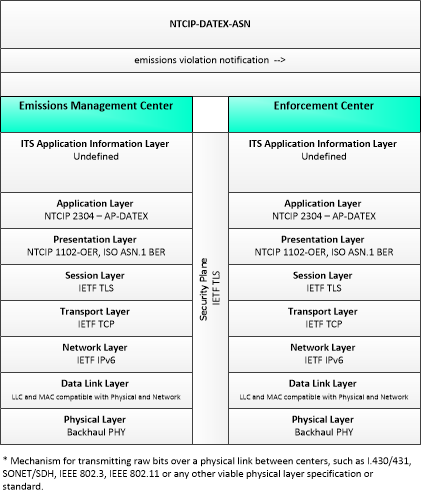
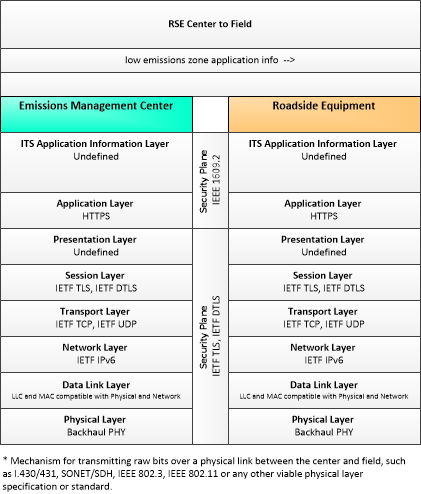
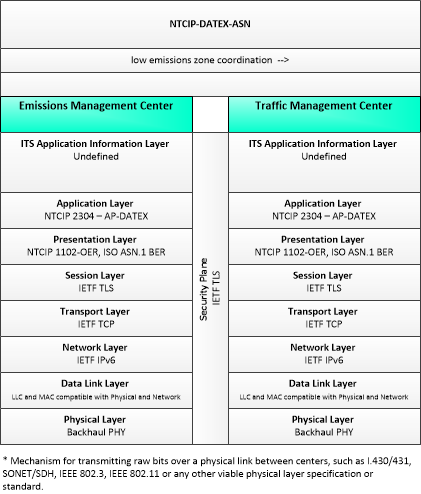
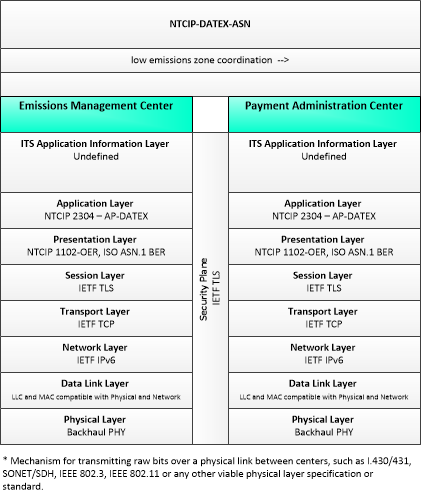
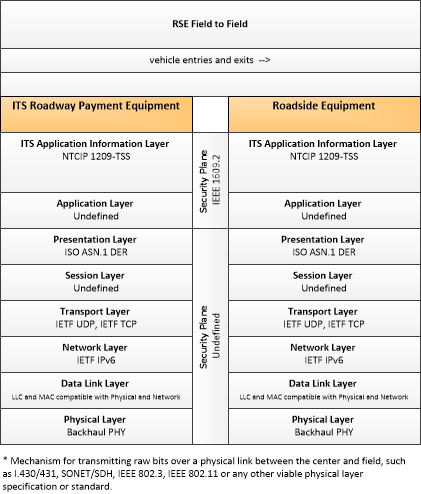
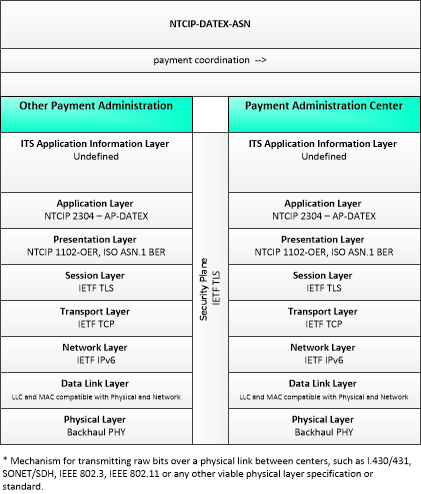
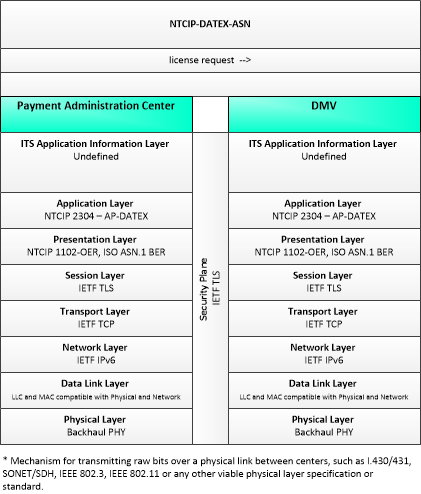
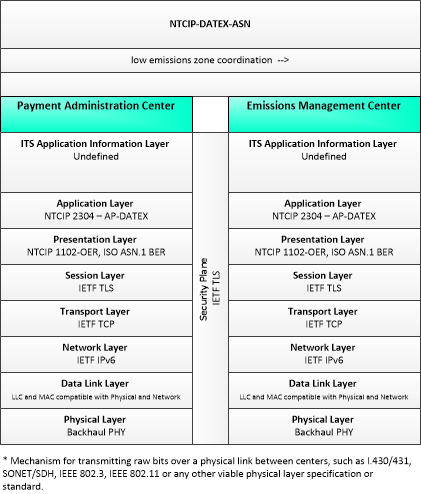
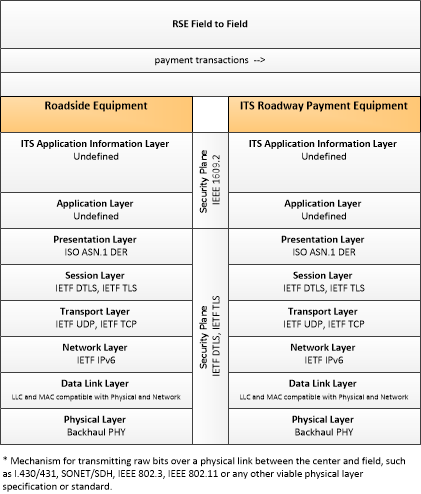
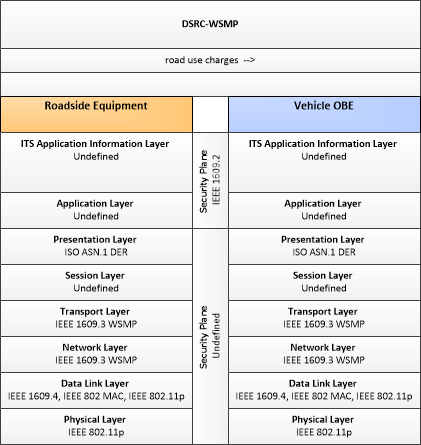
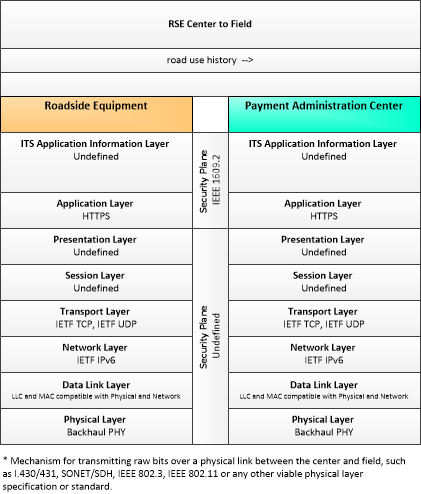
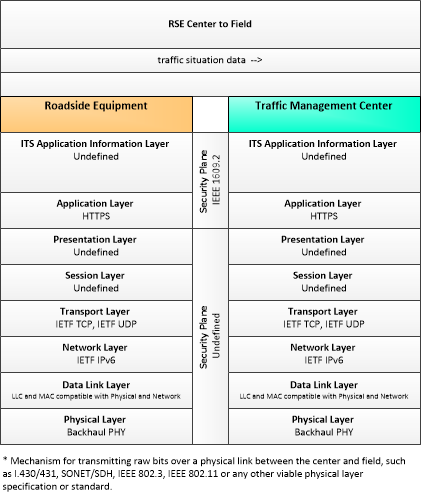
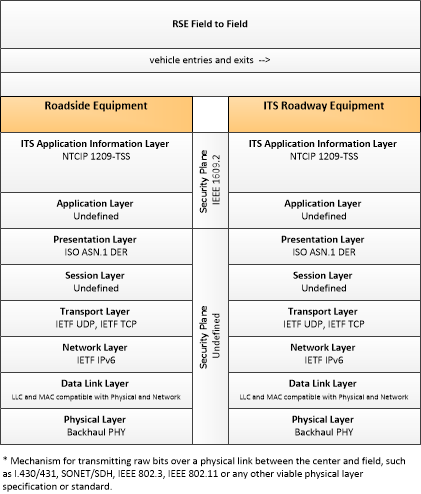
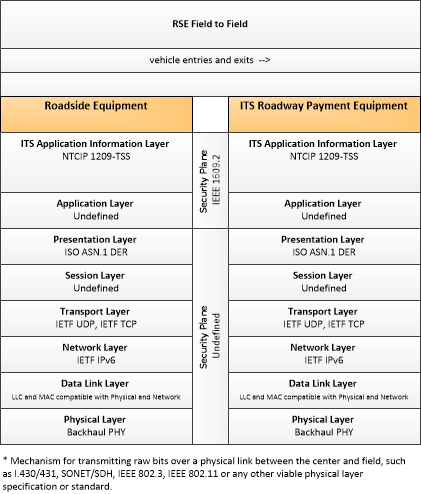
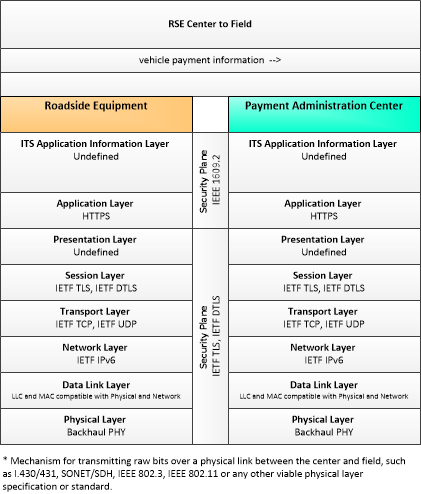
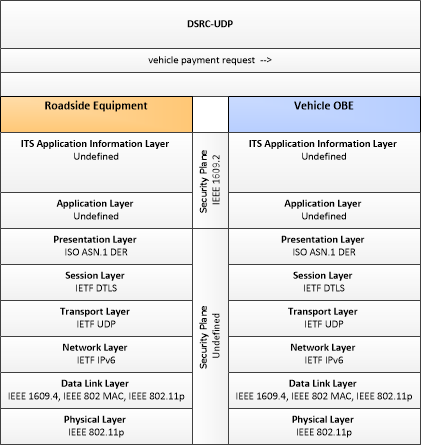
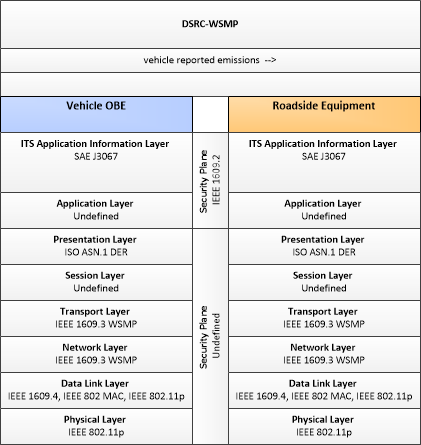
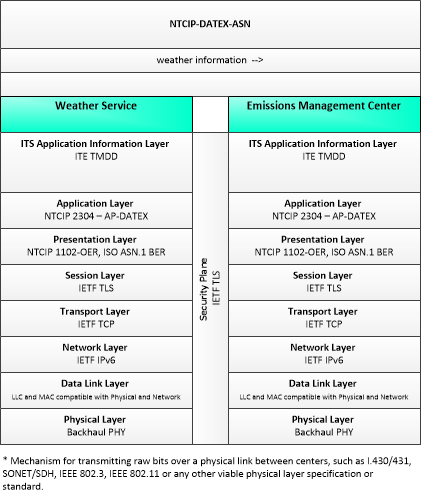
Type: Environmental
Groups:- AERIS/ Sustainable Travel
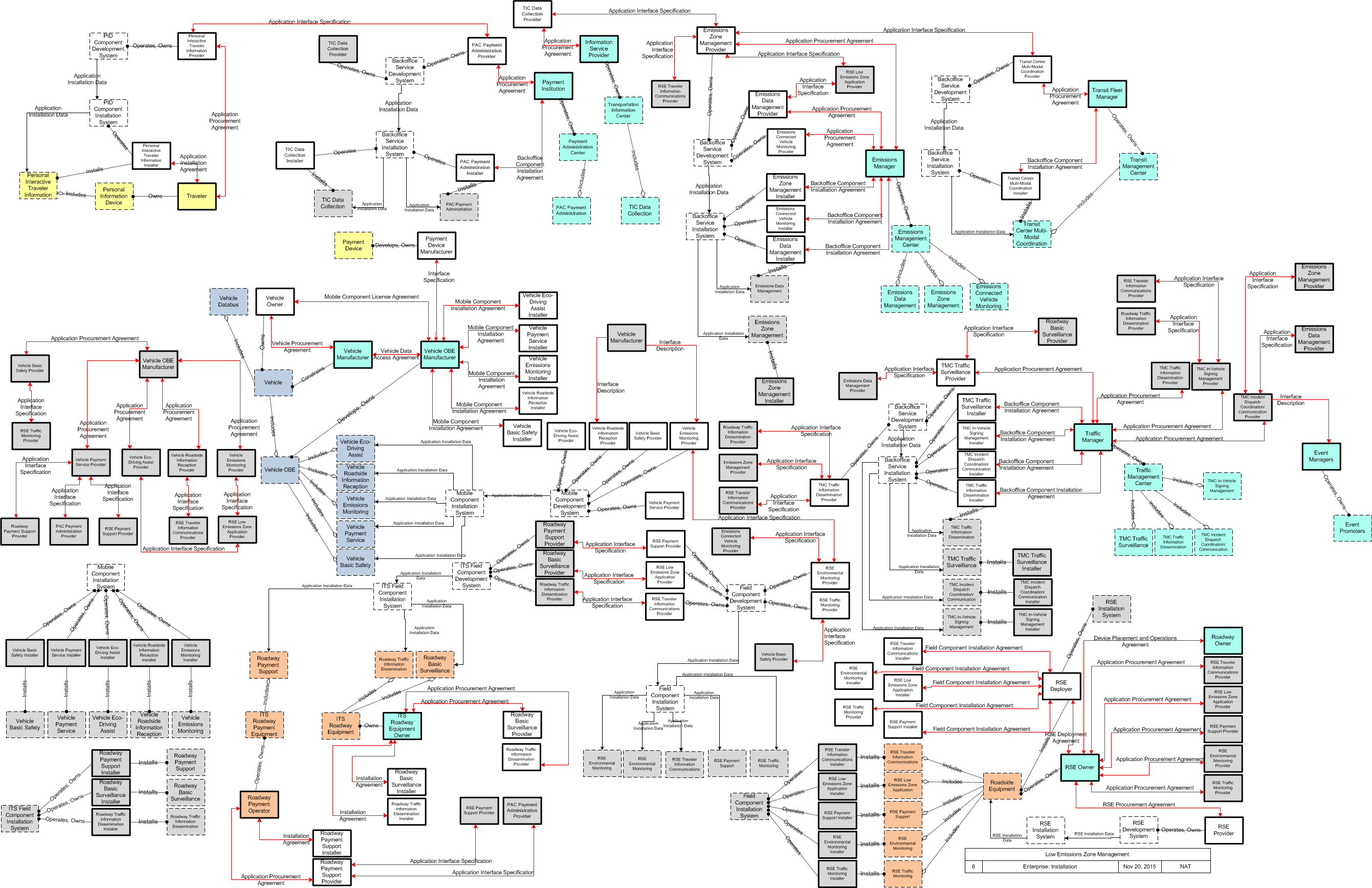
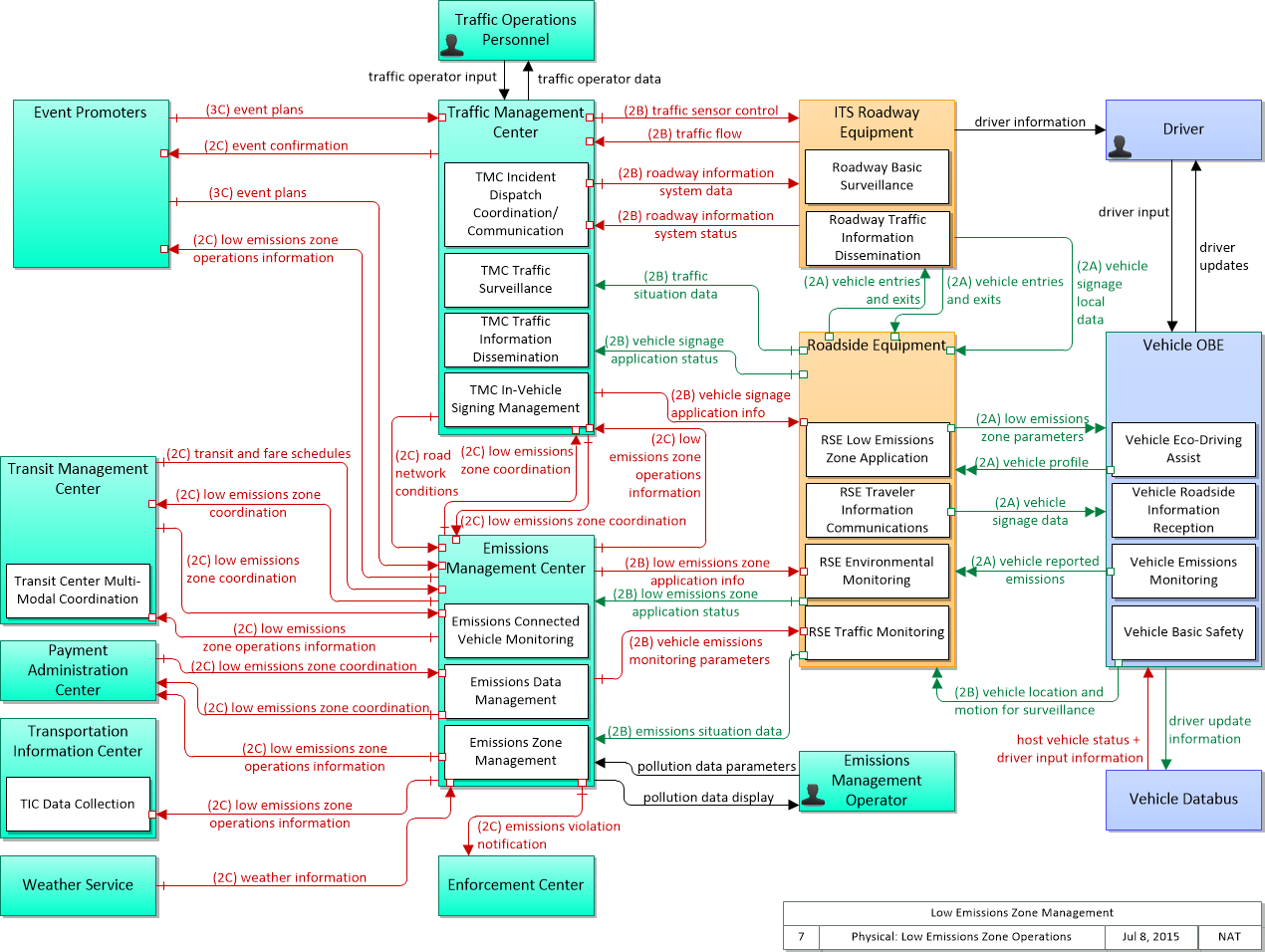
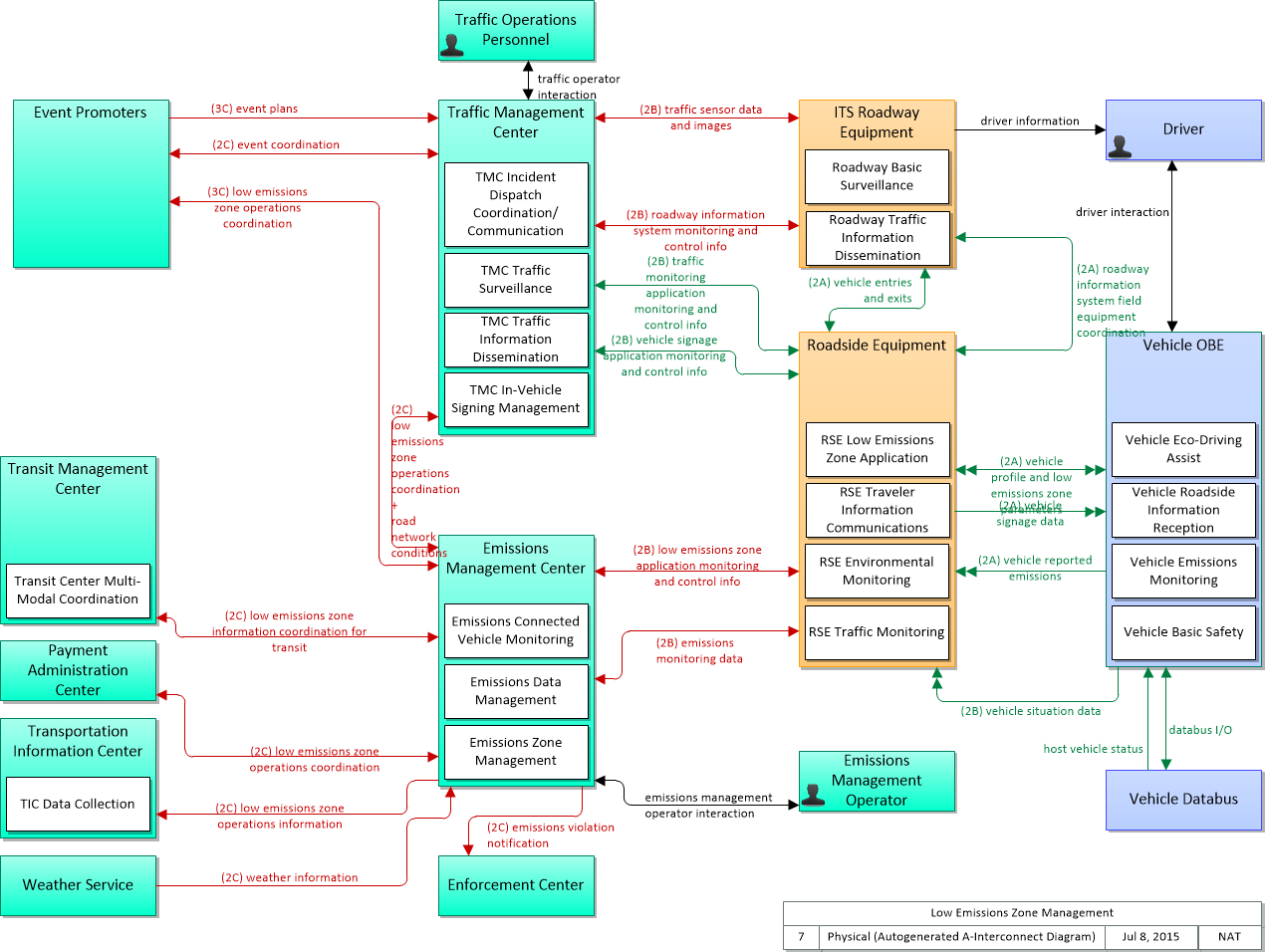
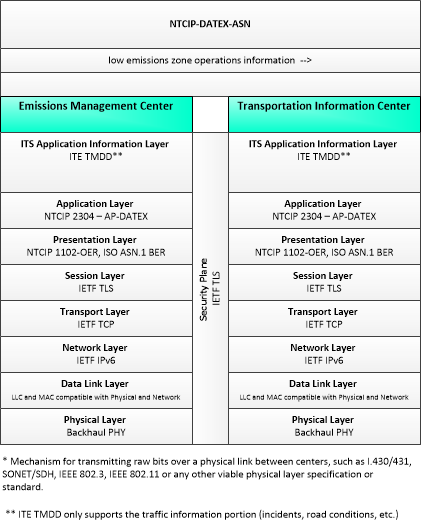
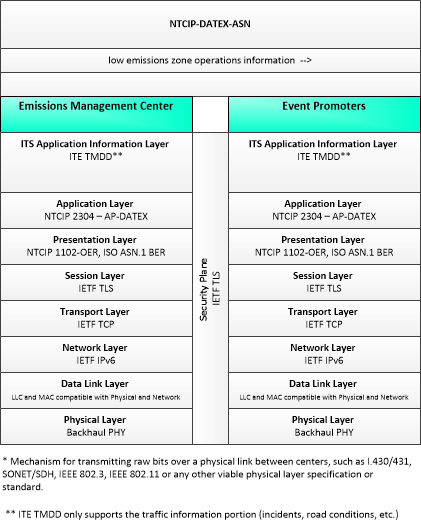
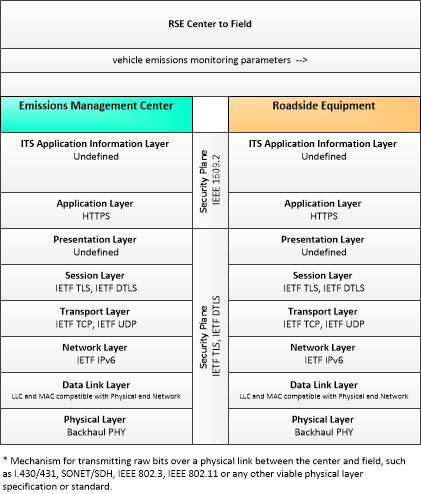
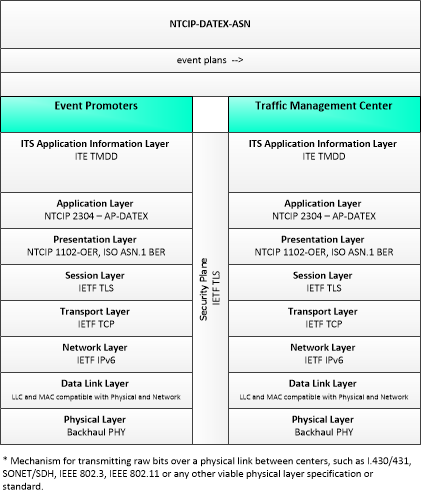
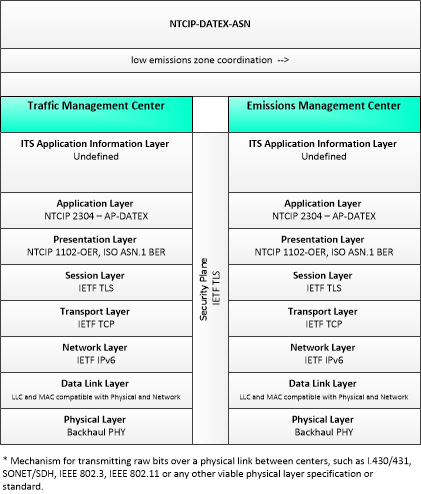
Low Emissions Zone Management
The Low Emissions Zone Management application supports the operation of a low emissions zone that is responsive to real-time traffic and environmental conditions. Low emissions zones are geographic areas that seek to restrict or deter access by specific categories of high-polluting vehicles into the area to improve the air quality within the geographic area. The application uses data collected from vehicles using connected vehicle technologies and from roadside equipment as input to the system. The Low Emissions Zone Management application supports the geo-fencing of a cordon that may be scalable and moveable (e.g., created for a day, removable, flexible in its boundaries) and would be less dependent on conventional ITS infrastructure. The application would establish parameters including the types of vehicles permitted to enter the zone, exemptions for transit vehicles, emissions criteria for entering the zone, fees or incentives for vehicles based on emissions data collected from the vehicle, and geographic boundaries for the low emissions zone. The application would also include electronic toll collection functions that support payments of fees or collection of incentives for registered vehicles using connected vehicle technologies. Finally, this application provides information about the low emissions zone to traveler information centers, including information about criteria for entering the zone, expected fees and incentives, current and predicted traffic conditions, and geographic boundaries of the zone.
