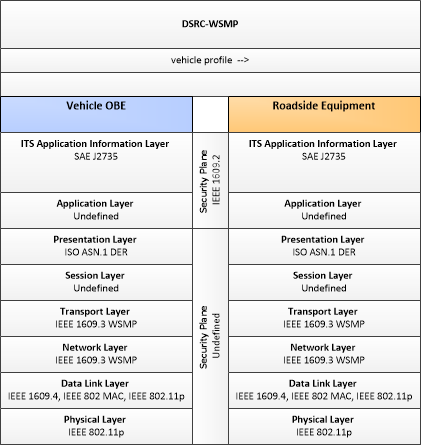
Type: Mobility
Groups:- Transit
Intermittent Bus Lanes
The Intermittent Bus Lane (IBL) application provides dedicated bus lanes during peak demand times to enhance transit operations mobility. IBL consists of a lane that can change its status from regular lane (accessible for all vehicles) to bus lane, for the time strictly necessary for a bus or set of buses to pass. The status of the IBL is communicated to drivers using roadside message signs and through in-vehicle signage. The creation and removal of dedicated bus lanes is managed through coordination between traffic and transit centers.
Enterprise
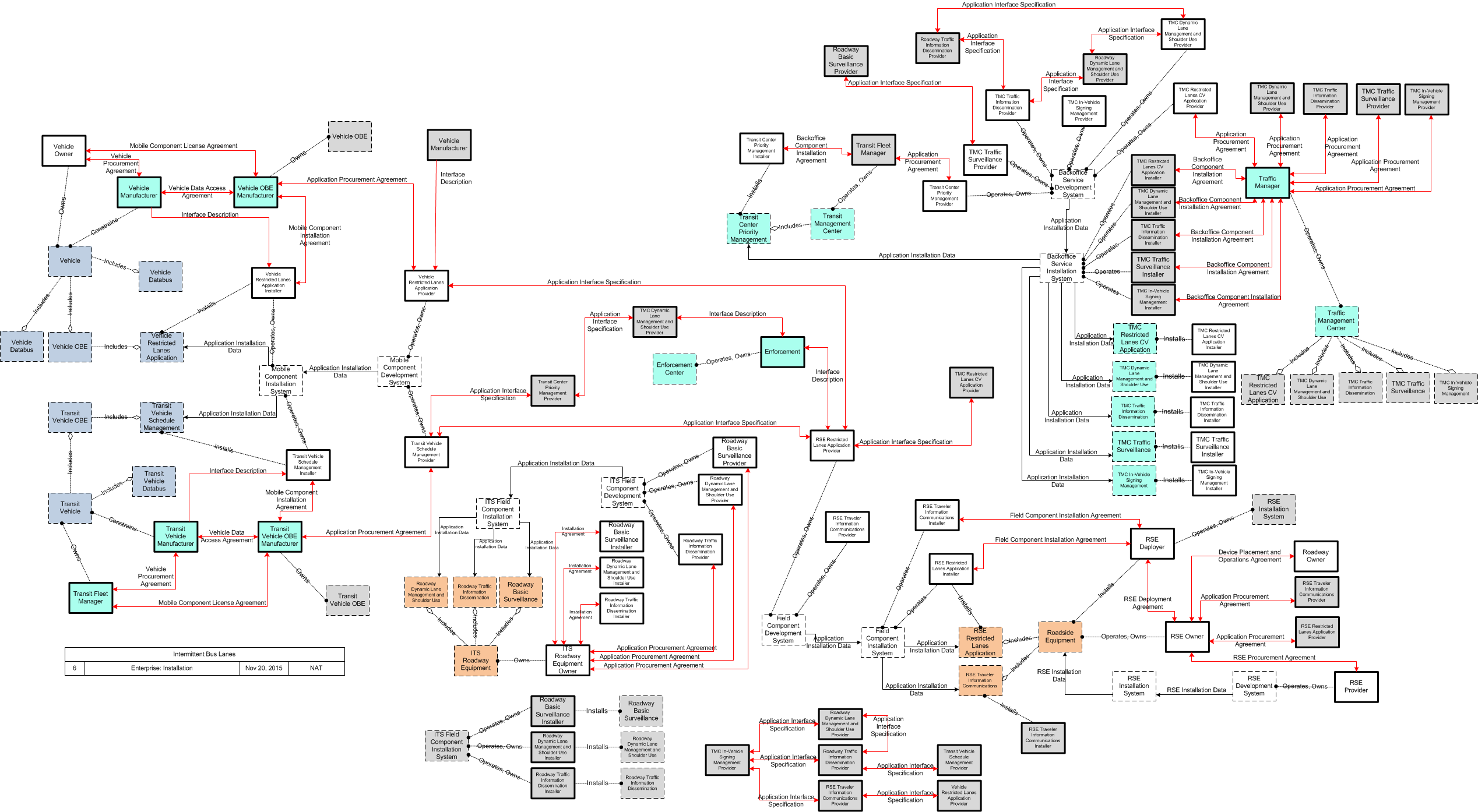
SVG Diagrams: Installation Operations Maintenance Certification
PNG Diagrams: Installation Operations Maintenance Certification
Business Interaction Matrix:
| Intermittent Bus Lanes Operations Stage | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Owner | Driver | Vehicle OBE Owner | Roadway Owner | RSE Owner | RSE Operator | ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Operator | Transit Vehicle Operator | Traffic Manager | RSE Restricted Lanes Application Provider | Enforcement | Transit Fleet Manager | Vehicle Restricted Lanes Application Provider | Transit Vehicle Schedule Management Provider | |
| Vehicle Owner | Vehicle Usage Agreement | Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||
| Driver | Vehicle Usage Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation of Information Provision | ||||||||||||
| Vehicle OBE Owner | Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation of Data Provision | ||||||||||||
| Roadway Owner | Service Delivery Agreement | ||||||||||||||
| RSE Owner | Service Delivery Agreement | Operations Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Information Provision Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | ||||||||
| RSE Operator | Expectation of Data Provision | Operations Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | ||||||||||||
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Information Exchange Agreement | Operations Agreement | |||||||||||||
| ITS Roadway Operator | Expectation of Information Provision | Operations Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | |||||||||||
| Transit Vehicle Operator | Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation of Information Provision | Vehicle Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||
| Traffic Manager | Information Exchange Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Information Provision Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | |||||||||||
| RSE Restricted Lanes Application Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||
| Enforcement | Information Provision Agreement | Information Provision Agreement | |||||||||||||
| Transit Fleet Manager | Information Exchange Agreement | Vehicle Usage Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | |||||||||||
| Vehicle Restricted Lanes Application Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||
| Transit Vehicle Schedule Management Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||
Includes Enterprise Objects:
| Enterprise Object | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Certification Entity | The body that determines whether an application may be deployed and operated in the Connected Vehicle Environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with application type. For example, applications with human safety component (crash avoidance, movement assistance etc.) may have stringent requirements and extensive testing in a variety of conditions, while applications that provide strictly mobility functionality may have far less testing requirements; possibly as little as just making sure the application doesn't interfere with any other applications. |
| Device Certification Entity | The body that determines whether a device may be deployed and operated in the Connected Vehicle Environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with device type. |
| Driver | The 'Driver' represents the person that operates a vehicle on the roadway. Included are operators of private, transit, commercial, and emergency vehicles where the interactions are not particular to the type of vehicle (e.g., interactions supporting vehicle safety applications). The Driver originates driver requests and receives driver information that reflects the interactions which might be useful to all drivers, regardless of vehicle classification. Information and interactions which are unique to drivers of a specific vehicle type (e.g., fleet interactions with transit, commercial, or emergency vehicle drivers) are covered by separate objects. |
| Enforcement | Agencies that are responsible for identifying and reporting violations of roadway regulations, including emissions, traffic violations, toll violations, etc. |
| Federal Regulatory | Federal regulatory bodies that have legal authority to control and/or provide input to policies regulating transportation infrastructure and operations. This includes entities such as the Federal Communications Commission and US Department of Transportation. |
| ITS Certification Entity | The body that determines whether an ITS device or application may be deployed and operated in the transportation environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with device and application type. Typically not a formal body, assigned on a project-by-project basis depending on the type of infrastructure involved. Since ITS projects are locally-focused (typically state or smaller), the entities that are part of this body are typically those with operational jurisdiction where the ITS is installed (e.g., state or local DOTs, state or local maintenance managers etc.) |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | The entity that owns the Roadway ITS equipment. |
| ITS Roadway Operator | The entity that operates the Roadway ITS equipment. |
| Roadway Basic Surveillance Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Basic Surveillance Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Basic Surveillance Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Roadway Dynamic Lane Management and Shoulder Use Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Dynamic Lane Management and Shoulder Use Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Dynamic Lane Management and Shoulder Use Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Roadway Owner | The owner of the roadway proximate to which roadside equipment will be/is installed. |
| Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Deployer | The entity responsible for the deployment, operations and maintenance of roadside equipment. |
| RSE Operator | The entity that operates roadside equipment in the transportation environment. |
| RSE Owner | The owner of roadside equipment. |
| RSE Provider | The "RSE Provider" is the entity that develops and (presumably) sells roadside equipment to other entities for deployment and research. |
| RSE Restricted Lanes Application Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Restricted Lanes Application Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Restricted Lanes Application Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Traveler Information Communications Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Traveler Information Communications Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Traveler Information Communications Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| State Regulatory | State regulatory bodies that have legal authority to control and/or provide input to policies regulating vehicles, transportation infrastructure and operations. This includes entities like Departments of Motor Vehicles, property tax authorities and tolling agencies. |
