and state of the target Resource. An Enterprise that Operates a resource is considered Responsible. |
| Owns | An Enterprise has financial ownership and control over the Resource. An Enterprise that Owns a resource is considered Accountable. |
Includes Coordination:
| Coordination | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Application Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity that controls an application component's use gives the other entity the necessary tools and permission to operate that application or application component. |
| Employment Agreement | Agreement | An agreement between an individual and a corporation or government entity, whereupon the individual agrees to provide labor to the corporation/agency, which in turn compensates the employee. Stipulates level of compensation, working conditions, necessary equipment and training and expectations of employee performance. |
| Expectation of Data Provision | Expectation | An expectation where one party believes another party will provide data on a regular and recurring basis, and that that data will be useful to the receiver in the context of the receiver's application. This thus includes some expectation of data fields, timeliness, quality, precision and similar qualities of data. |
| Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation | An expectation where one party believes another party will provide it information whenever such information is likely relevant to the recipient. |
| Extends | Includes | Indicates that one component includes all of the functionality of another component, and in provides additional functionality beyond that other component's. |
| Includes | Includes | Indicates that one component is entirely contained within another component. |
| Information Exchange Agreement | Agreement | An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. |
| Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Agreement | An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. This also includes a specification for action that shall, should or may be taken by one party in response to this information. |
| Operations Agreement | Agreement | An agreement where one entity agrees to operate a device or application on behalf of another, device/application controlling entity. |
| Service Delivery Agreement | Agreement | A relationship where one party agrees to provide a service to the other party. This agreement may specify the expected performance of this service in terms of availability and/or actions/time-type performance specifications. |
| Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one entity permission to use a Vehicle OBE that the other party controls. |
Functional
Includes Processes:
Includes Data Flows:
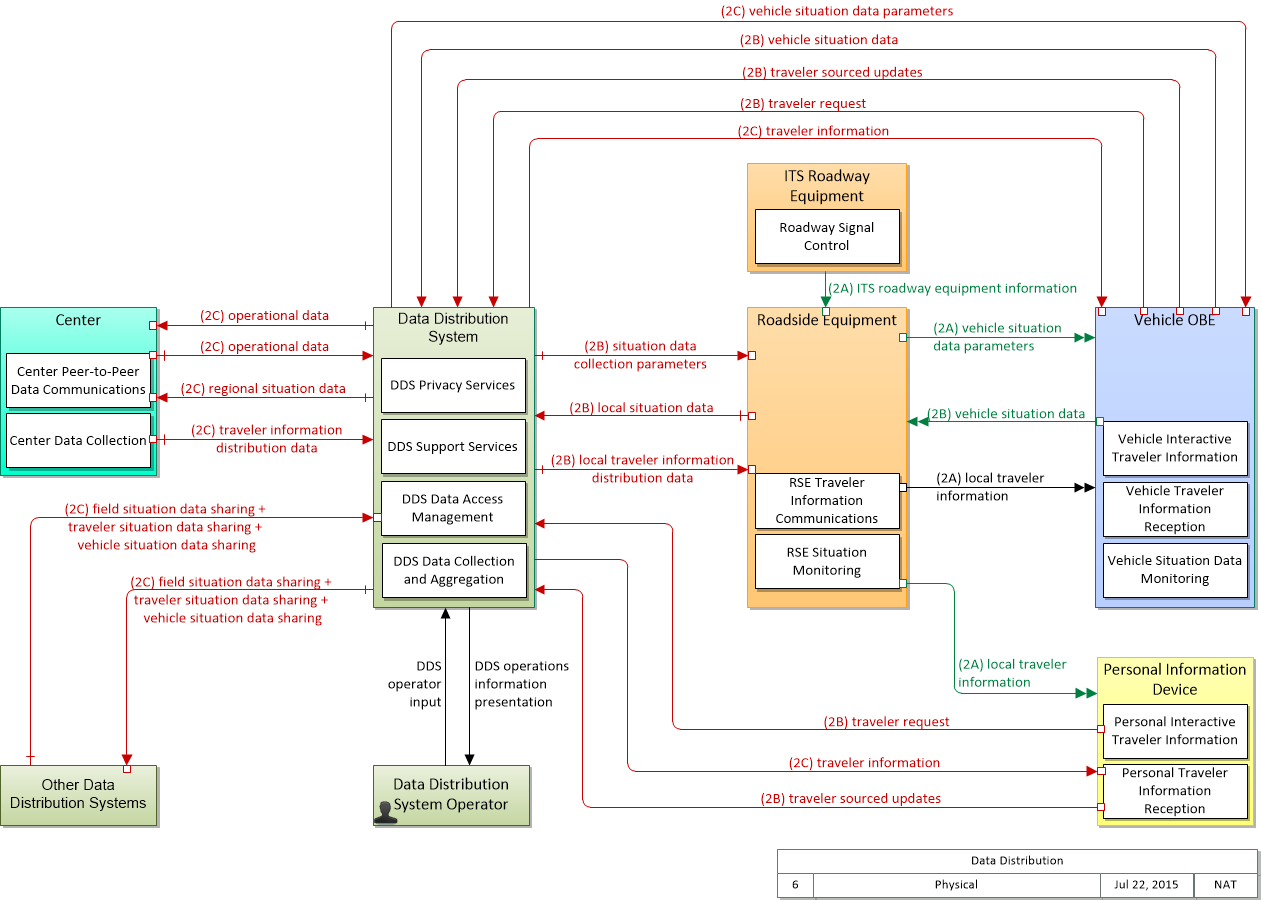
Physical
SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
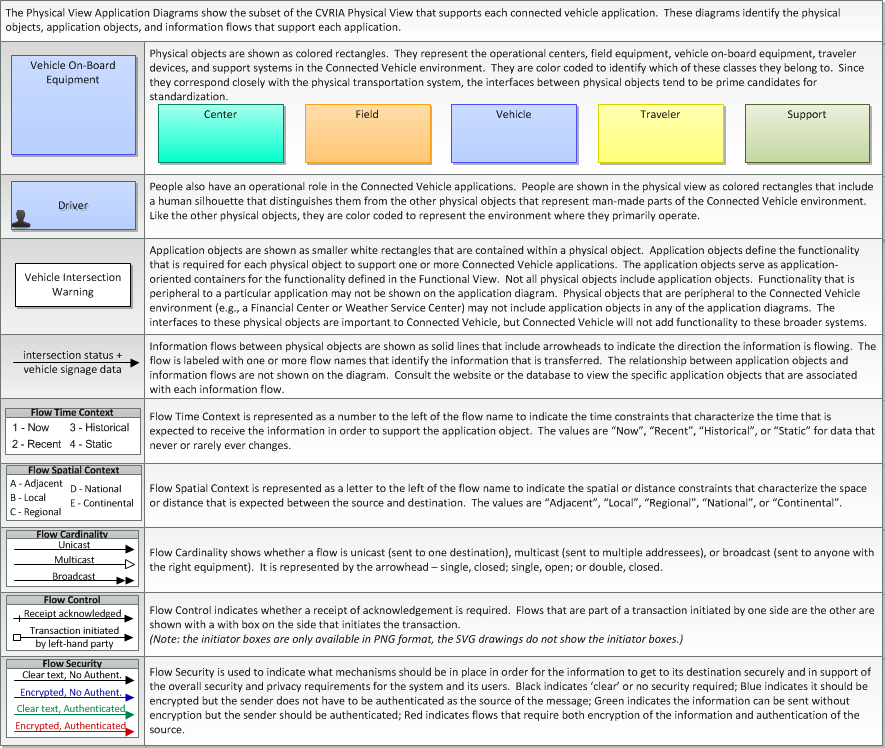
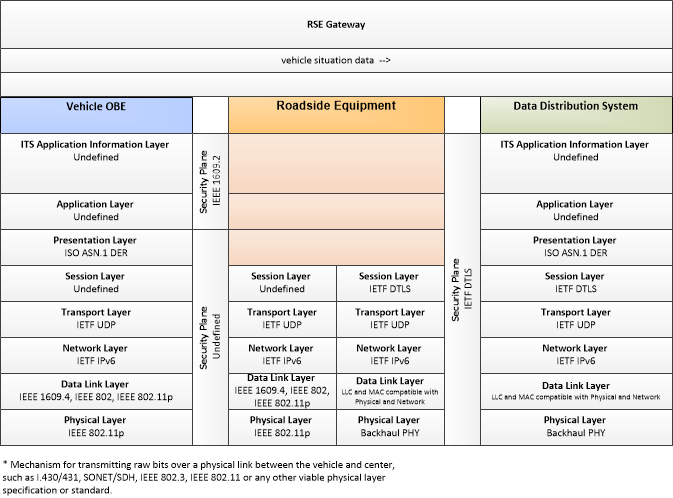
Includes Physical Objects:
| Physical Object | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Center | Center | This general physical object is used to model core capabilities that are common to any center. |
| Data Distribution System | Support | The 'Data Distribution System' collects, processes, and distributes connected vehicle data, connecting data producers with data consumers and facilitating data exchange in the Connected Vehicle Environment. |