Enterprise
SVG Diagrams: Installation Operations Maintenance Certification
PNG Diagrams: Installation Operations Maintenance Certification
Business Interaction Matrix:
| Low Emissions Zone Management Operations Stage | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Owner | Driver | Vehicle OBE Owner | Roadway Owner | RSE Owner | RSE Operator | ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Operator | Traffic Manager | Emissions Manager | Information Service Provider | Weather Service Operator | Traffic Operations Personnel | Vehicle Basic Safety Provider | RSE Environmental Monitoring Provider | RSE Traveler Information Communications Provider | RSE Traffic Monitoring Provider | Vehicle Emissions Monitoring Provider | Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist Provider | Traveler | Payment Institution | RSE Payment Support Provider | Vehicle Payment Service Provider | Event Managers | RSE Low Emissions Zone Application Provider | Financial Manager | DMV Owner | Enforcement | Other Payment Institution | Emissions Management Operator | Roadway Payment Operator | Vehicle Roadside Information Reception Provider | Transit Fleet Manager | |
| Vehicle Owner | Vehicle Usage Agreement | Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driver | Vehicle Usage Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation of Information Provision | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vehicle OBE Owner | Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation of Data Provision | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Roadway Owner | Service Delivery Agreement | Service Delivery Agreement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RSE Owner | Expectation of Data Provision | Service Delivery Agreement | Operations Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | Information Provision Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Application Usage Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||
| RSE Operator | Operations Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Information Exchange Agreement | Operations Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ITS Roadway Operator | Expectation of Information Provision | Operations Agreement | Information Provision Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traffic Manager | Information Provision Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Employment Agreement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emissions Manager | Information Exchange Agreement | Information Provision Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Information Provision Agreement | Information Provision Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | Employment Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Information Service Provider | Information Provision Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weather Service Operator | Information Provision Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traffic Operations Personnel | Employment Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vehicle Basic Safety Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RSE Environmental Monitoring Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RSE Traveler Information Communications Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RSE Traffic Monitoring Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vehicle Emissions Monitoring Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traveler | Service Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Payment Institution | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Service Usage Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | Information Exchange Agreement | Information Provision Agreement | Service Coordination Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RSE Payment Support Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vehicle Payment Service Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Event Managers | Information Exchange Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RSE Low Emissions Zone Application Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial Manager | Information Exchange Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DMV Owner | Information Exchange Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enforcement | Information Provision Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other Payment Institution | Service Coordination Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emissions Management Operator | Employment Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Roadway Payment Operator | Service Delivery Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vehicle Roadside Information Reception Provider | Application Usage Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transit Fleet Manager | Information Exchange and Action Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Includes Enterprise Objects:
| Enterprise Object | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Certification Entity | The body that determines whether an application may be deployed and operated in the Connected Vehicle Environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with application type. For example, applications with human safety component (crash avoidance, movement assistance etc.) may have stringent requirements and extensive testing in a variety of conditions, while applications that provide strictly mobility functionality may have far less testing requirements; possibly as little as just making sure the application doesn't interfere with any other applications. |
| Device Certification Entity | The body that determines whether a device may be deployed and operated in the Connected Vehicle Environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with device type. |
| DMV Owner | The DMV Owner is the agency charged with registering vehicles. |
| Driver | The 'Driver' represents the person that operates a vehicle on the roadway. Included are operators of private, transit, commercial, and emergency vehicles where the interactions are not particular to the type of vehicle (e.g., interactions supporting vehicle safety applications). The Driver originates driver requests and receives driver information that reflects the interactions which might be useful to all drivers, regardless of vehicle classification. Information and interactions which are unique to drivers of a specific vehicle type (e.g., fleet interactions with transit, commercial, or emergency vehicle drivers) are covered by separate objects. |
| Emissions Connected Vehicle Monitoring Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Emissions Connected Vehicle Monitoring Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Emissions Connected Vehicle Monitoring Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Emissions Data Management Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Emissions Data Management Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Emissions Data Management Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Emissions Management Operator | The 'Emissions Management Operator' represents personnel that monitor, operate, and manage emissions monitoring and management systems. These personnel monitor system operation and monitor collected emissions and air quality information and direct system operation through data and command inputs. |
| Emissions Manager | The entity responsible for the monitoring of and reaction to emissions. |
| Emissions Zone Management Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Emissions Zone Management Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Emissions Zone Management Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Enforcement | Agencies that are responsible for identifying and reporting violations of roadway regulations, including emissions, traffic violations, toll violations, etc. |
| Event Managers | The entity has knowledge of special events that might impact travel on roadways or other modes. |
| Federal Regulatory | Federal regulatory bodies that have legal authority to control and/or provide input to policies regulating transportation infrastructure and operations. This includes entities such as the Federal Communications Commission and US Department of Transportation. |
| Financial Manager | The organization that accepts and processes payment requests and other funds transfers through the Financial Center. |
| Information Service Provider | The "Information Service Provider" represents the owner of the Transportation Information Center. The Information Service Provider is responsible for collecting and disseminating information relevant to the traveling public. |
| ITS Certification Entity | The body that determines whether an ITS device or application may be deployed and operated in the transportation environment. This entity's composition, the requirements it applies and the procedures it uses to verify those requirements may vary with device and application type. Typically not a formal body, assigned on a project-by-project basis depending on the type of infrastructure involved. Since ITS projects are locally-focused (typically state or smaller), the entities that are part of this body are typically those with operational jurisdiction where the ITS is installed (e.g., state or local DOTs, state or local maintenance managers etc.) |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | The entity that owns the Roadway ITS equipment. |
| ITS Roadway Operator | The entity that operates the Roadway ITS equipment. |
| Other Payment Institution | Representing another Payment Institution, "Other Payment Institution" provides the source and destination for agreements and expectations between Payment Institutions, enabling payment administration activities to be coordinated across jurisdictional boundaries. |
| PAC Payment Administration Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| PAC Payment Administration Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| PAC Payment Administration Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Payment Device Manufacturer | The entity responsible for the design, manufacture and distribution of the Payment Device. |
| Payment Institution | The 'Payment Administrator' represents the person(s) that manage the back office payment administration systems for electronic toll, VMT road use payment, and other services paid for from a vehicle. It monitors the systems that support the electronic transfer of funds from the customer to the system operator. It monitors customer enrollment and supports the establishment of escrow accounts depending on the clearinghouse scheme and the type of payments involved. It also establishes and administers the pricing structures and policies. |
| Personal Interactive Traveler Information Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Personal Interactive Traveler Information Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Personal Interactive Traveler Information Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Roadway Basic Surveillance Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Basic Surveillance Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Basic Surveillance Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Roadway Owner | The owner of the roadway proximate to which roadside equipment will be/is installed. |
| Roadway Payment Operator | The entity that collects tolls and fees for roadway use, using technology placed roadside. |
| Roadway Payment Support Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Payment Support Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Payment Support Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Deployer | The entity responsible for the deployment, operations and maintenance of roadside equipment. |
| RSE Environmental Monitoring Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Environmental Monitoring Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Environmental Monitoring Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Low Emissions Zone Application Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Low Emissions Zone Application Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Low Emissions Zone Application Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Operator | The entity that operates roadside equipment in the transportation environment. |
| RSE Owner | The owner of roadside equipment. |
| RSE Payment Support Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Payment Support Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Payment Support Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Provider | The "RSE Provider" is the entity that develops and (presumably) sells roadside equipment to other entities for deployment and research. |
| RSE Traffic Monitoring Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Traffic Monitoring Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Traffic Monitoring Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| RSE Traveler Information Communications Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Traveler Information Communications Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| RSE Traveler Information Communications Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| State Regulatory | State regulatory bodies that have legal authority to control and/or provide input to policies regulating vehicles, transportation infrastructure and operations. This includes entities like Departments of Motor Vehicles, property tax authorities and tolling agencies. |
| TIC Data Collection Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TIC Data Collection Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TIC Data Collection Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| TMC Incident Dispatch Coordination/Communication Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Incident Dispatch Coordination/Communication Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Incident Dispatch Coordination/Communication Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| TMC In-Vehicle Signing Management Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC In-Vehicle Signing Management Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC In-Vehicle Signing Management Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| TMC Traffic Surveillance Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Traffic Surveillance Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| TMC Traffic Surveillance Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Traffic Manager | The entity responsible for the management of traffic, both freeway and arterial. |
| Traffic Operations Personnel | 'Traffic Operations Personnel' represents the people that operate a traffic management center. These personnel interact with traffic control systems, traffic surveillance systems, incident management systems, work zone management systems, and travel demand management systems. They provide operator data and command inputs to direct system operations to varying degrees depending on the type of system and the deployment scenario. |
| Transit Center Multi-Modal Coordination Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Transit Center Multi-Modal Coordination Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Transit Center Multi-Modal Coordination Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Transit Fleet Manager | The agency or organization that operates transit vehicles. This includes administration, routing, driver instruction, maintenance and any other responsibilities associated with the operations and maintenance of a transit system. |
| Traveler | The 'Traveler' represents any individual who uses transportation services. The interfaces to the traveler provide general pre-trip and en-route information supporting trip planning, personal guidance, and requests for assistance in an emergency that are relevant to all transportation system users. It also represents users of a public transportation system and addresses interfaces these users have within a transit vehicle or at transit facilities such as roadside stops and transit centers. |
| Vehicle Basic Safety Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Basic Safety Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Basic Safety Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Vehicle Emissions Monitoring Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Emissions Monitoring Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Emissions Monitoring Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Vehicle Manufacturer | The entity that builds, assembles, verifies and validates the Vehicle in which the Vehicle OBE will eventually operate. |
| Vehicle OBE Manufacturer | The entity that builds, assembles, verifies and validates the Vehicle OBE. This can be an OEM-equipped OBE, retrofit or aftermarket equipment. |