| TMC Dynamic Lane Management and Shoulder Use Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Dynamic Lane Management and Shoulder Use Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Dynamic Lane Management and Shoulder Use Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| TMC In-Vehicle Signing Management Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC In-Vehicle Signing Management Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC In-Vehicle Signing Management Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| TMC Restricted Lanes CV Application Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Restricted Lanes CV Application Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Restricted Lanes CV Application Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| TMC Traffic Surveillance Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Traffic Surveillance Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Traffic Surveillance Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Traffic Manager | The entity responsible for the management of traffic, both freeway and arterial. |
| Transit Center Priority Management Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Transit Center Priority Management Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Transit Center Priority Management Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Transit Fleet Manager | The agency or organization that operates transit vehicles. This includes administration, routing, driver instruction, maintenance and any other responsibilities associated with the operations and maintenance of a transit system. |
| Transit Vehicle Manufacturer | The entity which builds transit vehicles. This entity is complementary to the Vehicle Manufacturer entity in that it represents those aspects of vehicle manufacture which are unique to transit vehicles. |
| Transit Vehicle OBE Manufacturer | The Transit Vehicle OBE Manufacturer is the provider of the transit vehicle on-board equipment. This entity may design and build the OBE, or may integrate other components to form the OBE, or may use some combination of approaches to provide the on-board equipment. Since the OBE could be aftermarket, retrofit, built-in or nomadic, this entity is the one that builds whatever that-is. In some cases it may be a smart phone manufacturer, or in others a top tier parts supplier, or any other entity in the production chain, depending on the device and commercial vehicle in question. |
| Transit Vehicle Operator | The 'Transit Vehicle Operator' represents the person that receives and provides additional information that is specific to operating the ITS functions in all types of transit vehicles. The information received by the operator would include status of on-board systems. Additional information received depends upon the type of transit vehicle. In the case of fixed route transit vehicles, the Transit Vehicle Operator would receive operator instructions that might include actions to take to correct schedule deviations. In the case of flexible fixed routes and demand response routes the information would also include dynamic routing or passenger pickup information. |
| Transit Vehicle Schedule Management Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Transit Vehicle Schedule Management Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Transit Vehicle Schedule Management Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Vehicle Manufacturer | The entity that builds, assembles, verifies and validates the Vehicle in which the Vehicle OBE will eventually operate. |
| Vehicle OBE Manufacturer | The entity that builds, assembles, verifies and validates the Vehicle OBE. This can be an OEM-equipped OBE, retrofit or aftermarket equipment. |
| Vehicle OBE Owner | The entity, individual, group or corporation that owns the Vehicle On-Board equipment. This could be the same as the Vehicle Owner, but it could be a third part that licenses the use of the OBE to the Owner. |
| Vehicle Owner | The individual, group of individuals or corporate entity that is identified as the registered owner of the Vehicle under state law. |
| Vehicle Restricted Lanes Application Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Restricted Lanes Application Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Restricted Lanes Application Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
Includes Resources:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Component Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of an application component. Certification Requirements must be met in order for an application to be installed in the CVE. |
| Backoffice Service Development System | The systems used to develop backoffice (center) hardware and software components of applications. |
| Backoffice Service Installation System | The systems used to install and configure backoffice (center) hardware and software components. |
| Backoffice Service Maintenance System | The systems used to maintain and upgrade backoffice (center) hardware and software components. |
| Device Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of a connected vehicle device. Certification Requirements must be met in order for the device to be granted the credentials necessary to operate in the Connected Vehicle Environment. |
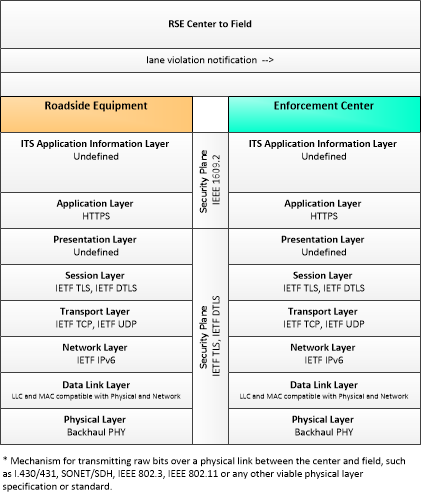
| Enforcement Center | The 'Enforcement Center' represents the systems that receive reports of violations detected by various ITS facilities including individual vehicle emissions, lane violations, toll violations, CVO violations, etc. |
| Field Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the field component of the application. |
| Field Component Installation System | The system used to install a field component of a connected vehicle application. |
| Field Component Maintenance System | The system used to install and configure changes and updates to the field component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| ITS Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of an ITS device or ITS application. Applicability varies with jurisdictions, but typically devices and applications must meet pre-defined acceptance criteria prior to usage in the transportation environment. |
| ITS Field Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the ITS field component of the application. |
| ITS Field Component Installation System | The system used to install a field component of a connected vehicle application. |
| ITS Field Component Maintenance System | The system used to install and configure changes and updates to the ITS field component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway itself. In CVRIA, this physical object represents all of the other ITS field equipment that interfaces with and supports the Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE). This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| Mobile Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the mobile component of the application. |
| Mobile Component Installation System | The system that interacts with the Vehicle OBE other mobile device and installs the mobile component of the application. |
| Mobile Component Maintenance System | The system used to configure changes and updates to the mobile component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| Roadside Equipment | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Roadway Basic Surveillance | "Roadway Basic Surveillance" monitors traffic conditions using fixed equipment such as loop detectors and CCTV cameras. |