| Data Distribution System Operator | Support | The 'Data Distribution System Operator' represents the person or people that monitor and manage the data services provided by the Data Distribution System (DDS). These personnel manage and monitor the systems that support the publish/subscribe services of the DDS. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Field | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway itself. In CVRIA, this physical object represents all of the other ITS field equipment that interfaces with and supports the Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE). This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| Other Data Distribution Systems | Support | Representing another Data Distribution System, 'Other Data Distribution Systems' is intended to provide a source and destination for information exchange between peer (e.g. inter-regional) data distribution systems. It supports modeling of projects or regions that include multiple interconnected data distribution systems that together manage data distribution in the connected vehicle environment. |
| Personal Information Device | Traveler | The 'Personal Information Device' provides the capability for travelers to receive formatted traveler information wherever they are. Capabilities include traveler information, trip planning, and route guidance. Frequently a smart phone, the Personal Information Device provides travelers with the capability to receive route planning and other personally focused transportation services from the infrastructure in the field, at home, at work, or while en-route. Personal Information Devices may operate independently or may be linked with connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| Roadside Equipment | Field | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Vehicle OBE | Vehicle | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
Includes Application Objects:
| Application Object | Description | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| Center Data Collection | "Center Data Collection" collects and stores information that is created in the course of center operations. This data can be used directly by operations personnel or it can be made available to other data users and archives in the region. | Center |
| Center Peer-to-Peer Data Communications | "Center Peer-to-Peer Data Communications" supports general back office communications services. It supports peer-to-peer communications with other regional centers supporting operational data sharing. It also supports general communications with vehicles, supporting the transfer of non-specified (proprietary) data using connected vehicle standards-based communications. | Center |
| DDS Data Access Management | "DDS Data Access Management" defines the access mechanisms, structures and restrictions for inbound (from providers) and outbound (to consumers) data. | Data Distribution System |
| DDS Data Collection and Aggregation | "DDS Data Collection and Aggregation" collects data "deposits" from producers including meta data such as the generation location and time. It authenticates and validates the data deposits and logs all associated meta data. Authenticated, valid data is bundled based on information type and location and made available as data products to consumers who are interested in the data. It establishes delivery parameters for data consumers that subscribe based on parameters including content type and geographic region of interest and delivers data to consumers based on these parameters. | Data Distribution System |
| DDS Privacy Services | "DDS Privacy Services" operates as a proxy, replacing the mobile device's network address with the DDS's, and tagging the message so that it can return replies to the mobile device. | Data Distribution System |