| Vehicle OBE Owner | The entity, individual, group or corporation that owns the Vehicle On-Board equipment. This could be the same as the Vehicle Owner, but it could be a third part that licenses the use of the OBE to the Owner. |
| Vehicle Owner | The individual, group of individuals or corporate entity that is identified as the registered owner of the Vehicle under state law. |
| Vehicle Payment Service Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Payment Service Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Payment Service Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Vehicle Roadside Information Reception Installer | Application Component Installers are specified more by role than by function. Installers are responsible for the installation of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Roadside Information Reception Maintainer | Application Component Maintainers are specified more by role than by function. Maintainers are responsible for the maintenance (configuration changes, patches and updates, hardware repairs) of the application component, which may require a support system, and may entail agreements and relationships between end users and application providers. |
| Vehicle Roadside Information Reception Provider | Application Component Providers are specified more by role than by function. Providers are responsible for the development of the application component, including initial creation, enhancement and bug fixes. Delivery of the application to the end user may require relationships with other entities (installers, maintainers) if the provider chooses not to fulfill those roles. |
| Weather Service Operator | The human operator of systems that provide weather, hydrologic and climate information, and warnings of hazardous weather and climate events. |
Includes Resources:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Component Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of an application component. Certification Requirements must be met in order for an application to be installed in the CVE. |
| Backoffice Service Development System | The systems used to develop backoffice (center) hardware and software components of applications. |
| Backoffice Service Installation System | The systems used to install and configure backoffice (center) hardware and software components. |
| Backoffice Service Maintenance System | The systems used to maintain and upgrade backoffice (center) hardware and software components. |
| Device Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of a connected vehicle device. Certification Requirements must be met in order for the device to be granted the credentials necessary to operate in the Connected Vehicle Environment. |
| DMV | The 'DMV' is a specific (state) public organization responsible for registering vehicles, e.g., the Department of Motor Vehicles. |
| Emissions Connected Vehicle Monitoring | "Emissions Connected Vehicle Monitoring" collects emissions data reported by passing vehicles and uses this data to support air quality management and planning. Coordination with traffic management supports air quality-responsive management of traffic. |
| Emissions Data Management | "Emissions Data Management" collects and stores air quality and vehicle emissions information by remotely monitoring and controlling area wide and point sensors. General air quality measures are distributed as general traveler information and also may be used in demand management programs. Collected roadside emissions are analyzed and used to detect, identify, and notify concerned parties regarding vehicles that exceed emissions standards. |
| Emissions Management Center | The 'Emissions Management Center' provides the capabilities for air quality managers to monitor and manage air quality. These capabilities include collecting emissions data from distributed emissions sensors (included in ITS Roadway Equipment in CVRIA) and directly from connected vehicles. The sensors monitor general air quality and also monitor the emissions of individual vehicles on the roadway. The measures are collected, processed, and used to support environmental monitoring applications. |
| Emissions Zone Management | "Emissions Zone Management" identifies existing and potential emissions hot spots and coordinates with transportation agencies and their systems to establish low emissions zones to manage air quality in these areas. Through this coordination, the geographic boundary, restrictions, and pricing for the low emissions zone are established and adjusted. |
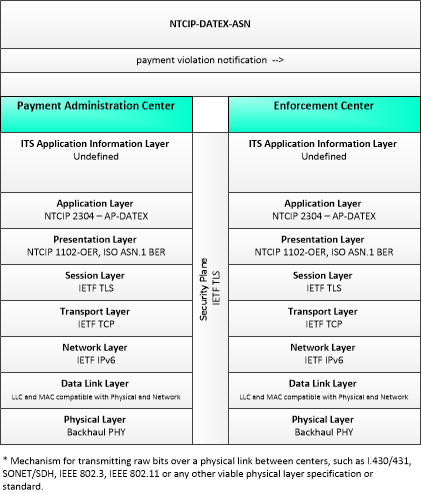
| Enforcement Center | The 'Enforcement Center' represents the systems that receive reports of violations detected by various ITS facilities including individual vehicle emissions, lane violations, toll violations, CVO violations, etc. |
| Event Promoters | 'Event Promoters' represents Special Event Sponsors that have knowledge of events that may impact travel on roadways or other modal means. Examples of special event sponsors include sporting events, conventions, motorcades/parades, and public/political events. These promoters interface to the ITS to provide event information such as date, time, estimated duration, location, and any other information pertinent to traffic movement in the surrounding area. |
| Field Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the field component of the application. |
| Field Component Installation System | The system used to install a field component of a connected vehicle application. |
| Field Component Maintenance System | The system used to install and configure changes and updates to the field component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
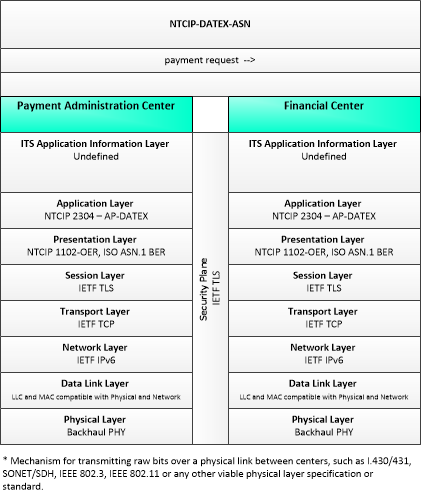
| Financial Center | The 'Financial Center' represents the organization that handles electronic fund transfer requests to enable the transfer of funds from the user of the service to the provider of the service. The functions and activities of financial clearinghouses are subsumed by this entity. |
| ITS Certification Requirements | The requirements that define the functionality, performance and operational environment of an ITS device or ITS application. Applicability varies with jurisdictions, but typically devices and applications must meet pre-defined acceptance criteria prior to usage in the transportation environment. |
| ITS Field Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the ITS field component of the application. |
| ITS Field Component Installation System | The system used to install a field component of a connected vehicle application. |
| ITS Field Component Maintenance System | The system used to install and configure changes and updates to the ITS field component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway itself. In CVRIA, this physical object represents all of the other ITS field equipment that interfaces with and supports the Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE). This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| ITS Roadway Payment Equipment | 'ITS Roadway Payment Equipment' represents the roadway components of a toll collection system. It provides the capability for vehicle operators to pay tolls without stopping their vehicles. It supports use of locally determined pricing structures and includes the capability to implement various variable pricing policies. Typically, transactions are accompanied by feedback to the customer and a record of the transactions is provided to a back office system (e.g., the Payment Administration Center). |
| Mobile Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the mobile component of the application. |
| Mobile Component Installation System | The system that interacts with the Vehicle OBE other mobile device and installs the mobile component of the application. |
| Mobile Component Maintenance System | The system used to configure changes and updates to the mobile component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
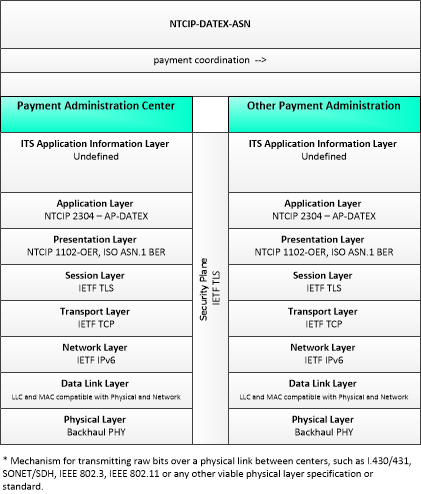
| Other Payment Administration | Representing another Payment Administration Center, 'Other Payment Administration' is intended to provide a source and destination for ITS information flows between payment administration functions. This interface allows reconciliation of toll charges and other payments across different agencies by allowing the exchange of information about clients who have incurred charges in jurisdictions other than their own (billing) customer service center. This interface enables apportioning charges and 'reciprocity' between participating customer service centers. |
| PAC Payment Administration | "PAC Payment Administration" enables payment for road use based on VMT, vehicle type, vehicle emissions, or other parameters. It establishes a price schedule based on these parameters that may vary by time, location or zone, vehicle type, and/or vehicle behavior. Pricing strategies may also include incentives that allow reimbursement of fees previously paid for good behavior (e.g., VMT reductions, economical driving behavior, avoidance of peak periods or congested zones). It receives vehicle data (e.g., time stamped roadways used by the vehicle since the last transmission) and computes the total cost to the vehicle owner for payment. Based on owner preference, this cost is either billed to the owner or requested from an in-vehicle payment instrument. Payment for use of roadways not operated by the specific instance of the VMT Payment Administration that the vehicle is registered with, will be reconciled. Payment violations can be reported to Enforcement Agencies when appropriate. Finally, vehicle owners can interact with this object using personal devices or public terminals to setup and edit account preferences for owned vehicles, get account reports, and make payments. |
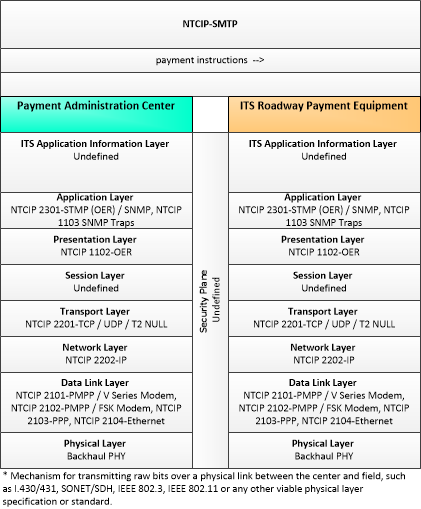
| Payment Administration Center | The 'Payment Administration Center' provides general payment administration capabilities and supports the electronic transfer of funds from the customer to the transportation system operator or other service provider. Charges can be recorded for tolls, vehicle-mileage charging, congestion charging, or other goods and services. It supports traveler enrollment and collection of both pre-payment and post-payment transportation fees in coordination with the financial infrastructure supporting electronic payment transactions. The system may establish and administer escrow accounts depending on the clearinghouse scheme and the type of payments involved. It may post a transaction to the customer account, generate a bill (for post-payment accounts), debit an escrow account, or interface to a financial infrastructure to debit a customer designated account. It supports communications with the ITS Roadway Payment Equipment to support fee collection operations. As an alternative, a wide-area wireless interface can be used to communicate directly with vehicle equipment. It also sets and administers the pricing structures and may implement road pricing policies in coordination with the Traffic Management Center. |
| Payment Device | The 'Payment Device' enables the electronic transfer of funds from the user of a service (I.e. a traveler) to the provider of the service. Potential implementations include smart cards that support payment for products and services, including transportation services and general purpose devices like smart phones that support a broad array of services, including electronic payment. In addition to user account information, the payment device may also hold and update associated user information such as personal profiles, preferences, and trip histories. |
| Personal Information Device | The 'Personal Information Device' provides the capability for travelers to receive formatted traveler information wherever they are. Capabilities include traveler information, trip planning, and route guidance. Frequently a smart phone, the Personal Information Device provides travelers with the capability to receive route planning and other personally focused transportation services from the infrastructure in the field, at home, at work, or while en-route. Personal Information Devices may operate independently or may be linked with connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| Personal Interactive Traveler Information | "Personal Interactive Traveler Information" provides traffic information, road conditions, transit information, yellow pages (traveler services) information, special event information, and other traveler information that is specifically tailored based on the traveler's request and/or previously submitted traveler profile information. It also supports interactive services that support enrollment, account management, and payments for transportation services. The interactive traveler information capability is provided by personal devices including personal computers and personal portable devices such as smart phones. |
| PID Component Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the PID component of the application. |
| PID Component Installation System | The system used to install the PID component of a connected vehicle application. |
| PID Component Maintenance System | The system used to configure changes and updates to the PID component of the application. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the application's configuration and performance. |
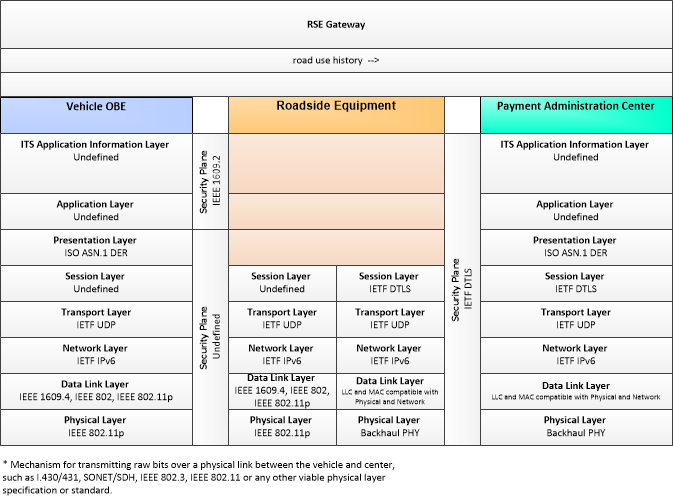
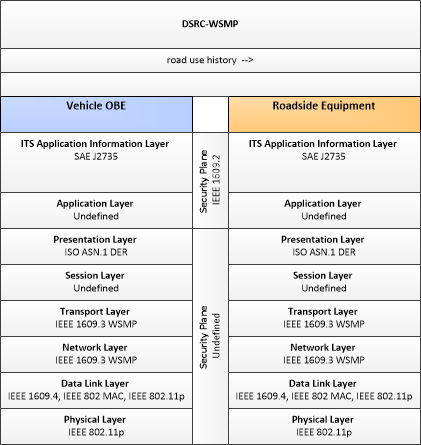
| Roadside Equipment | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Roadway Basic Surveillance | "Roadway Basic Surveillance" monitors traffic conditions using fixed equipment such as loop detectors and CCTV cameras. |
| Roadway Payment Support | "Roadway Payment Support" represents the equipment that works in conjunction with the RSE to detect vehicles and identify and process violators when the RSE is used to support electronic payment. Various fee structures and payment strategies are supported including strategies that support reimbursements or credits that incentivize desired driving behavior. |
| Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination | "Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination" includes field elements that provide information to drivers, including dynamic message signs and highway advisory radios. |
| RSE Development System | The system used in a backoffice environment to develop and test the roadside equipment. |
| RSE Environmental Monitoring | "RSE Environmental Monitoring" collects environmental situation (probe) data from passing vehicles that are equipped with short range communications capability. The collected data includes current environmental conditions as measured by on-board sensors (e.g., ambient temperature and precipitation measures), current status of vehicle systems that can be used to infer environmental conditions (e.g., status of lights, wipers, ABS, and traction control systems), and emissions measures reported by the vehicle. The application object collects the provided data, aggregates and filters the data based on provided configuration parameters, and sends the collected information back to a center for processing and distribution. This application object may also process the collected data locally and issue short-term road weather advisories for the road segment using short range communications. |
| RSE Installation System | The system used to install and configure the roadside equipment. |
| RSE Low Emissions Zone Application | "RSE Low Emissions Zone Application" provides information to vehicles regarding low emissions zones and checks vehicle profiles on entry to a designated low emissions zone to verify they are in compliance with the parameters established for the zone. |
| RSE Maintenance System | The system used to configure changes and updates to the roadside equipment. This system is capable of acquiring and reporting diagnostic information about the RSE's configuration and performance. |
| RSE Payment Support | "RSE Payment Support" manages vehicle payments for road use based on fee structures and payment strategies based on vehicle-reported data including VMT, emissions, vehicle class or type. Fees may vary by time or location and may include incentives or credits to reward desirable driving behavior. To support payment, it receives vehicle data (e.g., time stamped roadways used by the vehicle since the last transmission) and forwards this to the Payment Administration Center. It also receives equipment status from the vehicle and vehicle characteristics sensed from the vehicle (number of axles, weight, vehicle tag image/ID). Faults are identified and forwarded to the Payment Administration Center. Finally, it requests, receives, processes, and reports vehicle payment information. |