| Roadway Dynamic Lane Management and Shoulder Use | "Roadway Dynamic Lane Management and Shoulder Use" includes the field equipment, physical overhead lane signs and associated control electronics that are used to manage and control specific lanes and/or the shoulders. This equipment can be centrally controlled by a traffic management center or it can be autonomous and monitor traffic conditions and demand along the roadway and determine how to change the lane controls to respond to current conditions. Lane controls can be used to change the lane configuration of the roadway, reconfigure intersections and/or interchanges, allow use of shoulders as temporary travel lanes, designate lanes for use by special vehicles only, such as buses, high occupancy vehicles (HOVs), vehicles attending a special event, etc. and/or prohibit or restrict types of vehicles from using particular lanes. Guidance and information for drivers can be posted on dynamic message signs. |
| Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination | "Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination" includes field elements that provide information to drivers, including dynamic message signs and highway advisory radios. |
| RSE Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the roadside equipment. |
| RSE Installation System | The system used to install and configure the roadside equipment. |
| RSE Maintenance System | The system used to configure changes and updates to the roadside equipment. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the RSE's configuration and performance. |
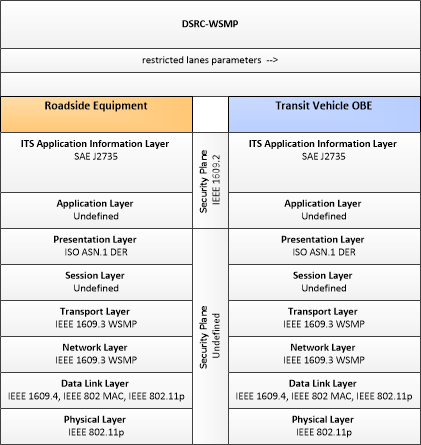
| RSE Restricted Lanes Application | The "RSE Restricted Lanes Application" uses short range communications to monitor and manage dynamic and static restricted lanes. It collects vehicle profile information from vehicles entering the lanes and monitors vehicles within the lanes, providing aggregate data to the back office center. It provides lane restriction information and signage data to the vehicles and optionally identifies vehicles that violate the current lane restrictions. These functions are performed based on operating parameters provided by the back office managing center(s). |
| RSE Traveler Information Communications | "RSE Traveler Information Communications" includes field elements that distribute information to vehicles for in-vehicle display. The information may be provided by a center (e.g., variable information on traffic and road conditions in the vicinity of the field equipment) or it may be determined and output locally (e.g., static sign information and signal phase and timing information). This includes the interface to the center or field equipment that controls the information distribution and the short range communications equipment that provides information to passing vehicles. |
| TMC Dynamic Lane Management and Shoulder Use | "TMC Dynamic Lane Management and Shoulder Use" remotely monitors and controls the system that is used to dynamically manage travel lanes, including temporary use of shoulders as travel lanes. It monitors traffic conditions and demand measured in the field and determines when the lane configuration of the roadway should be changed, when intersections and/or interchanges should be reconfigured, when the shoulders should be used for travel (as a lane), when lanes should be designated for use by special vehicles only, such as buses, high occupancy vehicles (HOVs), vehicles attending a special event, etc. and/or when types of vehicles should be prohibited or restricted from using particular lanes. It controls the field equipment used to manage and control specific lanes and the shoulders. It also can automatically notify the enforcement agency of lane control violations. |
| TMC In-Vehicle Signing Management | "TMC In-Vehicle Signing Management" controls and monitors RSEs that support in-vehicle signing. Sign information that may include static regulatory, service, and directional sign information as well as variable information such as traffic and road conditions can be provided to the RSE, which uses short range communications to send the information to in-vehicle equipment. Information that is currently being communicated to passing vehicles and the operational status of the field equipment is monitored by this application. The operational status of the field equipment is reported to operations personnel. |
| TMC Restricted Lanes CV Application | "TMC Restricted Lanes CV Application" manages dynamic lanes for connected vehicles. The application provides the back office functions and supports the TMC operator in establishing and managing dynamic lanes using communications to manage lane use for connected vehicles. |
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination | "TMC Traffic Information Dissemination" disseminates traffic and road conditions, closure and detour information, incident information, driver advisories, and other traffic-related data to other centers, the media, and driver information systems. It monitors and controls driver information system field equipment including dynamic message signs and highway advisory radio, managing dissemination of driver information through these systems. |
| TMC Traffic Surveillance | "TMC Traffic Surveillance" remotely monitors and controls traffic sensors and surveillance (e.g., CCTV) equipment, and collects, processes and stores the collected traffic data. Current traffic information and other real-time transportation information is also collected from other centers. The collected information is provided to traffic operations personnel and made available to other centers. |
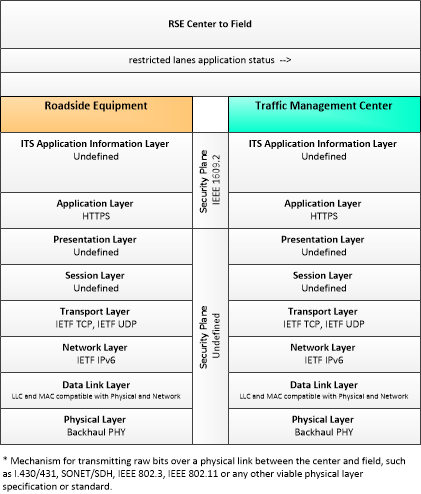
| Traffic Management Center | The 'Traffic Management Center' monitors and controls traffic and the road network. It represents centers that manage a broad range of transportation facilities including freeway systems, rural and suburban highway systems, and urban and suburban traffic control systems. It communicates with ITS Roadway Equipment and Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE) to monitor and manage traffic flow and monitor the condition of the roadway, surrounding environmental conditions, and field equipment status. It manages traffic and transportation resources to support allied agencies in responding to, and recovering from, incidents ranging from minor traffic incidents through major disasters. |
| Transit Center Priority Management | "Transit Center Priority Management" monitors transit schedule performance and generates requests for transit priority on routes and at certain intersections. It may coordinate with the Traffic Management Center to provide transit priority along the selected route, including allocation of dynamic lanes and granting signal priority. It also coordinates with the Transit Vehicle OBE to monitor and manage local transit signal priority requests at individual intersections. |
| Transit Management Center | The 'Transit Management Center' manages transit vehicle fleets and coordinates with other modes and transportation services. It provides operations, maintenance, customer information, planning and management functions for the transit property. It spans distinct central dispatch and garage management systems and supports the spectrum of fixed route, flexible route, paratransit services, transit rail, and bus rapid transit (BRT) service. The physical object's interfaces allow for communication between transit departments and with other operating entities such as emergency response services and traffic management systems. |
| Transit Vehicle | The vehicle that provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support safe and efficient movement of passengers. This includes buses, paratransit vehicles, light rail vehicles, other vehicles designed to carry passengers, and supervisory vehicles. |
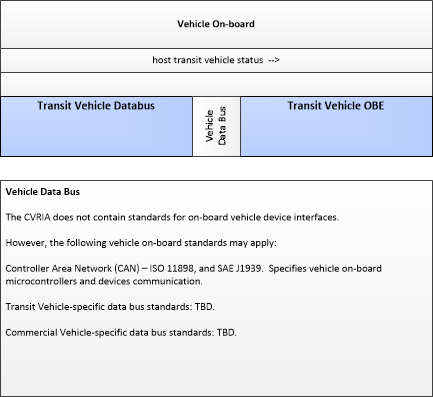