| DDS Support Services | "DDS Support Services" provides foundational functions that support data collection, management, and distribution. It coordinates with Object Registration and Discovery to maintain its registration with respect to location/geographic scope and credentialing information. It maintains the necessary security credentials, authorizations, and associated keys to support communications in the connected vehicle environment. It also provides an overall service monitoring function. | Data Distribution System |
| Personal Interactive Traveler Information | "Personal Interactive Traveler Information" provides traffic information, road conditions, transit information, yellow pages (traveler services) information, special event information, and other traveler information that is specifically tailored based on the traveler's request and/or previously submitted traveler profile information. It also supports interactive services that support enrollment, account management, and payments for transportation services. The interactive traveler information capability is provided by personal devices including personal computers and personal portable devices such as smart phones. | Personal Information Device |
| Personal Traveler Information Reception | "Personal Traveler Information Reception" receives formatted traffic advisories, road conditions, transit information, broadcast alerts, and other general traveler information broadcasts and presents the information to the traveler. The traveler information broadcasts are received by personal devices including personal computers and personal portable devices such as smart phones. | Personal Information Device |
| Roadway Signal Control | "Roadway Signal Control" includes the field elements that monitor and control signalized intersections. It includes the traffic signal controllers, detectors, conflict monitors, signal heads, and other ancillary equipment that supports traffic signal control. It also includes field masters, and equipment that supports communications with a central monitoring and/or control system, as applicable. The communications link supports upload and download of signal timings and other parameters and reporting of current intersection status. It represents the field equipment used in all levels of traffic signal control from basic actuated systems that operate on fixed timing plans through adaptive systems. It also supports all signalized intersection configurations, including those that accommodate pedestrians. In advanced, future implementations, environmental data may be monitored and used to support dilemma zone processing and other aspects of signal control that are sensitive to local environmental conditions. | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| RSE Situation Monitoring | "RSE Situation Monitoring" is a general application object that supports collection of traffic, environmental, and emissions data from passing vehicles. The data is collected, filtered, and forwarded based on parameters provided by the back office. Parameters are provided to passing vehicles that are equipped to collect and send situation data to the infrastructure in snapshots. In addition, this object collects current status information from local field devices including intersection status, sensor data, and signage data, providing complete, configurable monitoring of the situation for the local transportation system in the vicinity of the RSE. | Roadside Equipment |