| RSE Traffic Monitoring | "RSE Traffic Monitoring" monitors the basic safety messages that are shared between connected vehicles and distills this data into traffic flow measures that can be used to manage the network in combination with or in lieu of traffic data collected by infrastructure-based sensors. As connected vehicle penetration rates increase, the measures provided by this application can expand beyond vehicle speeds that are directly reported by vehicles to include estimated volume, occupancy, and other measures. This object also supports incident detection by monitoring for changes in speed and vehicle control events that indicate a potential incident. |
| RSE Traveler Information Communications | "RSE Traveler Information Communications" includes field elements that distribute information to vehicles for in-vehicle display. The information may be provided by a center (e.g., variable information on traffic and road conditions in the vicinity of the field equipment) or it may be determined and output locally (e.g., static sign information and signal phase and timing information). This includes the interface to the center or field equipment that controls the information distribution and the short range communications equipment that provides information to passing vehicles. |
| TIC Data Collection | "TIC Data Collection" collects transportation-related data from other centers, performs data quality checks on the collected data and then consolidates, verifies, and refines the data and makes it available in a consistent format to applications that support operational data sharing between centers and deliver traveler information to end-users. A broad range of data is collected including traffic and road conditions, transit data, emergency information and advisories, weather data, special event information, traveler services, parking, multimodal data, and toll/pricing data. It also shares data with other transportation information centers. |
| TMC Incident Dispatch Coordination/Communication | "TMC Incident Dispatch Coordination/Communication" formulates and manages an incident response that takes into account the incident potential, incident impacts, and resources required for incident management. It supports dispatch of emergency response and service vehicles as well as coordination with other cooperating agencies. It provides access to traffic management resources that provide surveillance of the incident, traffic control in the surrounding area, and support for the incident response. It monitors the incident response and collects performance measures such as incident response and clearance times. |
| TMC In-Vehicle Signing Management | "TMC In-Vehicle Signing Management" controls and monitors RSEs that support in-vehicle signing. Sign information that may include static regulatory, service, and directional sign information as well as variable information such as traffic and road conditions can be provided to the RSE, which uses short range communications to send the information to in-vehicle equipment. Information that is currently being communicated to passing vehicles and the operational status of the field equipment is monitored by this application. The operational status of the field equipment is reported to operations personnel. |
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination | "TMC Traffic Information Dissemination" disseminates traffic and road conditions, closure and detour information, incident information, driver advisories, and other traffic-related data to other centers, the media, and driver information systems. It monitors and controls driver information system field equipment including dynamic message signs and highway advisory radio, managing dissemination of driver information through these systems. |
| TMC Traffic Surveillance | "TMC Traffic Surveillance" remotely monitors and controls traffic sensors and surveillance (e.g., CCTV) equipment, and collects, processes and stores the collected traffic data. Current traffic information and other real-time transportation information is also collected from other centers. The collected information is provided to traffic operations personnel and made available to other centers. |
| Traffic Management Center | The 'Traffic Management Center' monitors and controls traffic and the road network. It represents centers that manage a broad range of transportation facilities including freeway systems, rural and suburban highway systems, and urban and suburban traffic control systems. It communicates with ITS Roadway Equipment and Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE) to monitor and manage traffic flow and monitor the condition of the roadway, surrounding environmental conditions, and field equipment status. It manages traffic and transportation resources to support allied agencies in responding to, and recovering from, incidents ranging from minor traffic incidents through major disasters. |
| Transit Center Multi-Modal Coordination | "Transit Center Multi-Modal Coordination" supports transit service coordination between transit properties and coordinates with other surface and air transportation modes. As part of service coordination, it shares schedule and trip information, as well as transit transfer cluster (a collection of stop points, stations, or terminals where transfers can be made conveniently) and transfer point information between Multimodal Transportation Service Providers, Transit Agencies, and ISPs. An interface to Traffic Management also supports demand management strategies. |
| Transit Management Center | The 'Transit Management Center' manages transit vehicle fleets and coordinates with other modes and transportation services. It provides operations, maintenance, customer information, planning and management functions for the transit property. It spans distinct central dispatch and garage management systems and supports the spectrum of fixed route, flexible route, paratransit services, transit rail, and bus rapid transit (BRT) service. The physical object's interfaces allow for communication between transit departments and with other operating entities such as emergency response services and traffic management systems. |
| Transportation Information Center | The 'Transportation Information Center' collects, processes, stores, and disseminates transportation information to system operators and the traveling public. The physical object can play several different roles in an integrated ITS. In one role, the TIC provides a data collection, fusing, and repackaging function, collecting information from transportation system operators and redistributing this information to other system operators in the region and other TICs. In this information redistribution role, the TIC provides a bridge between the various transportation systems that produce the information and the other TICs and their subscribers that use the information. The second role of a TIC is focused on delivery of traveler information to subscribers and the public at large. Information provided includes basic advisories, traffic and road conditions, transit schedule information, yellow pages information, ride matching information, and parking information. The TIC is commonly implemented as a website or a web-based application service, but it represents any traveler information distribution service. |
| Vehicle | The conveyance that provides the sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support efficient, safe, and convenient travel. These functions reside in general vehicles including personal automobiles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, or other vehicle types. |
| Vehicle Basic Safety | "Vehicle Basic Safety" exchanges current vehicle location and motion information with other vehicles in the vicinity, uses that information to calculate vehicle paths, and warns the driver when the potential for an impending collision is detected. If available, map data is used to filter and interpret the relative location and motion of vehicles in the vicinity. Information from on-board sensors (e.g., radars and image processing) are also used, if available, in combination with the V2V communications to detect non-equipped vehicles and corroborate connected vehicle data. Vehicle location and motion broadcasts are also received by the infrastructure and used by the infrastructure to support a wide range of roadside safety and mobility applications. This object represents a broad range of implementations ranging from basic Vehicle Awareness Devices that only broadcast vehicle location and motion and provide no driver warnings to advanced integrated safety systems that may, in addition to warning the driver, provide collision warning information to support automated control functions that can support control intervention. |
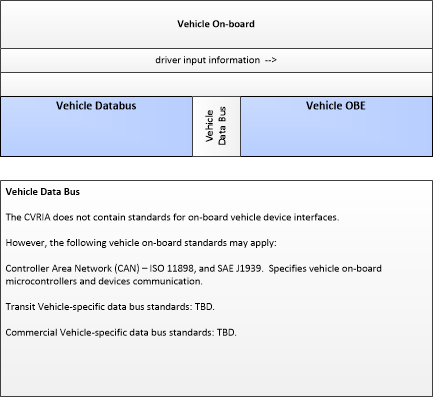
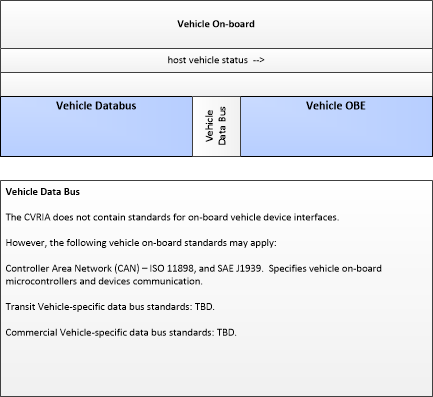
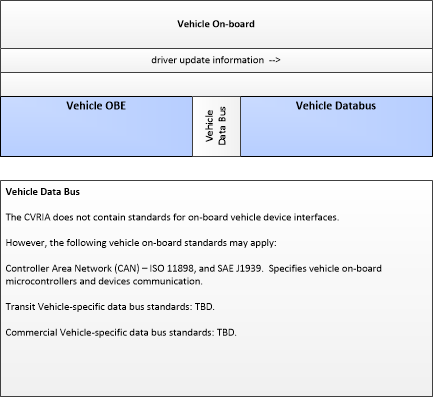
| Vehicle Databus | The 'Vehicle Databus' represents the interface to the vehicle databus (e.g., CAN, LIN, Ethernet/IP, FlexRay, and MOST) that may enable communication between the Vehicle OBE and other vehicle systems to support connected vehicle applications. The vehicle system statuses and/or sensor outputs available on the databus will vary based on the equipment installed on the vehicle and availability on databus. System statuses and sensor outputs may include select vehicle systems and sensors such as accelerometers, yaw rate sensors, and GPS derived location and timing information. In CVRIA, this physical object is used to represent the onboard interactions between the Vehicle OBE and the other systems included in a host vehicle. Note that the vehicle databus interface is not standardized across all vehicle classes. Also, some Vehicle OBE implementations will not have access to the vehicle databus. See 'Vehicle OBE' for more information. |
| Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist | "Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist" provides customized real-time driving advice to drivers, allowing them to adjust behaviors to save fuel and reduce emissions. This advice includes recommended driving speeds, optimal acceleration and deceleration profiles based on prevailing traffic conditions, and local interactions with nearby vehicles, i.e., processing Basic Safety Messages (BSMs) to determine position and speed of vehicles that are between the host vehicle and the intersection. When approaching and departing signalized intersections, it uses intersection geometry information, the relative position and speed of vehicles ahead of it, and signal phase movement information to provide speed advice to the driver so that the driver can adapt the vehicle's speed to pass the next traffic signal on green, decelerate to a stop in the most eco-friendly manner, or manage acceleration as the vehicle departs from a signalized intersection. It also provides feedback to drivers on their driving behavior to encourage them to drive in a more environmentally efficient manner. It may also support vehicle-assisted strategies, where the vehicle automatically implements the eco-driving strategy (e.g., changes gears, switches power sources, or reduces its speed in an eco-friendly manner as the vehicle approaches a traffic signal or queue). |
| Vehicle Emissions Monitoring | "Vehicle Emissions Monitoring" directly measures or estimates current and average vehicle emissions and makes this data available to the driver and connected vehicle infrastructure systems. |
| Vehicle OBE | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
| Vehicle Payment Service | "Vehicle Payment Service" supports vehicle payments including VMT- and zone-based payments and payments for other services including fuel/charging services. To support VMT-based payment, this application tracks the location of the vehicle at specific times and reports this VMT data along with vehicle identification. A variety of pricing strategies are supported, including strategies that include credits or incentives that reward desired driving patterns and behavior. |
| Vehicle Roadside Information Reception | "Vehicle Roadside Information Reception" receives advisories, vehicle signage data, and other driver information and presents this information to the driver using in-vehicle equipment. Information presented may include fixed sign information, traffic control device status (e.g., signal phase and timing data), advisory and detour information, warnings of adverse road and weather conditions, travel times, and other driver information. |
| Weather Service | The 'Weather Service' provides weather, hydrologic, and climate information and warnings of hazardous weather including thunderstorms, flooding, hurricanes, tornadoes, winter weather, tsunamis, and climate events. It provides atmospheric weather observations and forecasts that are collected and derived by the National Weather Service, private sector providers, and various research organizations. The interface provides formatted weather data products suitable for on-line processing and integration with other ITS data products as well as Doppler radar images, satellite images, severe storm warnings, and other products that are formatted for presentation to various ITS users. |
Includes Roles:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Certifies | An Enterprise verifies that a target Resource meets relevant performance, functional, environmental and quality requirements. |
| Constrains | A Resource or Enterprise applies requirements, constraints and associated tests to another Resource. |
| Develops | An Enterprise creates the target Resource or Document. |
| Installs | An Enterprise performs the initial delivery, integration and configuration of the target Resource. |
| Maintains | An Enterprise administers the hardware and software that comprise the target Resource. |
| Member | An Enterprise is part of another larger, target Enterprise. |
| Operates | An Enterprise controls the functionality and state of the target Resource. An Enterprise that Operates a resource is considered Responsible. |
| Owns | An Enterprise has financial ownership and control over the Resource. An Enterprise that Owns a resource is considered Accountable. |
Includes Coordination:
| Coordination | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Application Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one party permission to install an application component on a device controlled by the other party. |
| Application Installation Data | Information Sharing | Data needed to install the application, including the application executable code and any configuration data. Unidirectional flow. |
| Application Interface Specification | Agreement | The definition of an interface between two application components that operate on two distinct pieces of hardware. The Application Interface Specification is specific to the application in question. |
| Application Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of a software application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Application Maintenance Data | Information Sharing | Data used to facilitate the upgrade, patching and general health maintenance of an application component. |
| Application Performance Data | Information Sharing | Data used to characterize application performance, including such measures as availability, known errors and known uses. |
| Application Procurement Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity provides a copy of an application component to another entity. This component is capable of being installed and functioning, according to its requirements that passed through the application's certification process. |
| Application Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity that controls an application component's use gives the other entity the necessary tools and permission to operate that application or application component. |
| Backoffice Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one party permission to install a backoffice application component on a center-based device controlled by the other party. |
| Backoffice Component Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the backoffice component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Device Placement and Operations Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that enables the controller of a physical device to install it (so as to make it operational) at a fixed location controlled by another entity. |
| Employment Agreement | Agreement | An agreement between an individual and a corporation or government entity, whereupon the individual agrees to provide labor to the corporation/agency, which in turn compensates the employee. Stipulates level of compensation, working conditions, necessary equipment and training and expectations of employee performance. |