| Transit Vehicle Databus | The 'Transit Vehicle Databus' represents the vehicle databus that interfaces with on-board equipment on a transit vehicle. It is a specialized and extended form of the Vehicle Databus that is subject to different vehicle databus standards and hosts a broad range of components that are unique to a transit vehicle including the farebox and associated electronics, passenger counters, and transit security systems. As a specialized form of the Vehicle Databus, it also provides access to the general-purpose sensors (e.g., radars, cameras), GPS, drive train monitoring and control systems, and vehicle safety features that support connected vehicle applications. The Transit Vehicle may represent a bus, paratransit vehicle, light rail vehicle, or other vehicle designed to carry passengers. In CVRIA, the 'Transit Vehicle Databus' is used to represent the onboard interactions between the Transit Vehicle OBE and the other systems included in a host transit vehicle. |
| Transit Vehicle OBE | The Transit Vehicle On-Board equipment (OBE) resides in a transit vehicle and provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support safe and efficient movement of passengers. The types of transit vehicles containing this physical object include buses, paratransit vehicles, light rail vehicles, other vehicles designed to carry passengers, and supervisory vehicles. It collects ridership levels and supports electronic fare collection. It supports a traffic signal prioritization function that communicates with the roadside physical object to improve on-schedule performance. Automated vehicle location enhances the information available to the transit operator enabling more efficient operations. On-board sensors support transit vehicle maintenance. The physical object supports on-board security and safety monitoring. This monitoring includes transit user or vehicle operator activated alarms (silent or audible), as well as surveillance and sensor equipment. The surveillance equipment includes video (e.g. CCTV cameras), audio systems and/or event recorder systems. It also furnishes travelers with real-time travel information, continuously updated schedules, transfer options, routes, and fares. In CVRIA, a separate 'Vehicle OBE' physical object supports the general V2V and V2I safety applications and other applications that apply to all vehicles, including transit vehicles. The Transit Vehicle OBE supplements these general capabilities with capabilities that are specific to transit vehicles. |
| Transit Vehicle Schedule Management | "Transit Vehicle Schedule Management" monitors schedule performance and identifies corrective actions when a deviation is detected. It provides two-way communication between the transit vehicle and center, enabling the center to communicate with the vehicle operator and monitor on-board systems. |
| Vehicle | The conveyance that provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support efficient, safe, and convenient travel. These functions reside in general vehicles including personal automobiles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, or other vehicle types. |
| Vehicle Databus | The 'Vehicle Databus' represents the interface to the vehicle databus (e.g., CAN, LIN, Ethernet/IP, FlexRay, and MOST) that may enable communication between the Vehicle OBE and other vehicle systems to support connected vehicle applications. The vehicle system statuses and/or sensor outputs available on the databus will vary based on the equipment installed on the vehicle and availability on databus. System statuses and sensor outputs may include select vehicle systems and sensors such as accelerometers, yaw rate sensors, and GPS derived location and timing information. In CVRIA, this physical object is used to represent the onboard interactions between the Vehicle OBE and the other systems included in a host vehicle. Note that the vehicle databus interface is not standardized across all vehicle classes. Also, some Vehicle OBE implementations will not have access to the vehicle databus. See 'Vehicle OBE' for more information. |
| Vehicle OBE | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
| Vehicle Restricted Lanes Application | The "Vehicle Restricted Lanes Application" monitors and reports its own operating parameters and communicates with roadside equipment to safely enter, operate within, and exit eco-lanes and other controlled-access lanes. |
Includes Roles:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Certifies | An Enterprise verifies that a target Resource meets relevant performance, functional, environmental and quality requirements. |
| Constrains | A Resource or Enterprise applies requirements, constraints and associated tests to another Resource. |
| Installs | An Enterprise performs the initial delivery, integration and configuration of the target Resource. |
| Maintains | An Enterprise administers the hardware and software that comprise the target Resource. |
| Member | An Enterprise is part of another larger, target Enterprise. |
| Operates | An Enterprise controls the functionality and state of the target Resource. An Enterprise that Operates a resource is considered Responsible. |
| Owns | An Enterprise has financial ownership and control over the Resource. An Enterprise that Owns a resource is considered Accountable. |
Includes Coordination:
| Coordination | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Application Installation Data | Information Sharing | Data needed to install the application, including the application executable code and any configuration data. Unidirectional flow. |
| Application Interface Specification | Agreement | The definition of an interface between two application components that operate on two distinct pieces of hardware. The Application Interface Specification is specific to the application in question. |
| Application Maintenance Data | Information Sharing | Data used to facilitate the upgrade, patching and general health maintenance of an application component. |
| Application Performance Data | Information Sharing | Data used to characterize application performance, including such measures as availability, known errors and known uses. |
| Application Procurement Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity provides a copy of an application component to another entity. This component is capable of being installed and functioning, according to its requirements that passed through the application's certification process. |
| Application Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity that controls an application component's use gives the other entity the necessary tools and permission to operate that application or application component. |
| Backoffice Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one party permission to install a backoffice application component on a center-based device controlled by the other party. |
| Backoffice Component Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the backoffice component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Device Placement and Operations Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that enables the controller of a physical device to install it (so as to make it operational) at a fixed location controlled by another entity. |
| Expectation of Data Provision | Expectation | An expectation where one party believes another party will provide data on a regular and recurring basis, and that that data will be useful to the receiver in the context of the receiver's application. This thus includes some expectation of data fields, timeliness, quality, precision and similar qualities of data. |
| Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation | An expectation where one party believes another party will provide it information whenever such information is likely relevant to the recipient. |