| RSE Traveler Information Communications | "RSE Traveler Information Communications" includes field elements that distribute information to vehicles for in-vehicle display. The information may be provided by a center (e.g., variable information on traffic and road conditions in the vicinity of the field equipment) or it may be determined and output locally (e.g., static sign information and signal phase and timing information). This includes the interface to the center or field equipment that controls the information distribution and the short range communications equipment that provides information to passing vehicles. | Roadside Equipment |
| Vehicle Interactive Traveler Information | "Vehicle Interactive Traveler Information" provides drivers with personalized traveler information including traffic and road conditions, transit information, maintenance and construction information, multimodal information, event information, and weather information. The provided information is tailored based on driver requests. Both one-time requests for information and on-going information streams based on a submitted traveler profile and preferences are supported. | Vehicle OBE |
| Vehicle Situation Data Monitoring | "Vehicle Situation Data Monitoring" is the highest-level representation of the functionality required to collect traffic and environmental situation data by monitoring and storing the experience of the vehicle as it travels through the road network. Collected data is aggregated into snapshots that are reported when communications is available and with flow control based on parameters provided by the infrastructure. Note that this application object supports collection of data for areas remote from RSEs or other communications infrastructure. | Vehicle OBE |
| Vehicle Traveler Information Reception | "Vehicle Traveler Information Reception" provides the capability for drivers to receive general transportation information including traffic and road conditions, incident information, maintenance and construction information, event information, transit information, parking information, weather information, and broadcast alerts. | Vehicle OBE |
Includes Information Flows:
| Information Flow | Description |
|---|---|
| DDS operations information presentation | Presentation of information to the DDS Operator including current operational status of the Data Distribution System. |
| DDS operator input | User input from the DDS operator including requests to monitor current system operation and inputs to affect system operation. |
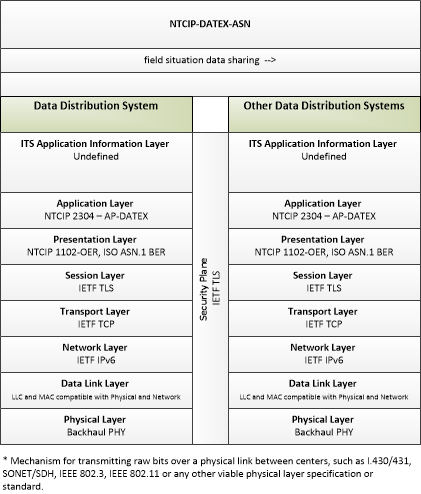
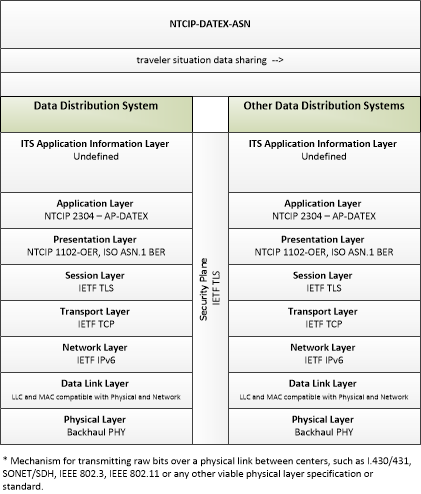
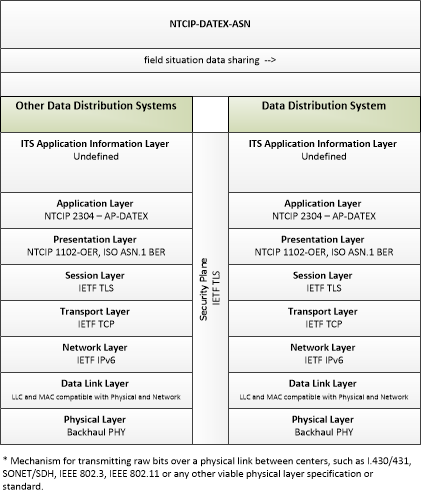
| field situation data sharing | Sharing of field situation data (data collected from ITS roadway equipment including intersection status, environmental sensor data, etc.) between data distribution systems. This sharing supports data deposits for storage and delivery of data to support distribution to end-users. |
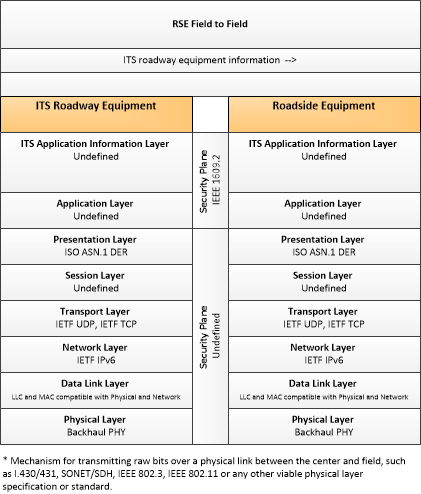
| ITS roadway equipment information | This general flow represents the information provided to the RSE by local field devices. This includes intersection status (SPAT), environmental sensor data, and signage data. |
| local situation data | This general flow represents the traffic, environmental, and emissions situation data that is collected from connected vehicles by an RSE, aggregated, filtered, and provided to a back-office center. It also includes data collected from ITS roadway equipment that provides current intersection and road network status for the area proximate to the RSE. |