| Expectation of Data Provision | Expectation | An expectation where one party believes another party will provide data on a regular and recurring basis, and that that data will be useful to the receiver in the context of the receiver's application. This thus includes some expectation of data fields, timeliness, quality, precision and similar qualities of data. |
| Expectation of Information Provision | Expectation | An expectation where one party believes another party will provide it information whenever such information is likely relevant to the recipient. |
| Field Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one party permission to install a field application component on a roadside device controlled by the other party. |
| Field Component Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the field component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Includes | Includes | Indicates that one component is entirely contained within another component. |
| Information Exchange Agreement | Agreement | An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. |
| Information Exchange and Action Agreement | Agreement | An agreement to exchange information, which may include data or control information; the exact information to be exchanged may vary from agreement to agreement. This also includes a specification for action that shall, should or may be taken by one party in response to this information. |
| Information Provision Agreement | Agreement | An agreement where one party agrees to provide information to another party. This is a unidirectional agreement. |
| Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity installs an application component on a device controlled by another entity. |
| Interface Description | Agreement | Documentation of the interface between two systems, where one system does not have an application component that is part of the application, but does provide and/or receive data and/or information that is used by or sourced from the application. In many cases this is an existing interface used by the application, so the description of the interface already exists and is imposed by the terminator. |
| Interface Specification | Agreement | The definition of interface between two hardware components that must share data. |
| Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of a system under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that states one entity will provide data related to maintenance of an application component to the other entity. |
| Mobile Component Installation Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon the controller of OBE gives another party permission to install, configure and make operational a component that enables the mobile portion of an application. |
| Mobile Component License Agreement | Agreement | An end-user license agreement allowing the operator of the mobile device to use the mobile application component that is part of the application in question. |
| Mobile Component Maintenance Agreement | Agreement | An agreement in which one entity maintains the operational status of the mobile component of an application under the control of another entity. This maintenance may include routine and as-needed maintenance, such as software update and configuration, hardware replacement and related system administration activities. |
| Operations Agreement | Agreement | An agreement where one entity agrees to operate a device or application on behalf of another, device/application controlling entity. |
| RSE Deployment Agreement | Agreement | Agreement to install, configure and make operational roadside equipment, between the provider of that equipment and the entity that controls access to the roadside. May define locations, expectation of power provision, backhaul responsibility and installation restrictions. |
| RSE Installation Data | Information Sharing | Data necessary to configure and make RSE operational. Uni-directional. |
| RSE Maintenance Data | Information Sharing | Data necessary to modify the operational configuration of RSE; assumes RSE is already configured. Uni-directional. |
| RSE Performance Data | Information Sharing | Data that includes metrics of RSE performance. Could include fields such as uptime, packets received/transmitted, distance vector from which packets received, as well as application-specific performance measures. |
| RSE Procurement Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereupon one entity provides roadside equipment to another entity. The RSE is capable of being installed and functioning, according to its requirements that passed through the device's certification process. |
| Service Coordination Agreement | Agreement | An agreement between two or more parties that operate similar or geographically adjacent or overlapping services, stipulating coordination, information sharing and other aspects of service provision relevant between these services. |
| Service Delivery Agreement | Agreement | A relationship where one party agrees to provide a service to the other party. This agreement may specify the expected performance of this service in terms of availability and/or actions/time-type performance specifications. |
| Service Usage Agreement | Agreement | A generic agreement between the provider of a service and a user. Stipulates the terms and conditions of service usage. |
| Vehicle Data Access Agreement | Agreement | An agreement whereby the party that controls access to on-board vehicle data grants another party the right and ability to access that data. Includes the conditions under which data may be accessed, and specifies the mechanisms, including physical and functional access methods, data formats and any other considerations necessary for the accessing party to acquire data. May also include caveats regarding responsibility for data quality and responsibility for use of the data. |
| Vehicle OBE Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement that grants one entity permission to use a Vehicle OBE that the other party controls. |
| Vehicle Procurement Agreement | Agreement | The exchange of a vehicle for compensation. One entity purchases the vehicle from the other. |
| Vehicle Usage Agreement | Agreement | An agreement between the owner of a vehicle and a prospective operator, whereupon the owner allows the operator to use the vehicle. |
| Warranty | Agreement | A guarantee or promise made by one entity to another, that provides assurance of the functionality and performance over time of an application component. |
Functional
Includes Processes:
Includes Data Flows:
Physical
SVG Diagrams: Low Emissions Zone Operations Fee Collection
PNG Diagrams: Low Emissions Zone Operations Fee Collection
Includes Physical Objects:
| Physical Object | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DMV | Center | The 'DMV' is a specific (state) public organization responsible for registering vehicles, e.g., the Department of Motor Vehicles. |
| Driver | Vehicle | The 'Driver' represents the person that operates a vehicle on the roadway. Included are operators of private, transit, commercial, and emergency vehicles where the interactions are not particular to the type of vehicle (e.g., interactions supporting vehicle safety applications). The Driver originates driver requests and receives driver information that reflects the interactions which might be useful to all drivers, regardless of vehicle classification. Information and interactions which are unique to drivers of a specific vehicle type (e.g., fleet interactions with transit, commercial, or emergency vehicle drivers) are covered by separate objects. |
| Emissions Management Center | Center | The 'Emissions Management Center' provides the capabilities for air quality managers to monitor and manage air quality. These capabilities include collecting emissions data from distributed emissions sensors (included in ITS Roadway Equipment in CVRIA) and directly from connected vehicles. The sensors monitor general air quality and also monitor the emissions of individual vehicles on the roadway. The measures are collected, processed, and used to support environmental monitoring applications. |
| Emissions Management Operator | Center | The 'Emissions Management Operator' represents personnel that monitor, operate, and manage emissions monitoring and management systems. These personnel monitor system operation and monitor collected emissions and air quality information and direct system operation through data and command inputs. |
| Enforcement Center | Center | The 'Enforcement Center' represents the systems that receive reports of violations detected by various ITS facilities including individual vehicle emissions, lane violations, toll violations, CVO violations, etc. |
| Event Promoters | Center | 'Event Promoters' represents Special Event Sponsors that have knowledge of events that may impact travel on roadways or other modal means. Examples of special event sponsors include sporting events, conventions, motorcades/parades, and public/political events. These promoters interface to the ITS to provide event information such as date, time, estimated duration, location, and any other information pertinent to traffic movement in the surrounding area. |
| Financial Center | Center | The 'Financial Center' represents the organization that handles electronic fund transfer requests to enable the transfer of funds from the user of the service to the provider of the service. The functions and activities of financial clearinghouses are subsumed by this entity. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Field | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway itself. In CVRIA, this physical object represents all of the other ITS field equipment that interfaces with and supports the Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE). This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| ITS Roadway Payment Equipment | Field | 'ITS Roadway Payment Equipment' represents the roadway components of a toll collection system. It provides the capability for vehicle operators to pay tolls without stopping their vehicles. It supports use of locally determined pricing structures and includes the capability to implement various variable pricing policies. Typically, transactions are accompanied by feedback to the customer and a record of the transactions is provided to a back office system (e.g., the Payment Administration Center). |
| Other Payment Administration | Center | Representing another Payment Administration Center, 'Other Payment Administration' is intended to provide a source and destination for ITS information flows between payment administration functions. This interface allows reconciliation of toll charges and other payments across different agencies by allowing the exchange of information about clients who have incurred charges in jurisdictions other than their own (billing) customer service center. This interface enables apportioning charges and 'reciprocity' between participating customer service centers. |
| Payment Administration Center | Center | The 'Payment Administration Center' provides general payment administration capabilities and supports the electronic transfer of funds from the customer to the transportation system operator or other service provider. Charges can be recorded for tolls, vehicle-mileage charging, congestion charging, or other goods and services. It supports traveler enrollment and collection of both pre-payment and post-payment transportation fees in coordination with the financial infrastructure supporting electronic payment transactions. The system may establish and administer escrow accounts depending on the clearinghouse scheme and the type of payments involved. It may post a transaction to the customer account, generate a bill (for post-payment accounts), debit an escrow account, or interface to a financial infrastructure to debit a customer designated account. It supports communications with the ITS Roadway Payment Equipment to support fee collection operations. As an alternative, a wide-area wireless interface can be used to communicate directly with vehicle equipment. It also sets and administers the pricing structures and may implement road pricing policies in coordination with the Traffic Management Center. |
| Payment Administrator | Center | The 'Payment Administrator' represents the person(s) that manage the back office payment administration systems for electronic toll, VMT road use payment, and other services paid for from a vehicle. It monitors the systems that support the electronic transfer of funds from the customer to the system operator. It monitors customer enrollment and supports the establishment of escrow accounts depending on the clearinghouse scheme and the type of payments involved. It also establishes and administers the pricing structures and policies. |
| Payment Device | Traveler | The 'Payment Device' enables the electronic transfer of funds from the user of a service (I.e. a traveler) to the provider of the service. Potential implementations include smart cards that support payment for products and services, including transportation services and general purpose devices like smart phones that support a broad array of services, including electronic payment. In addition to user account information, the payment device may also hold and update associated user information such as personal profiles, preferences, and trip histories. |
| Personal Information Device | Traveler | The 'Personal Information Device' provides the capability for travelers to receive formatted traveler information wherever they are. Capabilities include traveler information, trip planning, and route guidance. Frequently a smart phone, the Personal Information Device provides travelers with the capability to receive route planning and other personally focused transportation services from the infrastructure in the field, at home, at work, or while en-route. Personal Information Devices may operate independently or may be linked with connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| Roadside Equipment | Field | 'Roadside Equipment' (RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices that are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles using Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or other alternative wireless communications technologies. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Traffic Management Center | Center | The 'Traffic Management Center' monitors and controls traffic and the road network. It represents centers that manage a broad range of transportation facilities including freeway systems, rural and suburban highway systems, and urban and suburban traffic control systems. It communicates with ITS Roadway Equipment and Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE) to monitor and manage traffic flow and monitor the condition of the roadway, surrounding environmental conditions, and field equipment status. It manages traffic and transportation resources to support allied agencies in responding to, and recovering from, incidents ranging from minor traffic incidents through major disasters. |
| Traffic Operations Personnel | Center | 'Traffic Operations Personnel' represents the people that operate a traffic management center. These personnel interact with traffic control systems, traffic surveillance systems, incident management systems, work zone management systems, and travel demand management systems. They provide operator data and command inputs to direct system operations to varying degrees depending on the type of system and the deployment scenario. |
| Transit Management Center | Center | The 'Transit Management Center' manages transit vehicle fleets and coordinates with other modes and transportation services. It provides operations, maintenance, customer information, planning and management functions for the transit property. It spans distinct central dispatch and garage management systems and supports the spectrum of fixed route, flexible route, paratransit services, transit rail, and bus rapid transit (BRT) service. The physical object's interfaces allow for communication between transit departments and with other operating entities such as emergency response services and traffic management systems. |