| Field Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one party permission to install a field application component on a roadside device controlled by the other party. |
| Field Component Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the field component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Includes | Includes | Indicates that one component is entirely contained within another component. |
| Information Exchange Agreement | Agreement | An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. |
| Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Agreement | An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. This also includes a specification for action that shall, should or may be taken by one party in response to this information. |
| Information Provision Agreement | Agreement | An agreement where one party agrees to provide information to another party. This is a unidirectional agreement. |
| Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity installs an application component on a device controlled by another entity. |
| Interface Description | Agreement | Documentation of the interface between two systems, where one system does not have an application component that is part of the application, but does provide and/or receive data and/or information that is used by or sourced from the application. In many cases this is an existing interface used by the application, so the description of the interface already exists and is imposed by the terminator. |
| Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of a system under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that states one entity will provide data related to maintenance of an application component to the other entity. |
| Mobile Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon the controller of OBE gives another party permission to install, configure and make operational a component that enables the mobile portion of an application. |
| Mobile Component License Agreement | Agreement | An end-user license agreement allowing the operator of the mobile device to use the mobile application component that is part of the application in question. |
| Mobile Component Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the mobile component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Operations Agreement | Agreement | An agreement where one entity agrees to operate a device or application on behalf of another, device/application controlling entity. |
| RSE Deployment Agreement | Agreement | Agreement to install, configure and make operational roadside equipment, between the provider of that equipment and the entity that controls access to the roadside. May define locations, expectation of power provision, backhaul responsibility and installation restrictions. |
| RSE Installation Data | Information Sharing | Data necessary to configure and make RSE operational. Uni-directional. |
| RSE Maintenance Data | Information Sharing | Data necessary to modify the operational configuration of RSE; assumes RSE is already configured. Uni-directional. |
| RSE Performance Data | Information Sharing | Data that includes metrics of RSE performance. Could include fields such as uptime, packets received/transmitted, distance vector from which packets received, as well as application-specific performance measures. |
| RSE Procurement Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity provides roadside equipment to another entity. The RSE is capable of being installed and functioning, according to its requirements that passed through the device's certification process. |
| Service Delivery Agreement | Agreement | A relationship where one party agrees to provide a service to the other party. This agreement may specify the expected performance of this service in terms of availability and/or actions/time-type performance specifications. |
| Vehicle Data Access Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereby the party that controls access to on-board vehicle data grants another party the right and ability to access that data. Includes the conditions under which data may be accessed, and specifies the mechanisms, including physical and functional access methods, data formats and any other considerations necessary for the accessing party to acquire data. May also include caveats regarding responsibility for data quality and responsibility for use of the data. |
| Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one entity permission to use a Vehicle OBE that the other party controls. |
| Vehicle Procurement Agreement | Agreement | The exchange of a vehicle for compensation. One entity purchases the vehicle from the other. |
| Vehicle Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement between the owner of a vehicle and a prospective operator, whereupon the owner allows the operator to use the vehicle. |
| Warranty | Agreement | A guarantee or promise made by one entity to another, that provides assurance of the functionality and performance over time of an application component. |
Functional
Includes Processes:
Includes Data Flows:
Physical
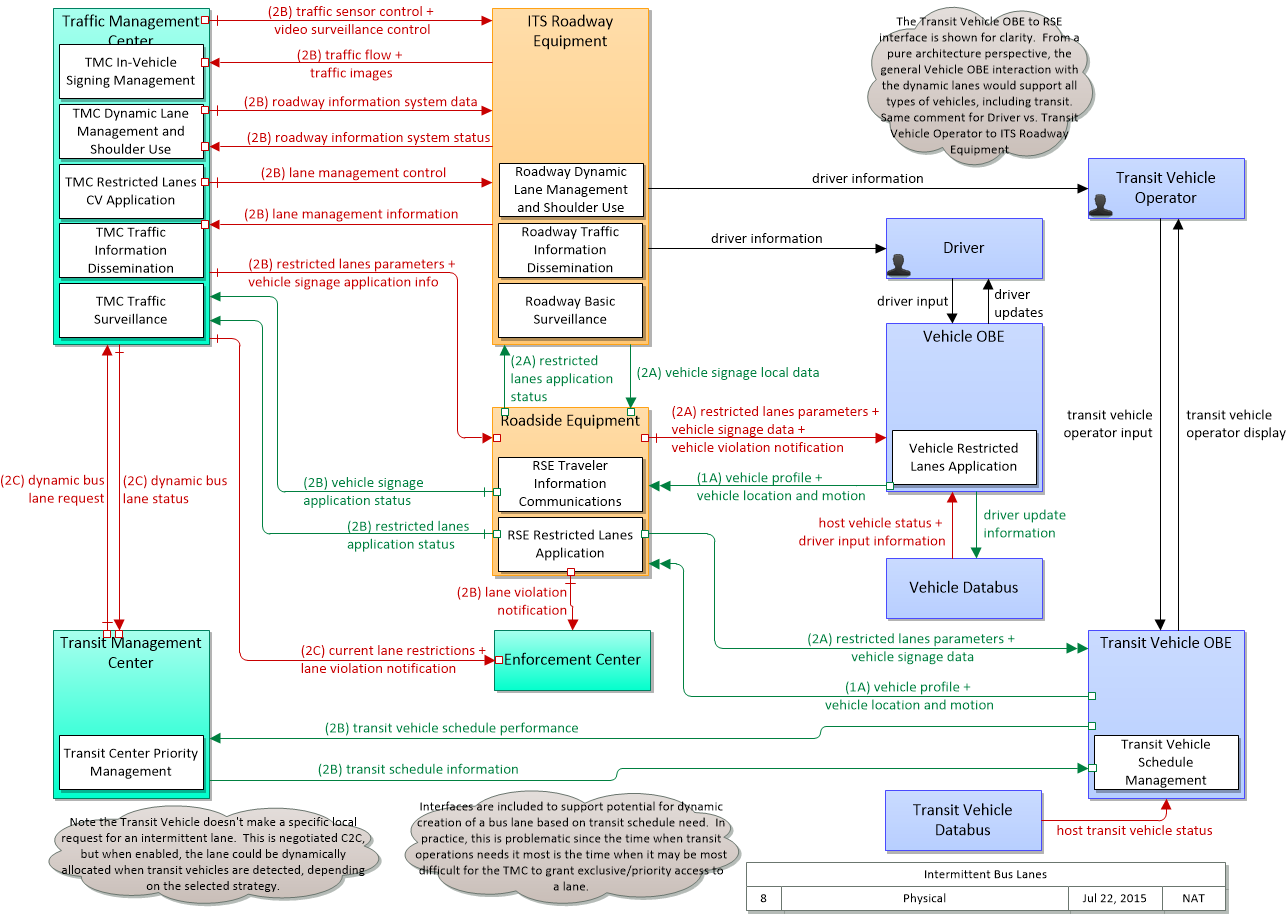
SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
Includes Physical Objects:
| Physical Object | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Driver | Vehicle | The 'Driver' represents the person that operates a vehicle on the roadway. Included are operators of private, transit, commercial, and emergency vehicles where the interactions are not particular to the type of vehicle (e.g., interactions supporting vehicle safety applications). The Driver originates driver requests and receives driver information that reflects the interactions which might be useful to all drivers, regardless of vehicle classification. Information and interactions which are unique to drivers of a specific vehicle type (e.g., fleet interactions with transit, commercial, or emergency vehicle drivers) are covered by separate objects. |
| Enforcement Center | Center | The 'Enforcement Center' represents the systems that receive reports of violations detected by various ITS facilities including individual vehicle emissions, lane violations, toll violations, CVO violations, etc. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Field | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway itself. In CVRIA, this physical object represents all of the other ITS field equipment that interfaces with and supports the Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE). This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| Roadside Equipment | Field | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Traffic Management Center | Center | The 'Traffic Management Center' monitors and controls traffic and the road network. It represents centers that manage a broad range of transportation facilities including freeway systems, rural and suburban highway systems, and urban and suburban traffic control systems. It communicates with ITS Roadway Equipment and Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE) to monitor and manage traffic flow and monitor the condition of the roadway, surrounding environmental conditions, and field equipment status. It manages traffic and transportation resources to support allied agencies in responding to, and recovering from, incidents ranging from minor traffic incidents through major disasters. |