| local traveler information | Traveler information including traffic, road, and weather conditions for a particular locality. This flow includes the location-specific traveler information and time effectivity of the information. |
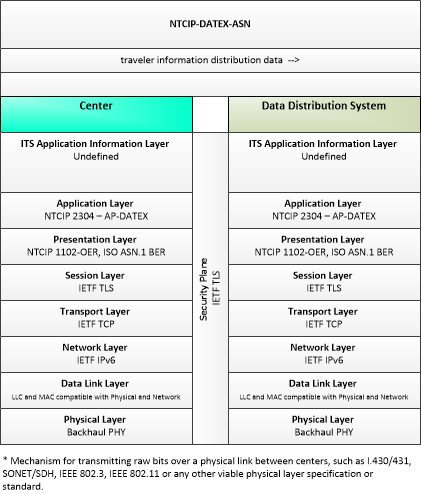
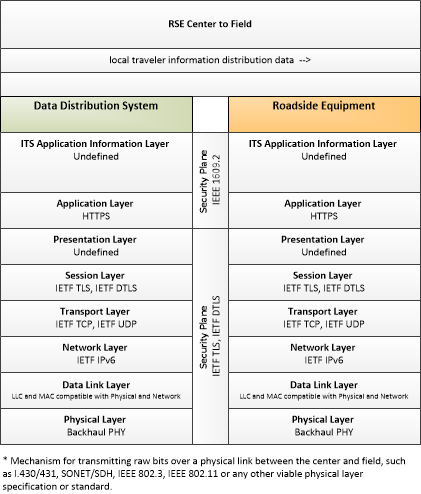
| local traveler information distribution data | A request to an RSE to distribute traveler information. The flow includes the traveler information to be distributed and parameters that establish the start and end times and relative priority of the traveler information. |
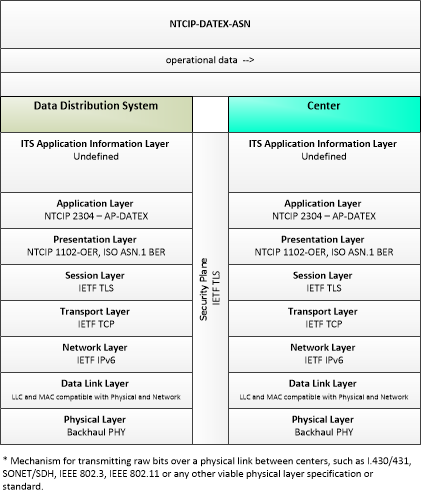
| operational data | This general flow represents data that is contributed to an operational data repository by an operating center. This data includes the current operational status and performance of the assets operated by the center. |
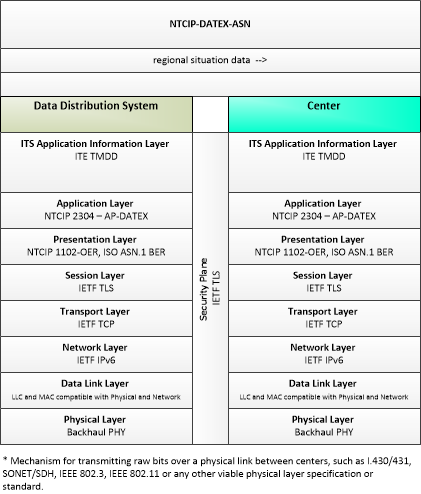
| regional situation data | This general flow represents the traffic, environmental, and emissions situation data that is collected from connected vehicles and aggregated, filtered, and distributed to other centers as a regional information product for use in operations, performance monitoring, and analysis. |
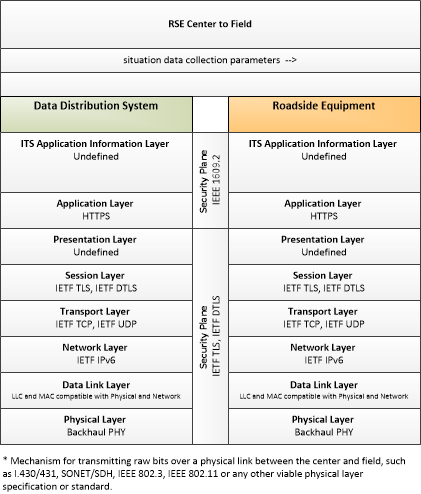
| situation data collection parameters | The parameters that are used to control the flow of situation data from the RSE. This flow identifies the type of data/snapshots that are requested from passing vehicles and reporting parameters such as snapshot frequency, filtering criteria (data thresholds for reporting), and reporting interval that control the type and volume of data reported to the back office center. |
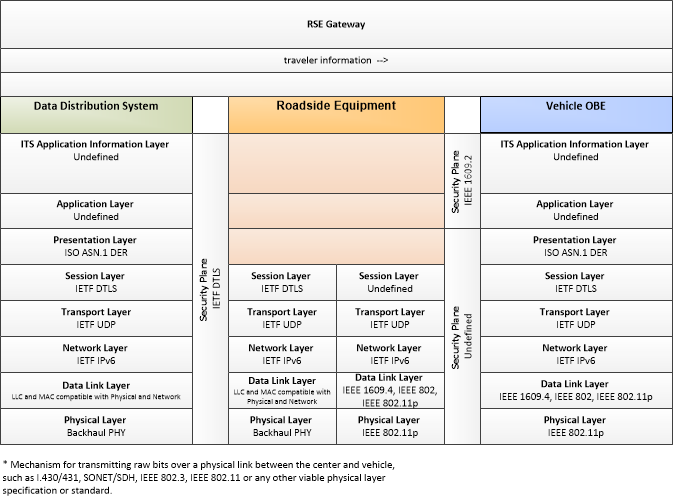
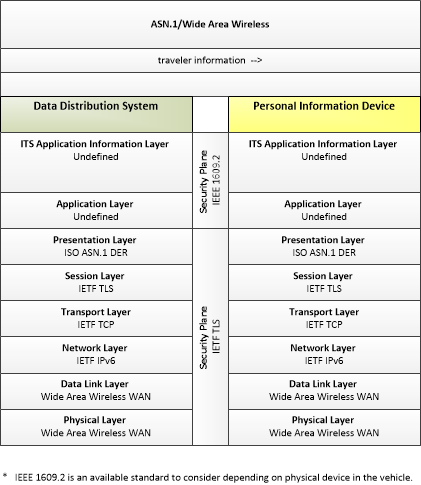
| traveler information | This general flow represents the distribution of traveler information to end users. Flow control is not explicitly shown, but this flow supports general broadcast, interactive request/response, and publish/subscribe delivery of traveler information. |
| traveler information distribution data | This general flow is a request to distribute traveler information. The flow includes the traveler information to be distributed and parameters that establish the timing, relative priority, and geographic scope of the distribution. |
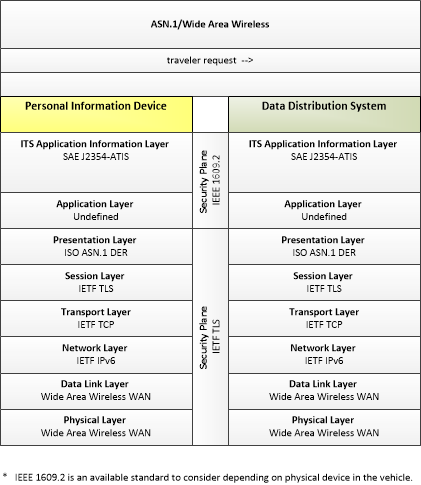
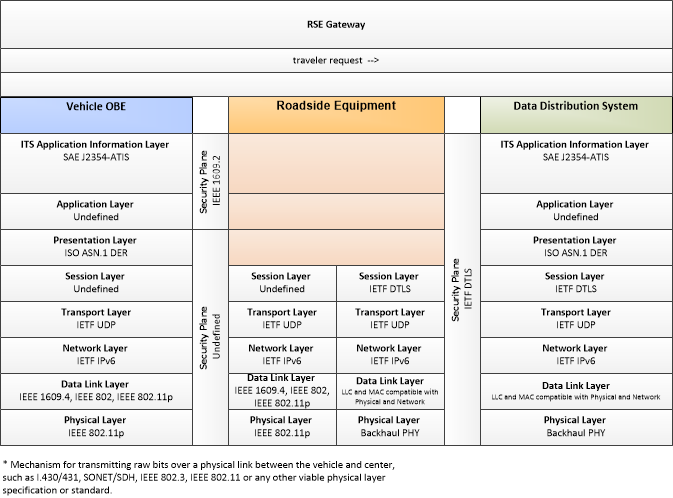
| traveler request | A request for traveler information including traffic, transit, toll, parking, road weather conditions, event, and passenger rail information. The request identifies the type of information, the area of interest, parameters that are used to prioritize or filter the returned information, and sorting preferences. |
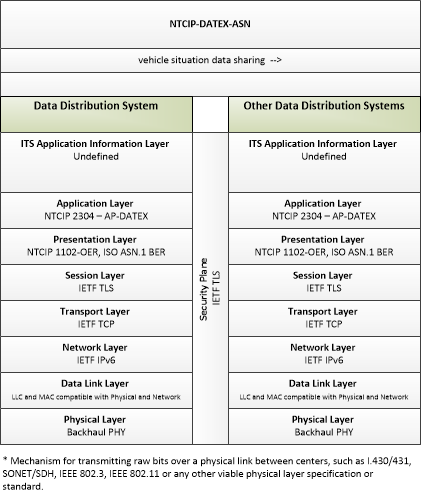
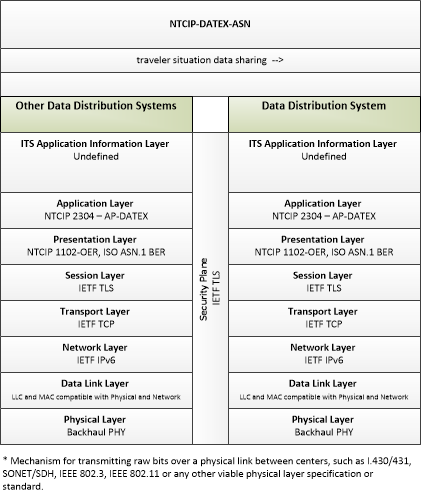
| traveler situation data sharing | Sharing of traveler situation data between data distribution systems. This sharing supports data deposits for storage and delivery of data to support distribution to end-users. |
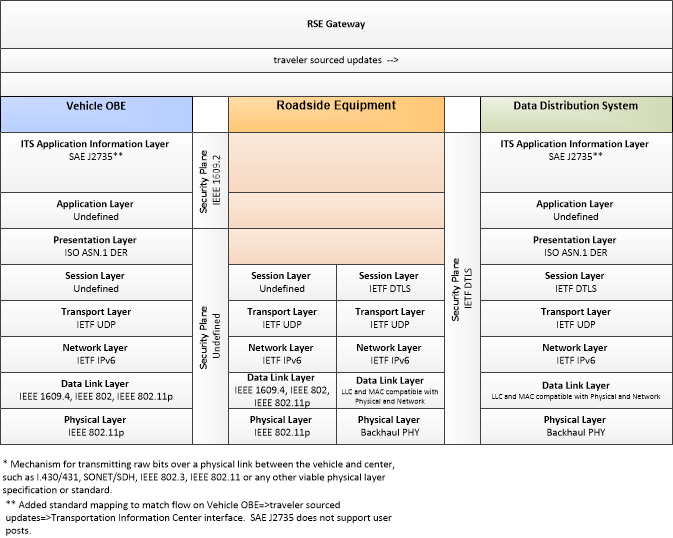
| traveler sourced updates | Traveler posts on traffic and road conditions, transit services, traveler services, shelter information and other real-time crowd-sourced data that may be shared with other travelers. |
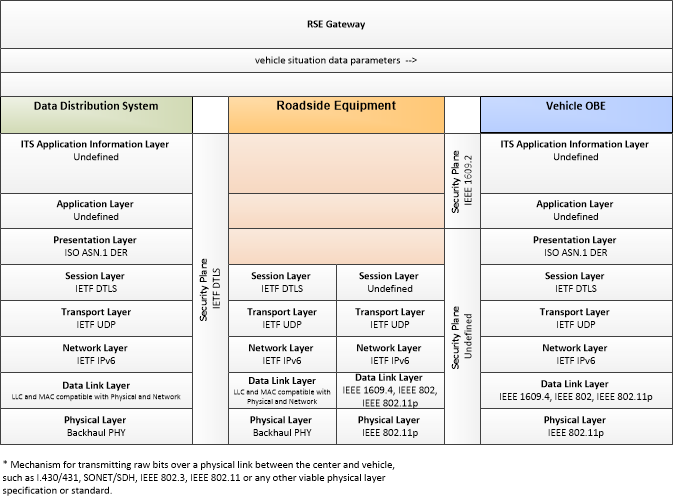
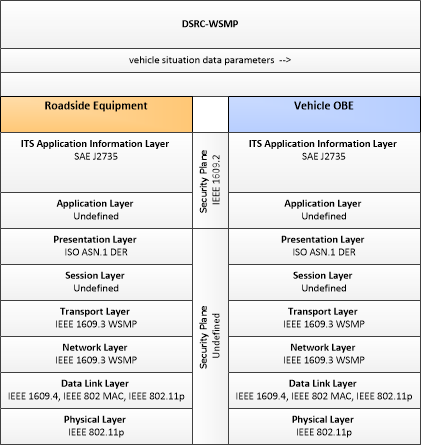
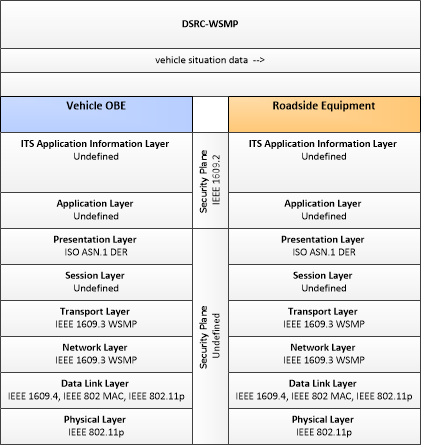