| Transportation Information Center | Center | The 'Transportation Information Center' collects, processes, stores, and disseminates transportation information to system operators and the traveling public. The physical object can play several different roles in an integrated ITS. In one role, the TIC provides a data collection, fusing, and repackaging function, collecting information from transportation system operators and redistributing this information to other system operators in the region and other TICs. In this information redistribution role, the TIC provides a bridge between the various transportation systems that produce the information and the other TICs and their subscribers that use the information. The second role of a TIC is focused on delivery of traveler information to subscribers and the public at large. Information provided includes basic advisories, traffic and road conditions, transit schedule information, yellow pages information, ride matching information, and parking information. The TIC is commonly implemented as a website or a web-based application service, but it represents any traveler information distribution service. |
| Vehicle Databus | Vehicle | The 'Vehicle Databus' represents the interface to the vehicle databus (e.g., CAN, LIN, Ethernet/IP, FlexRay, and MOST) that may enable communication between the Vehicle OBE and other vehicle systems to support connected vehicle applications. The vehicle system statuses and/or sensor outputs available on the databus will vary based on the equipment installed on the vehicle and availability on databus. System statuses and sensor outputs may include select vehicle systems and sensors such as accelerometers, yaw rate sensors, and GPS derived location and timing information. In CVRIA, this physical object is used to represent the onboard interactions between the Vehicle OBE and the other systems included in a host vehicle. Note that the vehicle databus interface is not standardized across all vehicle classes. Also, some Vehicle OBE implementations will not have access to the vehicle databus. See 'Vehicle OBE' for more information. |
| Vehicle OBE | Vehicle | The Vehicle On-Board Equipment (OBE) provides the vehicle-based processing, storage, and communications functions necessary to support connected vehicle operations. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle OBE. This communication platform is augmented with processing and data storage capability that supports the connected vehicle applications. In CVRIA, the Vehicle OBE includes the functions and interfaces that support connected vehicle applications for passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Many of these applications (e.g., V2V Safety applications) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle OBE includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. |
| Weather Service | Center | The 'Weather Service' provides weather, hydrologic, and climate information and warnings of hazardous weather including thunderstorms, flooding, hurricanes, tornadoes, winter weather, tsunamis, and climate events. It provides atmospheric weather observations and forecasts that are collected and derived by the National Weather Service, private sector providers, and various research organizations. The interface provides formatted weather data products suitable for on-line processing and integration with other ITS data products as well as Doppler radar images, satellite images, severe storm warnings, and other products that are formatted for presentation to various ITS users. |
Includes Application Objects:
| Application Object | Description | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| Emissions Connected Vehicle Monitoring | "Emissions Connected Vehicle Monitoring" collects emissions data reported by passing vehicles and uses this data to support air quality management and planning. Coordination with traffic management supports air quality-responsive management of traffic. | Emissions Management Center |
| Emissions Data Management | "Emissions Data Management" collects and stores air quality and vehicle emissions information by remotely monitoring and controlling area wide and point sensors. General air quality measures are distributed as general traveler information and also may be used in demand management programs. Collected roadside emissions are analyzed and used to detect, identify, and notify concerned parties regarding vehicles that exceed emissions standards. | Emissions Management Center |
| Emissions Zone Management | "Emissions Zone Management" identifies existing and potential emissions hot spots and coordinates with transportation agencies and their systems to establish low emissions zones to manage air quality in these areas. Through this coordination, the geographic boundary, restrictions, and pricing for the low emissions zone are established and adjusted. | Emissions Management Center |
| PAC Payment Administration | "PAC Payment Administration" enables payment for road use based on VMT, vehicle type, vehicle emissions, or other parameters. It establishes a price schedule based on these parameters that may vary by time, location or zone, vehicle type, and/or vehicle behavior. Pricing strategies may also include incentives that allow reimbursement of fees previously paid for good behavior (e.g., VMT reductions, economical driving behavior, avoidance of peak periods or congested zones). It receives vehicle data (e.g., time stamped roadways used by the vehicle since the last transmission) and computes the total cost to the vehicle owner for payment. Based on owner preference, this cost is either billed to the owner or requested from an in-vehicle payment instrument. Payment for use of roadways not operated by the specific instance of the VMT Payment Administration that the vehicle is registered with, will be reconciled. Payment violations can be reported to Enforcement Agencies when appropriate. Finally, vehicle owners can interact with this object using personal devices or public terminals to setup and edit account preferences for owned vehicles, get account reports, and make payments. | Payment Administration Center |
| Personal Interactive Traveler Information | "Personal Interactive Traveler Information" provides traffic information, road conditions, transit information, yellow pages (traveler services) information, special event information, and other traveler information that is specifically tailored based on the traveler's request and/or previously submitted traveler profile information. It also supports interactive services that support enrollment, account management, and payments for transportation services. The interactive traveler information capability is provided by personal devices including personal computers and personal portable devices such as smart phones. | Personal Information Device |
| Roadway Basic Surveillance | "Roadway Basic Surveillance" monitors traffic conditions using fixed equipment such as loop detectors and CCTV cameras. | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| Roadway Payment Support | "Roadway Payment Support" represents the equipment that works in conjunction with the RSE to detect vehicles and identify and process violators when the RSE is used to support electronic payment. Various fee structures and payment strategies are supported including strategies that support reimbursements or credits that incentivize desired driving behavior. | ITS Roadway Payment Equipment |
| Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination | "Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination" includes field elements that provide information to drivers, including dynamic message signs and highway advisory radios. | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| RSE Environmental Monitoring | "RSE Environmental Monitoring" collects environmental situation (probe) data from passing vehicles that are equipped with short range communications capability. The collected data includes current environmental conditions as measured by on-board sensors (e.g., ambient temperature and precipitation measures), current status of vehicle systems that can be used to infer environmental conditions (e.g., status of lights, wipers, ABS, and traction control systems), and emissions measures reported by the vehicle. The application object collects the provided data, aggregates and filters the data based on provided configuration parameters, and sends the collected information back to a center for processing and distribution. This application object may also process the collected data locally and issue short-term road weather advisories for the road segment using short range communications. | Roadside Equipment |
| RSE Low Emissions Zone Application | "RSE Low Emissions Zone Application" provides information to vehicles regarding low emissions zones and checks vehicle profiles on entry to a designated low emissions zone to verify they are in compliance with the parameters established for the zone. | Roadside Equipment |
| RSE Payment Support | "RSE Payment Support" manages vehicle payments for road use based on fee structures and payment strategies based on vehicle-reported data including VMT, emissions, vehicle class or type. Fees may vary by time or location and may include incentives or credits to reward desirable driving behavior. To support payment, it receives vehicle data (e.g., time stamped roadways used by the vehicle since the last transmission) and forwards this to the Payment Administration Center. It also receives equipment status from the vehicle and vehicle characteristics sensed from the vehicle (number of axles, weight, vehicle tag image/ID). Faults are identified and forwarded to the Payment Administration Center. Finally, it requests, receives, processes, and reports vehicle payment information. | Roadside Equipment |
| RSE Traffic Monitoring | "RSE Traffic Monitoring" monitors the basic safety messages that are shared between connected vehicles and distills this data into traffic flow measures that can be used to manage the network in combination with or in lieu of traffic data collected by infrastructure-based sensors. As connected vehicle penetration rates increase, the measures provided by this application can expand beyond vehicle speeds that are directly reported by vehicles to include estimated volume, occupancy, and other measures. This object also supports incident detection by monitoring for changes in speed and vehicle control events that indicate a potential incident. | Roadside Equipment |
| RSE Traveler Information Communications | "RSE Traveler Information Communications" includes field elements that distribute information to vehicles for in-vehicle display. The information may be provided by a center (e.g., variable information on traffic and road conditions in the vicinity of the field equipment) or it may be determined and output locally (e.g., static sign information and signal phase and timing information). This includes the interface to the center or field equipment that controls the information distribution and the short range communications equipment that provides information to passing vehicles. | Roadside Equipment |
| TIC Data Collection | "TIC Data Collection" collects transportation-related data from other centers, performs data quality checks on the collected data and then consolidates, verifies, and refines the data and makes it available in a consistent format to applications that support operational data sharing between centers and deliver traveler information to end-users. A broad range of data is collected including traffic and road conditions, transit data, emergency information and advisories, weather data, special event information, traveler services, parking, multimodal data, and toll/pricing data. It also shares data with other transportation information centers. | Transportation Information Center |
| TMC Incident Dispatch Coordination/Communication | "TMC Incident Dispatch Coordination/Communication" formulates and manages an incident response that takes into account the incident potential, incident impacts, and resources required for incident management. It supports dispatch of emergency response and service vehicles as well as coordination with other cooperating agencies. It provides access to traffic management resources that provide surveillance of the incident, traffic control in the surrounding area, and support for the incident response. It monitors the incident response and collects performance measures such as incident response and clearance times. | Traffic Management Center |
| TMC In-Vehicle Signing Management | "TMC In-Vehicle Signing Management" controls and monitors RSEs that support in-vehicle signing. Sign information that may include static regulatory, service, and directional sign information as well as variable information such as traffic and road conditions can be provided to the RSE, which uses short range communications to send the information to in-vehicle equipment. Information that is currently being communicated to passing vehicles and the operational status of the field equipment is monitored by this application. The operational status of the field equipment is reported to operations personnel. | Traffic Management Center |
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination | "TMC Traffic Information Dissemination" disseminates traffic and road conditions, closure and detour information, incident information, driver advisories, and other traffic-related data to other centers, the media, and driver information systems. It monitors and controls driver information system field equipment including dynamic message signs and highway advisory radio, managing dissemination of driver information through these systems. | Traffic Management Center |
| TMC Traffic Surveillance | "TMC Traffic Surveillance" remotely monitors and controls traffic sensors and surveillance (e.g., CCTV) equipment, and collects, processes and stores the collected traffic data. Current traffic information and other real-time transportation information is also collected from other centers. The collected information is provided to traffic operations personnel and made available to other centers. | Traffic Management Center |
| Transit Center Multi-Modal Coordination | "Transit Center Multi-Modal Coordination" supports transit service coordination between transit properties and coordinates with other surface and air transportation modes. As part of service coordination, it shares schedule and trip information, as well as transit transfer cluster (a collection of stop points, stations, or terminals where transfers can be made conveniently) and transfer point information between Multimodal Transportation Service Providers, Transit Agencies, and ISPs. An interface to Traffic Management also supports demand management strategies. | Transit Management Center |
| Vehicle Basic Safety | "Vehicle Basic Safety" exchanges current vehicle location and motion information with other vehicles in the vicinity, uses that information to calculate vehicle paths, and warns the driver when the potential for an impending collision is detected. If available, map data is used to filter and interpret the relative location and motion of vehicles in the vicinity. Information from on-board sensors (e.g., radars and image processing) are also used, if available, in combination with the V2V communications to detect non-equipped vehicles and corroborate connected vehicle data. Vehicle location and motion broadcasts are also received by the infrastructure and used by the infrastructure to support a wide range of roadside safety and mobility applications. This object represents a broad range of implementations ranging from basic Vehicle Awareness Devices that only broadcast vehicle location and motion and provide no driver warnings to advanced integrated safety systems that may, in addition to warning the driver, provide collision warning information to support automated control functions that can support control intervention. | Vehicle OBE |
| Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist | "Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist" provides customized real-time driving advice to drivers, allowing them to adjust behaviors to save fuel and reduce emissions. This advice includes recommended driving speeds, optimal acceleration and deceleration profiles based on prevailing traffic conditions, and local interactions with nearby vehicles, i.e., processing Basic Safety Messages (BSMs) to determine position and speed of vehicles that are between the host vehicle and the intersection. When approaching and departing signalized intersections, it uses intersection geometry information, the relative position and speed of vehicles ahead of it, and signal phase movement information to provide speed advice to the driver so that the driver can adapt the vehicle's speed to pass the next traffic signal on green, decelerate to a stop in the most eco-friendly manner, or manage acceleration as the vehicle departs from a signalized intersection. It also provides feedback to drivers on their driving behavior to encourage them to drive in a more environmentally efficient manner. It may also support vehicle-assisted strategies, where the vehicle automatically implements the eco-driving strategy (e.g., changes gears, switches power sources, or reduces its speed in an eco-friendly manner as the vehicle approaches a traffic signal or queue). | Vehicle OBE |