| Transit Management Center | Center | The 'Transit Management Center' manages transit vehicle fleets and coordinates with other modes and transportation services. It provides operations, maintenance, customer information, planning and management functions for the transit property. It spans distinct central dispatch and garage management systems and supports the spectrum of fixed route, flexible route, paratransit services, transit rail, and bus rapid transit (BRT) service. The physical object's interfaces allow for communication between transit departments and with other operating entities such as emergency response services and traffic management systems. |
| Transit Vehicle Databus | Vehicle | The 'Transit Vehicle Databus' represents the vehicle databus that interfaces with on-board equipment on a transit vehicle. It is a specialized and extended form of the Vehicle Databus that is subject to different vehicle databus standards and hosts a broad range of components that are unique to a transit vehicle including the farebox and associated electronics, passenger counters, and transit security systems. As a specialized form of the Vehicle Databus, it also provides access to the general-purpose sensors (e.g., radars, cameras), GPS, drive train monitoring and control systems, and vehicle safety features that support connected vehicle applications. The Transit Vehicle may represent a bus, paratransit vehicle, light rail vehicle, or other vehicle designed to carry passengers. In CVRIA, the 'Transit Vehicle Databus' is used to represent the onboard interactions between the Transit Vehicle OBE and the other systems included in a host transit vehicle. |
| Transit Vehicle OBE | Vehicle | The Transit Vehicle On-Board equipment (OBE) resides in a transit vehicle and provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support safe and efficient movement of passengers. The types of transit vehicles containing this physical object include buses, paratransit vehicles, light rail vehicles, other vehicles designed to carry passengers, and supervisory vehicles. It collects ridership levels and supports electronic fare collection. It supports a traffic signal prioritization function that communicates with the roadside physical object to improve on-schedule performance. Automated vehicle location enhances the information available to the transit operator enabling more efficient operations. On-board sensors support transit vehicle maintenance. The physical object supports on-board security and safety monitoring. This monitoring includes transit user or vehicle operator activated alarms (silent or audible), as well as surveillance and sensor equipment. The surveillance equipment includes video (e.g. CCTV cameras), audio systems and/or event recorder systems. It also furnishes travelers with real-time travel information, continuously updated schedules, transfer options, routes, and fares. In CVRIA, a separate 'Vehicle OBE' physical object supports the general V2V and V2I safety applications and other applications that apply to all vehicles, including transit vehicles. The Transit Vehicle OBE supplements these general capabilities with capabilities that are specific to transit vehicles. |
| Transit Vehicle Operator | Vehicle | The 'Transit Vehicle Operator' represents the person that receives and provides additional information that is specific to operating the ITS functions in all types of transit vehicles. The information received by the operator would include status of on-board systems. Additional information received depends upon the type of transit vehicle. In the case of fixed route transit vehicles, the Transit Vehicle Operator would receive operator instructions that might include actions to take to correct schedule deviations. In the case of flexible fixed routes and demand response routes the information would also include dynamic routing or passenger pickup information. |
| Vehicle Databus | Vehicle | The 'Vehicle Databus' represents the interface to the vehicle databus (e.g., CAN, LIN, Ethernet/IP, FlexRay, and MOST) that may enable communication between the Vehicle OBE and other vehicle systems to support connected vehicle applications. The vehicle system statuses and/or sensor outputs available on the databus will vary based on the equipment installed on the vehicle and availability on databus. System statuses and sensor outputs may include select vehicle systems and sensors such as accelerometers, yaw rate sensors, and GPS derived location and timing information. In CVRIA, this physical object is used to represent the onboard interactions between the Vehicle OBE and the other systems included in a host vehicle. Note that the vehicle databus interface is not standardized across all vehicle classes. Also, some Vehicle OBE implementations will not have access to the vehicle databus. See 'Vehicle OBE' for more information. |
| Vehicle OBE | Vehicle | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
Includes Application Objects:
| Application Object | Description | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| Roadway Basic Surveillance | "Roadway Basic Surveillance" monitors traffic conditions using fixed equipment such as loop detectors and CCTV cameras. | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| Roadway Dynamic Lane Management and Shoulder Use | "Roadway Dynamic Lane Management and Shoulder Use" includes the field equipment, physical overhead lane signs and associated control electronics that are used to manage and control specific lanes and/or the shoulders. This equipment can be centrally controlled by a traffic management center or it can be autonomous and monitor traffic conditions and demand along the roadway and determine how to change the lane controls to respond to current conditions. Lane controls can be used to change the lane configuration of the roadway, reconfigure intersections and/or interchanges, allow use of shoulders as temporary travel lanes, designate lanes for use by special vehicles only, such as buses, high occupancy vehicles (HOVs), vehicles attending a special event, etc. and/or prohibit or restrict types of vehicles from using particular lanes. Guidance and information for drivers can be posted on dynamic message signs. | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination | "Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination" includes field elements that provide information to drivers, including dynamic message signs and highway advisory radios. | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| RSE Restricted Lanes Application | The "RSE Restricted Lanes Application" uses short range communications to monitor and manage dynamic and static restricted lanes. It collects vehicle profile information from vehicles entering the lanes and monitors vehicles within the lanes, providing aggregate data to the back office center. It provides lane restriction information and signage data to the vehicles and optionally identifies vehicles that violate the current lane restrictions. These functions are performed based on operating parameters provided by the back office managing center(s). | Roadside Equipment |
| RSE Traveler Information Communications | "RSE Traveler Information Communications" includes field elements that distribute information to vehicles for in-vehicle display. The information may be provided by a center (e.g., variable information on traffic and road conditions in the vicinity of the field equipment) or it may be determined and output locally (e.g., static sign information and signal phase and timing information). This includes the interface to the center or field equipment that controls the information distribution and the short range communications equipment that provides information to passing vehicles. | Roadside Equipment |