| vehicle situation data | This flow represents vehicle snapshots that may be provided by the vehicle to support traffic and environmental conditions monitoring. Snapshots are collected by the vehicle for specific events (e.g., when a sensor exceeds a threshold) or periodically and reported based on control parameters when communications is available. Traffic-related data includes snapshots of measured speed and heading and events including starts and stops, speed changes, and other vehicle control events. Environmental data may include measured air temperature, exterior light status, wiper status, sun sensor status, rain sensor status, traction control status, anti-lock brake status, and other collected vehicle system status and sensor information. The collected data is reported along with the location, heading, and time that the data was collected. |
| vehicle situation data parameters | A request for vehicle situation data that includes parameters used to control the data that is reported and the flow of data reported by the vehicle. This flow identifies the type of data/snapshots that are requested and reporting parameters such as snapshot frequency, filtering criteria (data thresholds for reporting), and reporting interval. |
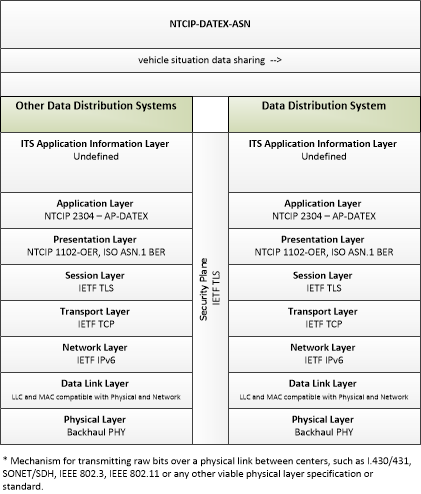
| vehicle situation data sharing | Sharing of vehicle situation data between data distribution systems. This sharing supports data deposits for storage and delivery of data to support distribution to end-users. |
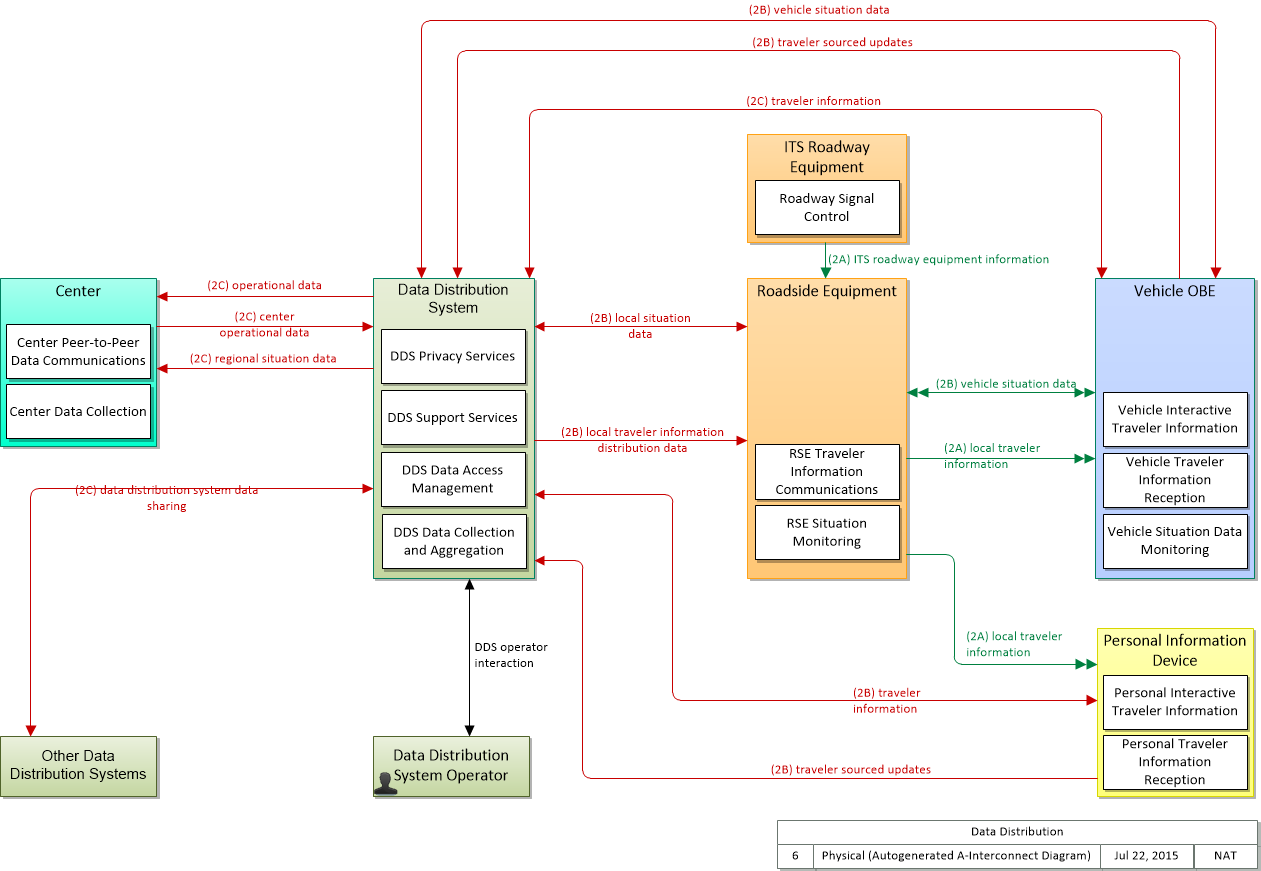
Application Interconnect Diagram
SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
Application Triples
Requirements
| Need | Requirement | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N4.001 | Applications need to protect data they handle from unauthorized access. This is required to support applications that exchange sensitive information, such as personally identifying or financial information, which if intercepted could compromise the privacy or financial records of the user. | 4.001 | Applications that function by exchanging data between entities shall be able to exchange encrypted data between those entities. |
| N4.002 | Applications need to establish trust between entities that operate components of the application. Such trust relationships are necessary so that applications can be assured that entities are who they say they are, and therefore trust the source and data it receives. | 4.002 | Applications shall verify that, for each entity on which an application component is installed, that entity is trusted by the provider of the application. |
| 4.003 | Applications shall be able to digitally sign all messages sent between entities. | ||
| 4.004 | Applications shall be able to verify the digital signature of received messages. | ||
| 4.005 | Digital signatures used to ensure trust shall be generated independently of the application sending the message to be signed. | ||
| N4.003 | Applications need to revoke the trust relationship they have between entities when necessary. A trusted entity may operate in a fashion that indicates it should no longer be trusted, in which case applications must have a way of revoking that trust. | 4.006 | Applications shall identify entities that provide messages to the application that are improperly formatted. |
| 4.007 | Applications shall identify entities that provide messages to the application that are logically inconsistent. | ||
| 4.008 | Applications shall revoke personal trust (trust by the application) when a repeated pattern of messages from a given entity falls outside of the applications tolerances. | ||
| 4.009 | Applications shall be able to report suspicious behavior to third party authentication providers. | ||
| 4.010 | Applications shall be able to accept messages from the third party authentication provider that identifies entities unworthy of trust. | ||
| 4.011 | Applications shall be able to revoke trust between itself and an entity if that entity is identified by the third party authentication provider as untrustworthy. | ||
| N4.004 | All participants in the Connected Vehicle Environment need to operate on a common time base. Coordination of time between the entities that operate applications as well as those providing Core services prevents internal errors and enables time-sensitive interactions between application components. | 4.012 | All applications shall use the same time source as the basis for timing. |
| N4.007 | Data Distribution needs to provide a mechanism for data consumers to request data that is produced by data providers. This is a single request for a subscription to a certain type of data, and subsequent modification of the request to change data types or subscription parameters. Parameters include data frequency, type and location of where the data was generated. This enables the distribution of anonymously-provided data to interested data consumers, without requiring them to enter into a relationship with data providers. Request formats need to provide data consumers with the ability to differentiate and receive only the types of data they requested. For example this includes data type, geographic range, frequency and sampling rate. This request method supports a wide variety of user needs, from planners requesting all traffic data all the time, to traveler information services requesting a subset of traffic data, to weather information services only interested in windshield wiper status for vehicles in a specific area. | 4.019 | Data Distribution shall maintain a list of data subscriptions. |
| 4.020 | Data Distribution shall provide a mechanism for subscriptions to select based on geographic area and data type. | ||
| 4.021 | Data Distribution shall provide a mechanism for applications to specify a maximum frequency for data reception. | ||
| 4.022 | Data Distribution shall provide a mechanism for applications to specify a sampling rate for data packages (e.g., for every 10 elements of one type, give me only 1). | ||
| 4.023 | Data Distribution shall provide a mechanism for applications to modify data subscriptions. | ||
| N4.008 | Data Distribution needs to supply information to data providers enabling them to transmit data to interested data consumers. At a minimum, data characteristics need to include type, frequency and location where data was generated, so that users that have requested data (see need data request) can differentiate between available data. This need enables data providers to direct the data they create to data consumers, and serves as the provider-side corollary to the data request need. This supports a variety of applications, including those focused on the center provision of data to users. It also serves as the answer to the mobile entity's question of "I have data, how do I provide it and to whom?" | 4.024 | Data Distribution shall be able to accept data from applications. |
| 4.025 | Data Distribution shall inform other applications of its ability to acquire and redistribute data. | ||
| 4.026 | Data Distribution shall categorize data it receives according to source type and location. | ||
| 4.027 | Data Distribution shall be able to maintain source type and location information along with data contents. | ||