| TMC Dynamic Lane Management and Shoulder Use | "TMC Dynamic Lane Management and Shoulder Use" remotely monitors and controls the system that is used to dynamically manage travel lanes, including temporary use of shoulders as travel lanes. It monitors traffic conditions and demand measured in the field and determines when the lane configuration of the roadway should be changed, when intersections and/or interchanges should be reconfigured, when the shoulders should be used for travel (as a lane), when lanes should be designated for use by special vehicles only, such as buses, high occupancy vehicles (HOVs), vehicles attending a special event, etc. and/or when types of vehicles should be prohibited or restricted from using particular lanes. It controls the field equipment used to manage and control specific lanes and the shoulders. It also can automatically notify the enforcement agency of lane control violations. | Traffic Management Center |
| TMC In-Vehicle Signing Management | "TMC In-Vehicle Signing Management" controls and monitors RSEs that support in-vehicle signing. Sign information that may include static regulatory, service, and directional sign information as well as variable information such as traffic and road conditions can be provided to the RSE, which uses short range communications to send the information to in-vehicle equipment. Information that is currently being communicated to passing vehicles and the operational status of the field equipment is monitored by this application. The operational status of the field equipment is reported to operations personnel. | Traffic Management Center |
| TMC Restricted Lanes CV Application | "TMC Restricted Lanes CV Application" manages dynamic lanes for connected vehicles. The application provides the back office functions and supports the TMC operator in establishing and managing dynamic lanes using communications to manage lane use for connected vehicles. | Traffic Management Center |
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination | "TMC Traffic Information Dissemination" disseminates traffic and road conditions, closure and detour information, incident information, driver advisories, and other traffic-related data to other centers, the media, and driver information systems. It monitors and controls driver information system field equipment including dynamic message signs and highway advisory radio, managing dissemination of driver information through these systems. | Traffic Management Center |
| TMC Traffic Surveillance | "TMC Traffic Surveillance" remotely monitors and controls traffic sensors and surveillance (e.g., CCTV) equipment, and collects, processes and stores the collected traffic data. Current traffic information and other real-time transportation information is also collected from other centers. The collected information is provided to traffic operations personnel and made available to other centers. | Traffic Management Center |
| Transit Center Priority Management | "Transit Center Priority Management" monitors transit schedule performance and generates requests for transit priority on routes and at certain intersections. It may coordinate with the Traffic Management Center to provide transit priority along the selected route, including allocation of dynamic lanes and granting signal priority. It also coordinates with the Transit Vehicle OBE to monitor and manage local transit signal priority requests at individual intersections. | Transit Management Center |
| Transit Vehicle Schedule Management | "Transit Vehicle Schedule Management" monitors schedule performance and identifies corrective actions when a deviation is detected. It provides two-way communication between the transit vehicle and center, enabling the center to communicate with the vehicle operator and monitor on-board systems. | Transit Vehicle OBE |
| Vehicle Restricted Lanes Application | The "Vehicle Restricted Lanes Application" monitors and reports its own operating parameters and communicates with roadside equipment to safely enter, operate within, and exit eco-lanes and other controlled-access lanes. | Vehicle OBE |
Includes Information Flows:
| Information Flow | Description |
|---|---|
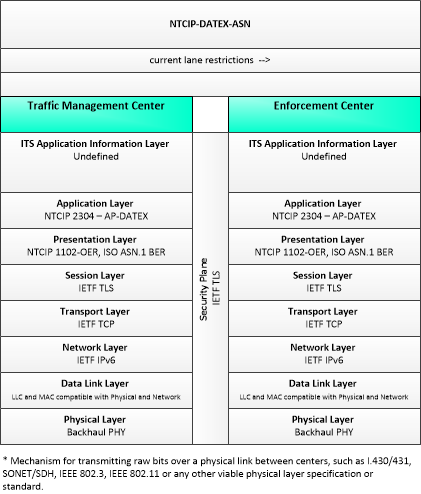
| current lane restrictions | Information provided to an enforcement agency that defines the current enforceable lane restrictions. It defines the location, duration, and restrictions for lanes that are reserved for the exclusive use of certain types of vehicles (e.g., transit vehicles) or vehicles that meet other qualifications (e.g., number of occupants, low emissions criteria). It identifies the lane(s), the start and stop locations, start and end times, vehicle restrictions, and speed limits. |
| driver information | Regulatory, warning, and guidance information provided to the driver while en route to support safe and efficient vehicle operation. |
| driver input | Driver input to the vehicle on-board equipment including configuration data, settings and preferences, interactive requests, and control commands. |
| driver input information | Driver input received from the driver-vehicle interface equipment via the vehicle bus. It includes configuration data, settings and preferences, interactive requests, and control commands for the connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| driver update information | Information provided to the driver-vehicle interface to inform the driver about current conditions, potential hazards, and the current status of vehicle on-board equipment. The flow includes the information to be presented to the driver and associated metadata that supports processing, prioritization, and presentation by the DVI as visual displays, audible information and warnings, and/or haptic feedback. |
| driver updates | Information provided to the driver including visual displays, audible information and warnings, and haptic feedback. The updates inform the driver about current conditions, potential hazards, and the current status of vehicle on-board equipment. |
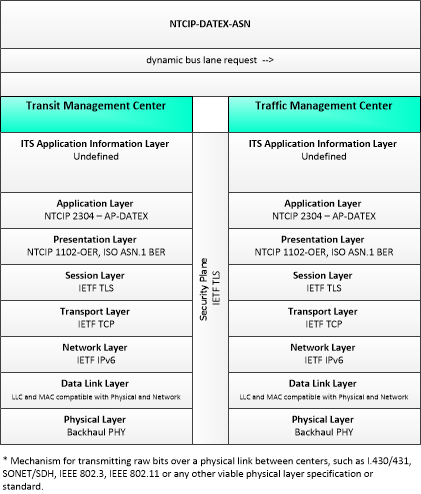
| dynamic bus lane request | Request for a restricted bus lane. |
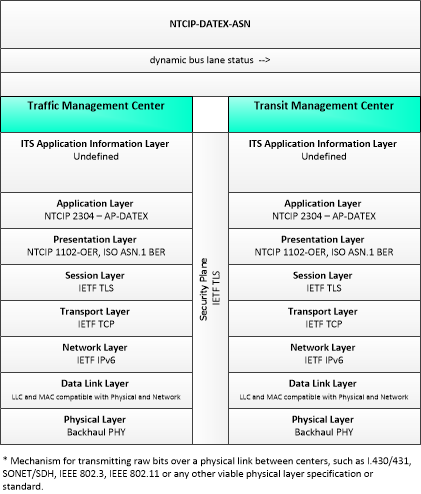
| dynamic bus lane status | Status of dynamic lane request, identifying if the request can be met, and the specific lane, start, end location, and time period where priority or exclusive access is to be granted. |
| host transit vehicle status | Information provided to the Connected Vehicle on-board equipment from other systems on the Transit Vehicle Platform. |
| host vehicle status | Information provided to the connected vehicle on-board equipment from other systems on the vehicle platform. This includes data from on-board sensors, the current status of the powertrain, steering, and braking systems, and status of safety and convenience systems. In implementations where GPS is not integrated into the Vehicle On-Board Equipment, the host vehicle is also the source for data describing the vehicle's location in three dimensions (latitude, longitude, elevation) and accurate time that can be used for time synchronization across the Connected Vehicle environment. |
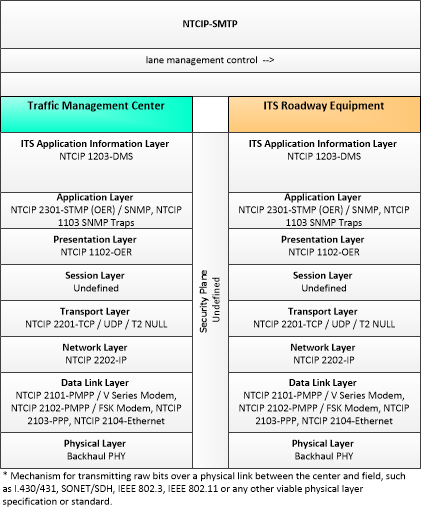
| lane management control | Information used to configure and control dynamic lane management systems. |
| lane management information | System status of managed lanes including current operational state, violations, and logged information. |
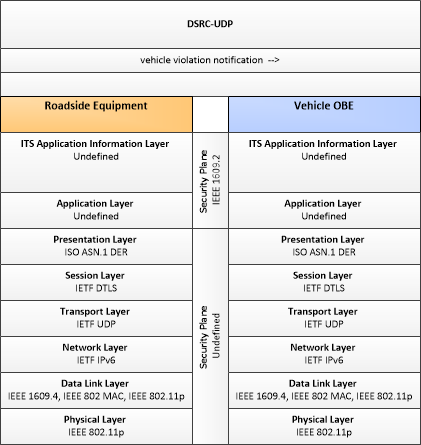
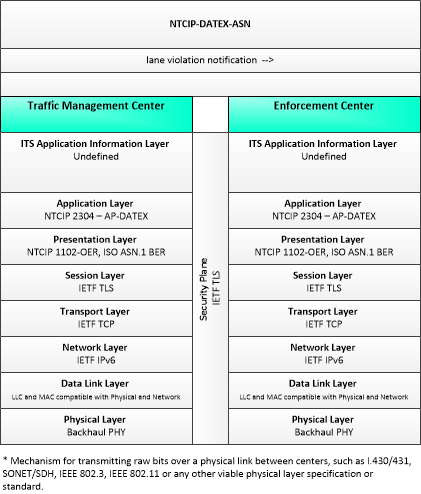
| lane violation notification | Notification to enforcement agency of detected lane entry violations, lane speed violations, or other dynamic lane violations. Lane entry violations may be issued for restricted vehicle types or vehicles that do not meet required emissions or passenger occupancy standards that enter a managed lane. This notification identifies the vehicle and documents the lane parameter that was violated. |
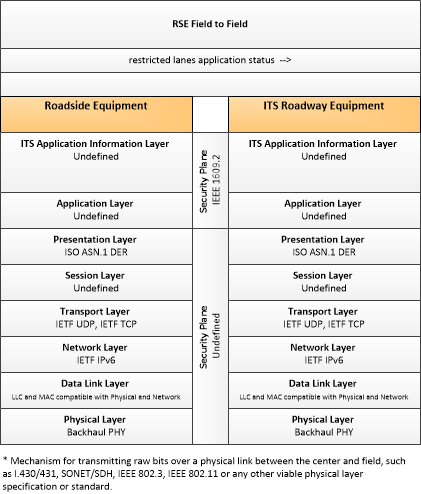