| N4.009 | Data Distribution needs to provide a mechanism to distribute data it receives. Data Distribution needs to provide this distribution mechanism, rather than relying on individual provider-consumer relationships, because multiple consumers may want access to the same data. By having Data Distribution distribute the data, data creators are relieved of the need to transmit the data multiple times. Also, some data that may be critical to the proper functioning of mandatory applications, such as data supporting geo-location of users (position corrections), time base data and roadway geometry data, all of which likely comes from a single source and needs to be distributed to large numbers of users. Additionally, mobile users may interact over resource-constrained communication links, so Core-provided data redistribution reduces the potential load on those links. | 4.030 | Data Distribution shall examine the data it receives and compare it to the subscriptions it maintains. |
| 4.031 | Data Distribution shall provide the data it receives that match subscriptions to the subscriber, contingent on the subscriber's ability to receive the data it has subscribed to. | ||
| N4.010 | Data Distribution needs to connect to the Internet. This allows Data Distribution to provide services to any entity capable of connecting to the Internet. | 4.032 | Data Distribution shall provide all of its services through the Internet. |
| N4.011 | Probe Data Management needs to modify probe data generation and transmission rates and content. This helps manage the available bandwidth at the roadside in congested areas, and also leaves open the possibility of probe data enhancements that only apply to limited geographic areas and can be enabled in those places. | 4.028 | Probe Data Management shall be able to modify probe data transmission parameters. |
| 4.029 | Probe Data Management shall be able to modify probe data generation parameters. | ||
| N4.012 | Data Distribution needs to provide the information necessary for applications that wish to communicate with a group of entities in a specific area to do so. This capability enables applications to target those in a specific area for information they wish to distribute without having to send individual messages to each recipient. Examples of applications that might use this include Amber Alerts, traffic information, and air quality alerts. | 4.033 | Data Distribution shall provide a mechanism for applications to provide a message to be distributed over an application-specified area. |
| 4.034 | Data Distribution message specifications shall include geographic area, activation time, repeat frequency. | ||
| 4.035 | Data Distribution shall maintain a listing of communications devices that can be used for geographic broadcast (including base location, range and availability). | ||
Related Sources
- Core System Concept of Operations (ConOps), Final revE, 10/24/2011
- SAE J3067- Candidate Improvements to Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) Message Set Dictionary (SAE J2735)Using Systems Engineering Methods, 8/15/2014
Security
In order to participate in this application, each physical object should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Physical Object Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Object | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability | Security Class |
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | ||||
In order to participate in this application, each information flow triple should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Information Flow Security | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Destination | Information Flow | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability |
| Basis | Basis | Basis | |||
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | |||||