| restricted lanes application status | Current RSE application status that is monitored by the back office center including the operational state of the RSE, current configuration parameters, and a log of lane use (aggregate profiles of vehicles that checked in to the lane and reported vehicle speeds in the lanes) and RSE communications activity. |
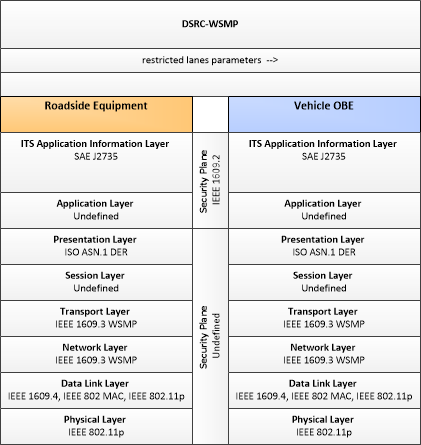
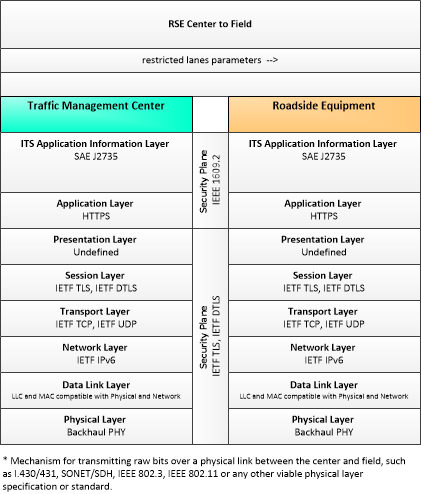
| restricted lanes parameters | Information that defines the location, duration, and operating parameters for lanes that are reserved for the exclusive use of certain types of vehicles (e.g., transit vehicles) or vehicles that meet other qualifications (e.g., number of occupants, low emissions criteria). It identifies the lane(s), the start and stop locations, start and end times, vehicle restrictions, speed limits and platooning parameters. |
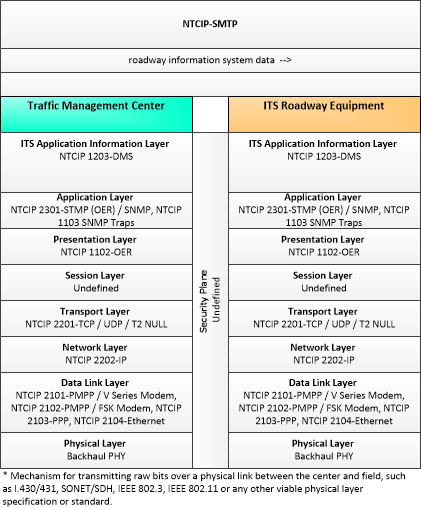
| roadway information system data | Information used to initialize, configure, and control roadside systems that provide driver information (e.g., dynamic message signs, highway advisory radio). This flow can provide message content and delivery attributes, local message store maintenance requests, control mode commands, status queries, and all other commands and associated parameters that support remote management of these systems. |
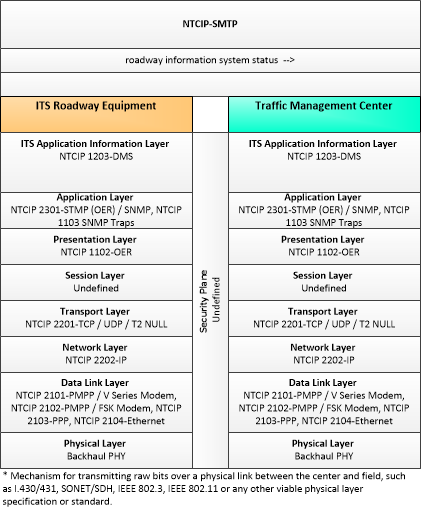
| roadway information system status | Current operating status of dynamic message signs, highway advisory radios, or other configurable field equipment that provides dynamic information to the driver. |
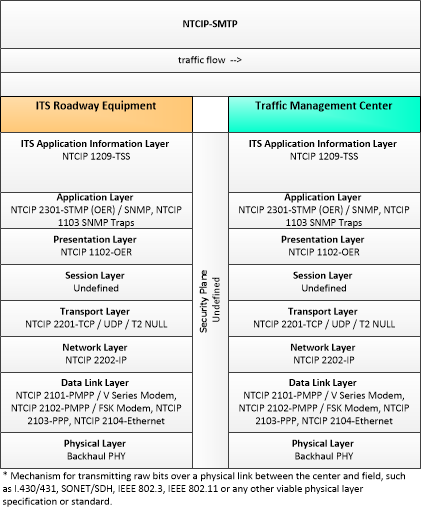
| traffic flow | Raw and/or processed traffic detector data which allows derivation of traffic flow variables (e.g., speed, volume, and density measures) and associated information (e.g., congestion, potential incidents). This flow includes the traffic data and the operational status of the traffic detectors. |
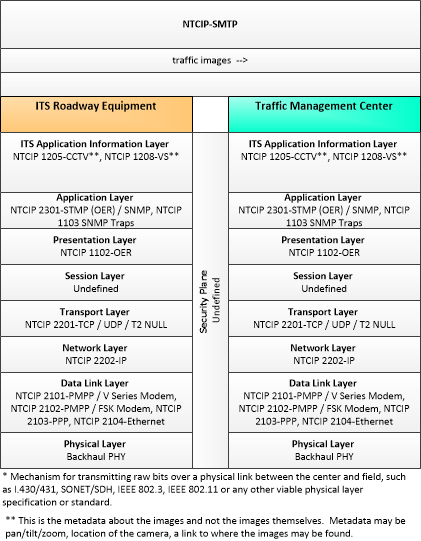
| traffic images | High fidelity, real-time traffic images suitable for surveillance monitoring by the operator or for use in machine vision applications. This flow includes the images and meta data that describes the images. |
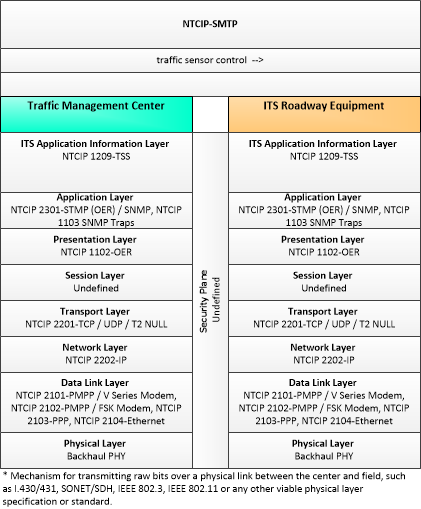
| traffic sensor control | Information used to configure and control traffic sensor systems. |
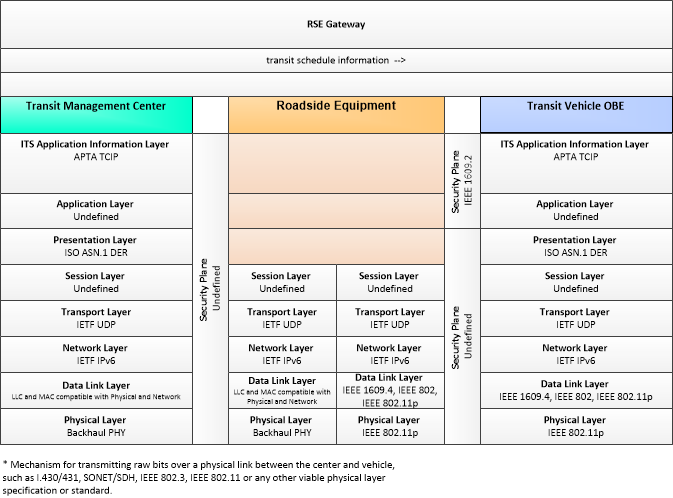
| transit schedule information | Current and projected transit schedule information used to initialize the transit vehicle with a vehicle assignment, monitor schedule performance, and develop corrective actions on-board. |
| transit vehicle operator display | Visual, audible, and tactile outputs to the transit vehicle operator including vehicle surveillance information, alarm information, vehicle system status, information from the operations center, and information indicating the status of all other on-board ITS services. |
| transit vehicle operator input | Transit vehicle operator inputs to on-board ITS equipment, including tactile and verbal inputs. Includes authentication information, on-board system control, emergency requests, and fare transaction data. |
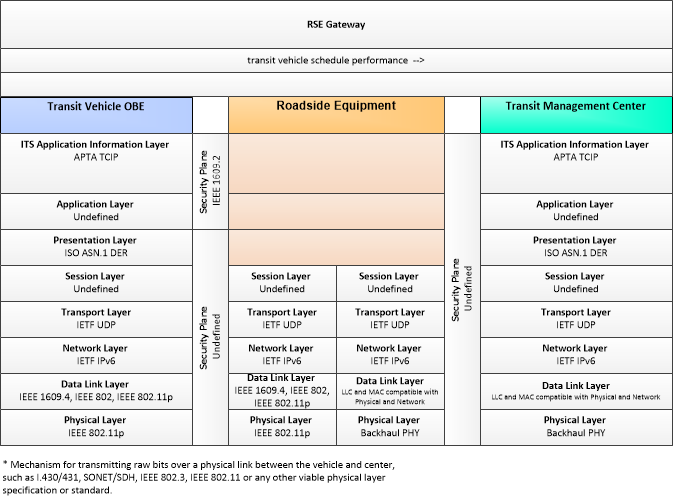
| transit vehicle schedule performance | Estimated times of arrival and anticipated schedule deviations reported by a transit vehicle. |
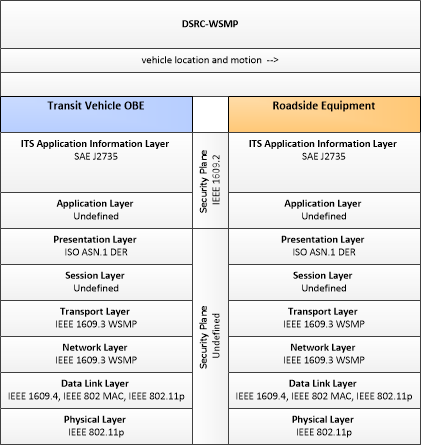
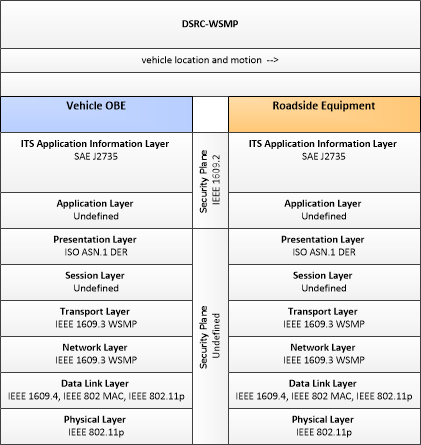
| vehicle location and motion | Data describing the vehicle's location in three dimensions, heading, speed, acceleration, braking status, and size. |
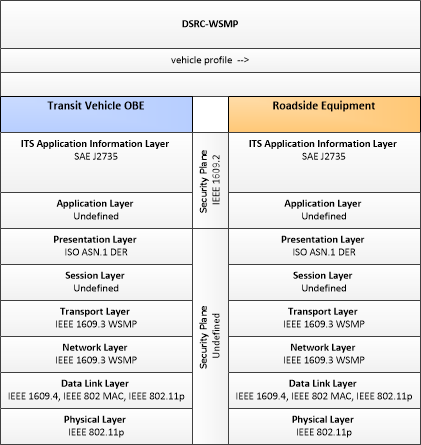
| vehicle profile | Information about a vehicle such as vehicle make and model, fuel type, engine type, average emissions, average fuel consumption, passenger occupancy, or other data that can be used to classify vehicle eligibility for access to specific lanes, road segments, or regions. |
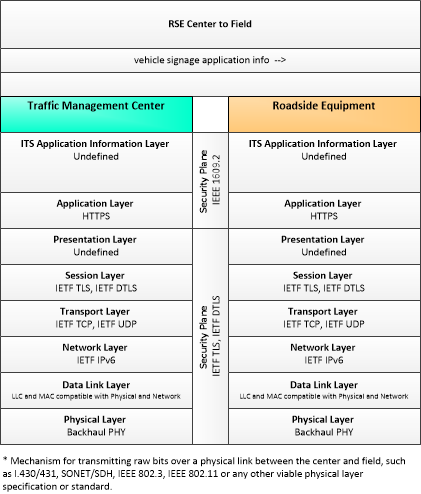
| vehicle signage application info | In-vehicle signing application configuration data and messaging parameters. This flow provides a list of regulatory, warning, and information messages to be displayed and parameters that support scheduling and prioritizing messages to be issued to passing vehicles. This flow also supports remote control of the application so the application can be taken offline, reset, or restarted. |
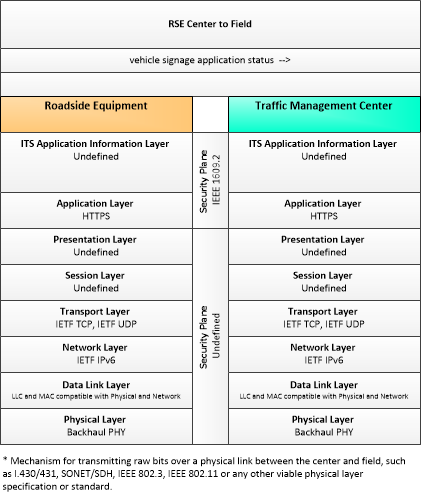
| vehicle signage application status | In-vehicle signing application status reported by the RSE. This includes current operational state and status of the RSE and a log of messages sent to passing vehicles. |
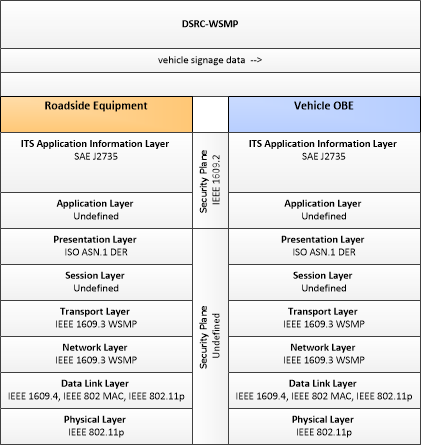
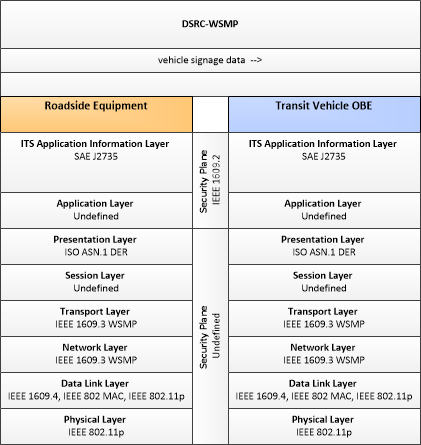
| vehicle signage data | In-vehicle signing data that augments regulatory, warning, and informational road signs and signals. The information provided would include static sign information (e.g., stop, curve warning, guide signs, service signs, and directional signs) and dynamic information (e.g., current signal states, grade crossing information, local traffic and road conditions, detours, advisories, and warnings). |
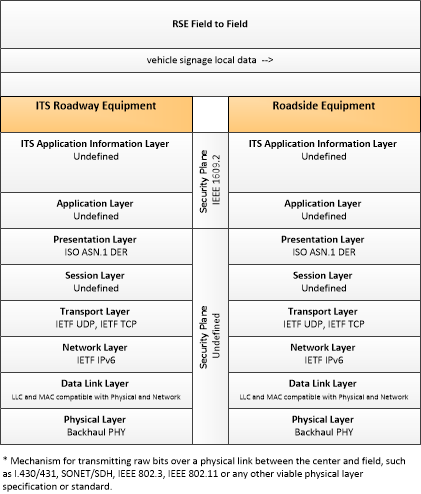
| vehicle signage local data | Information provided by adjacent field equipment to support in-vehicle signing of dynamic information that is currently being displayed to passing drivers. This includes the dynamic information (e.g., current signal states, grade crossing information, local traffic and road conditions, detours, advisories, parking availability, etc.) and control parameters that identify the desired timing, duration, and priority of the signage data. |
| vehicle violation notification | Notification to an individual vehicle that it has committed a lane violation. The flow identifies the nature of the violation and the time and location where the violation was recorded. |
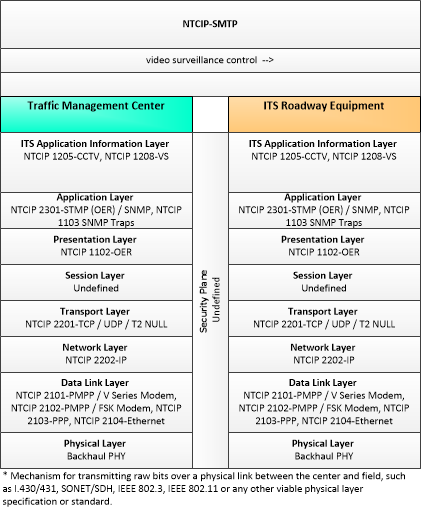
| video surveillance control | Information used to configure and control video surveillance systems. |
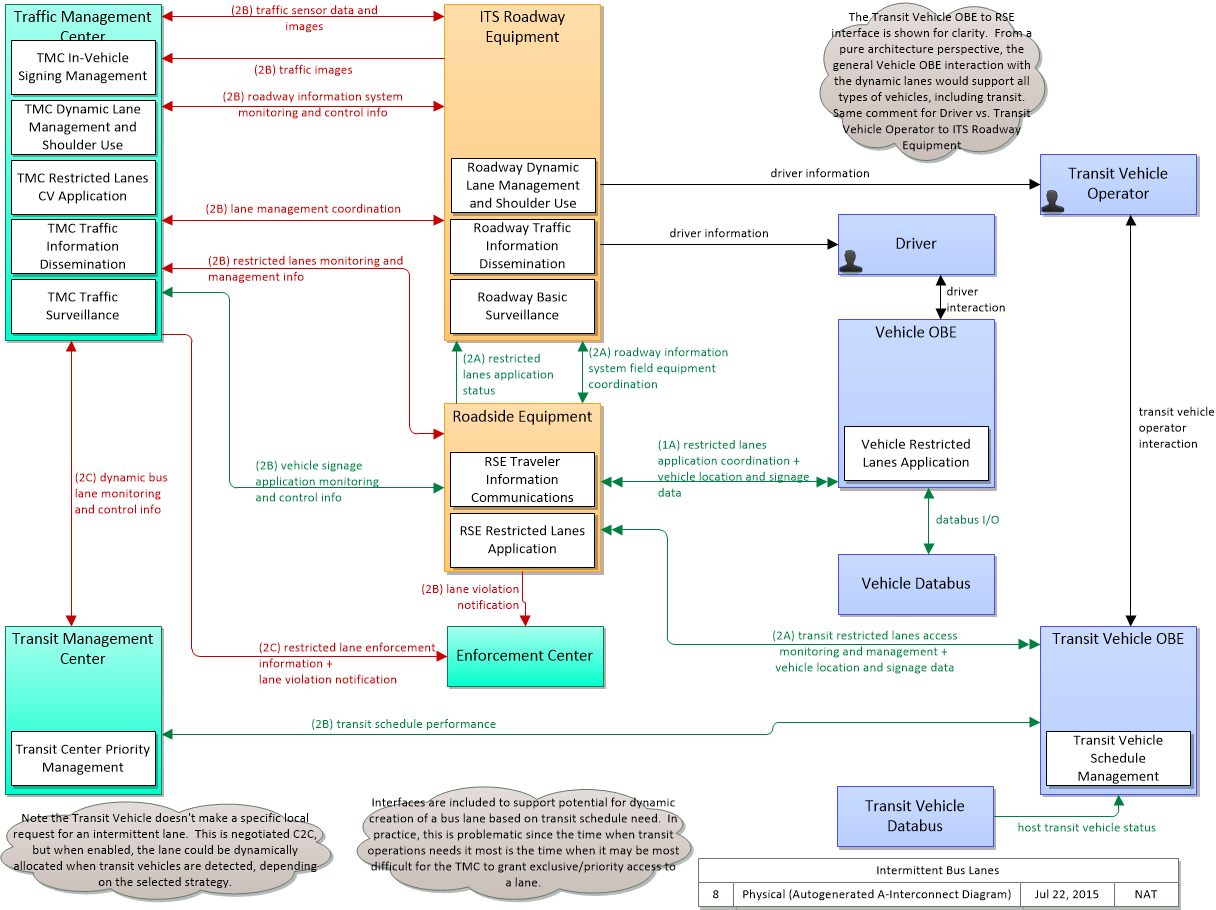
Application Interconnect Diagram
SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
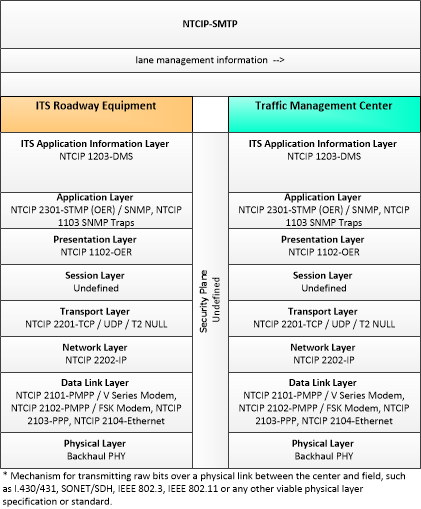
Application Triples
Requirements
| Need | Requirement | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N2.086 | Intermittent Bus Lanes (IBL) needs to determine times when travel lanes will change between open travel lanes and dedicated bus lanes. | 2.189 | Intermittent Bus Lanes (IBL) shall provide a mechanism for the roadway operator to specify when travel lanes are open and when they are dedicated bus lanes. |
| 2.190 | IBL shall maintain a listing of when travel lanes are open and when they are dedicated bus lanes. | ||
| N2.087 | IBL needs to notify drivers when a normally open travel lane is a bus lane. | 2.191 | IBL shall notify vehicles (including transit vehicles) when a travel lane near to the vehicle is a dedicated bus lane. |
| 2.192 | IBL shall notify vehicles (including transit vehicles) when a dedicated bus lane becomes an open travel lane. | ||
Related Sources
- ConOps for Transit Connected Vehicle, Draft, 3/31/2012
Security
In order to participate in this application, each physical object should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Physical Object Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Object | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability | Security Class |
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | ||||
In order to participate in this application, each information flow triple should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Information Flow Security | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Destination | Information Flow | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability |
| Basis | Basis | Basis | |||
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | |||||