| Vehicle Emissions Monitoring | "Vehicle Emissions Monitoring" directly measures or estimates current and average vehicle emissions and makes this data available to the driver and connected vehicle infrastructure systems. | Vehicle OBE |
| Vehicle Payment Service | "Vehicle Payment Service" supports vehicle payments including VMT- and zone-based payments and payments for other services including fuel/charging services. To support VMT-based payment, this application tracks the location of the vehicle at specific times and reports this VMT data along with vehicle identification. A variety of pricing strategies are supported, including strategies that include credits or incentives that reward desired driving patterns and behavior. | Vehicle OBE |
| Vehicle Roadside Information Reception | "Vehicle Roadside Information Reception" receives advisories, vehicle signage data, and other driver information and presents this information to the driver using in-vehicle equipment. Information presented may include fixed sign information, traffic control device status (e.g., signal phase and timing data), advisory and detour information, warnings of adverse road and weather conditions, travel times, and other driver information. | Vehicle OBE |
Includes Information Flows:
| Information Flow | Description |
|---|---|
| driver information | Regulatory, warning, and guidance information provided to the driver while en route to support safe and efficient vehicle operation. |
| driver input | Driver input to the vehicle on-board equipment including configuration data, settings and preferences, interactive requests, and control commands. |
| driver input information | Driver input received from the driver-vehicle interface equipment via the vehicle bus. It includes configuration data, settings and preferences, interactive requests, and control commands for the connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| driver update information | Information provided to the driver-vehicle interface to inform the driver about current conditions, potential hazards, and the current status of vehicle on-board equipment. The flow includes the information to be presented to the driver and associated metadata that supports processing, prioritization, and presentation by the DVI as visual displays, audible information and warnings, and/or haptic feedback. |
| driver updates | Information provided to the driver including visual displays, audible information and warnings, and haptic feedback. The updates inform the driver about current conditions, potential hazards, and the current status of vehicle on-board equipment. |
| emissions situation data | Emissions-related data as measured and reported by connected vehicles. This flow carries aggregated and filtered data including average and current emissions reported by vehicles as well as associated data (vehicle profiles and speeds) that can be used to estimate aggregate emissions. |
| emissions violation notification | Notification to enforcement agency of a detected vehicle emissions violation. This information flow identifies the vehicle and documents the emissions violation. |
| event confirmation | Confirmation that special event details have been received and processed. |
| event plans | Plans for major events possibly impacting traffic. |
| host vehicle status | Information provided to the connected vehicle on-board equipment from other systems on the vehicle platform. This includes data from on-board sensors, the current status of the powertrain, steering, and braking systems, and status of safety and convenience systems. In implementations where GPS is not integrated into the Vehicle On-Board Equipment, the host vehicle is also the source for data describing the vehicle's location in three dimensions (latitude, longitude, elevation) and accurate time that can be used for time synchronization across the Connected Vehicle environment. |
| license request | Request supporting registration data based on license plate read during violation. |
| low emissions zone application info | Low emissions zone application parameters and thresholds. This flow also supports remote control of the application so the application can be taken offline, reset, or restarted. |
| low emissions zone application status | Low emissions zone application status reported by the RSE. This includes current operational state and status of the RSE and a record of system operation. |
| low emissions zone coordination | Coordination of geographic boundaries, time period, fee structure, and restrictions for a low emissions zone. This flow supports negotiation between centers that establishes low emissions zone parameters based on air quality and transportation needs, as constrained by infrastructure and transportation services that are available to manage the defined zone and applicable laws and regulations. |
| low emissions zone operations information | Information on the state of transportation system operations within the low emissions zone including emissions zone parameters, traffic and road conditions within the zone, advisories, incidents, transit service information, weather information, parking information, and other related data. |
| low emissions zone parameters | The geographic boundaries, time period, and fee structure for a low emissions zone. This flow also provides the specific restrictions that are in place for the zone including admittance requirements and rules and restrictions for driving within the zone. |
| payment | Payment of some kind (e.g., toll, parking, fare) by traveler which, in most cases, can be related to a credit account. |
| payment administration requests | Personnel inputs that control system operations, including requests to change toll fees, confirmation that alerts should be provided to toll operators, management of VMT charge policies and management of VMT account processing, etc. |
| payment coordination | Coordinate apportionment charges between jurisdictions (e.g. federal government, states, various jurisdictions that might be public or private within a state). Apportionment reconciliation includes either sharing information about mileage or zone-based charges in other jurisdictions (so that the Other Payment Administration subsystems can make appropriate charges), or sharing revenue collected. When sharing revenue, this flow also includes charging rate policies |
| payment information presentation | Presentation of information to personnel including revenues, reports, operational status information, and alert information. |
| payment instructions | Information provided to configure and support fixed point payment operations including pricing information. |
| payment request | Request for payment from financial institution. |
| payment transactions | Detailed list of transactions including violations. |
| payment violation notification | Notification to enforcement agency of a toll, parking, or transit fare payment violation. |
| pollution data display | Presentation of information to the operator supporting both area-wide air quality monitoring and vehicle emissions monitoring. Includes both reference and current pollution status details for a given geographic area. |
| pollution data parameters | User input from the system operator including nominal pollution data compliance (reference) levels for each sector of an urban area. |
| registration | Registered owner of vehicle and associated vehicle information. |
| request for payment | Request to deduct cost of service from user's payment account. |
| road network conditions | Current and forecasted traffic information, road and weather conditions, and other road network status. Either raw data, processed data, or some combination of both may be provided by this flow. Information on diversions and alternate routes, closures, and special traffic restrictions (lane/shoulder use, weight restrictions, width restrictions, HOV requirements) in effect is included. |
| road use charges | Road use charges per link. |
| road use history | A vehicle's road use history that records where the vehicle has traveled over time. Optionally includes vehicle speeds as well as distance traveled for some applications. Information is accurate enough to distinguish between adjacent roads, adjacent lanes, and identify direction of travel on the roads. |
| roadway information system data | Information used to initialize, configure, and control roadside systems that provide driver information (e.g., dynamic message signs, highway advisory radio). This flow can provide message content and delivery attributes, local message store maintenance requests, control mode commands, status queries, and all other commands and associated parameters that support remote management of these systems. |
| roadway information system status | Current operating status of dynamic message signs, highway advisory radios, or other configurable field equipment that provides dynamic information to the driver. |
| traffic flow | Raw and/or processed traffic detector data which allows derivation of traffic flow variables (e.g., speed, volume, and density measures) and associated information (e.g., congestion, potential incidents). This flow includes the traffic data and the operational status of the traffic detectors. |
| traffic operator data | Presentation of traffic operations data to the operator including traffic conditions, current operating status of field equipment, maintenance activity status, incident status, video images, security alerts, emergency response plan updates and other information. This data keeps the operator appraised of current road network status, provides feedback to the operator as traffic control actions are implemented, provides transportation security inputs, and supports review of historical data and preparation for future traffic operations activities. |
| traffic operator input | User input from traffic operations personnel including requests for information, configuration changes, commands to adjust current traffic control strategies (e.g., adjust signal timing plans, change DMS messages), and other traffic operations data entry. |
| traffic sensor control | Information used to configure and control traffic sensor systems. |
| traffic situation data | Current, aggregate traffic data collected from connected vehicles that can be used to supplement or replace information collected by roadside traffic detectors. It includes raw and/or processed reported vehicle speeds, counts, and other derived measures. Raw and/or filtered vehicle control events may also be included to support incident detection. |
| transaction status | Response to transaction request. Normally dealing with a request for payment. |
| transit and fare schedules | Transit service information including routes, schedules, and fare information. |
| traveler payment information | Payment information for road use charges. |
| traveler payment request | Request for payment for road use charges. |
| user account reports | Reports on charges |
| user account setup | Billing information, vehicle information (or registration information), and requests for reports. |
| vehicle emissions monitoring parameters | Data used to configure and control roadside equipment applications that monitor emissions-related data reported by passing vehicles. The parameters include identification of the emissions-related data to be monitored and thresholds for aggregating, filtering, and reporting the collected data. |
| vehicle entries and exits | Information exchanged between an RSE and ITS Roadway Equipment that supports detection of non-equipped vehicles in an automated lane, low emissions zone, or other facility where V2I communications is used to monitor vehicles at entry or exit points. This exchange also supports identification of non-equipped vehicles where an RSE is used for payment collection. This generic exchange can be implemented by any approach that compares vehicle detections with V2I communications by the RSE to identify vehicles that are not equipped or are otherwise unable to communicate with the RSE. |
| vehicle location and motion for surveillance | Data describing the vehicle's location in three dimensions, heading, speed, acceleration, braking status, and size. This flow represents monitoring of basic safety data ('vehicle location and motion') broadcast by passing connected vehicles for use in vehicle detection and traffic monitoring applications. |
| vehicle payment information | Information provided for payment of tolls or parking fees including identification that can be used to identify the payment account or source and related vehicle and service information that are used to determine the type and price of service requested. The information exchange normally supports an account debit to pay fees, but an account credit may be initiated where pricing strategies include incentives. |
| vehicle payment request | Request for information supporting payments. For fee structures that include incentives, the request may support either an account debit or an account credit or reimbursement. |
| vehicle profile | Information about a vehicle such as vehicle make and model, fuel type, engine type, average emissions, average fuel consumption, passenger occupancy, or other data that can be used to classify vehicle eligibility for access to specific lanes, road segments, or regions. |
| vehicle reported emissions | Current and average vehicle emissions data as measured by vehicle diagnostics systems and reported by the vehicle. |
| vehicle signage application info | In-vehicle signing application configuration data and messaging parameters. This flow provides a list of regulatory, warning, and information messages to be displayed and parameters that support scheduling and prioritizing messages to be issued to passing vehicles. This flow also supports remote control of the application so the application can be taken offline, reset, or restarted. |
| vehicle signage application status | In-vehicle signing application status reported by the RSE. This includes current operational state and status of the RSE and a log of messages sent to passing vehicles. |
| vehicle signage data | In-vehicle signing data that augments regulatory, warning, and informational road signs and signals. The information provided would include static sign information (e.g., stop, curve warning, guide signs, service signs, and directional signs) and dynamic information (e.g., current signal states, grade crossing information, local traffic and road conditions, detours, advisories, and warnings). |
| vehicle signage local data | Information provided by adjacent field equipment to support in-vehicle signing of dynamic information that is currently being displayed to passing drivers. This includes the dynamic information (e.g., current signal states, grade crossing information, local traffic and road conditions, detours, advisories, parking availability, etc.) and control parameters that identify the desired timing, duration, and priority of the signage data. |
| weather information | Accumulated forecasted and current weather data (e.g., temperature, pressure, wind speed, wind direction, humidity, precipitation, visibility, light conditions, etc.). |
Application Interconnect Diagram
SVG Diagrams: Low Emissions Zone Operations Fee Collection
PNG Diagrams: Low Emissions Zone Operations Fee Collection
Application Triples
Requirements
| Need | Requirement | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N1.001 | Transportation agencies need to gather data from vehicles or infrastructure to support environmental monitoring. | 1.001 | All environmental applications shall collect data from mobile devices to support environmental monitoring, including ambient air quality, emissions, temperature, precipitation, and other road weather information. |
| 1.002 | All environmental applications shall collect data from infrastructure devices to support environmental monitoring, including ambient air quality, emissions, temperature, precipitation, wind speed, and other road weather information. | ||
| N1.026 | Low Emissions Zone Management needs to collect traffic, environmental, event, and transit data for low emission zone operations. | 1.089 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall collect traffic data (e.g., volume, speed, occupancy, vehicle classification, turning movements, incidents). |
| 1.090 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall collect environmental data (e.g. ambient air quality, emissions, temperature, wind speed, and other road weather information). | ||
| 1.091 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall collect vehicle-specific data about individual vehicles' parameters (e.g., emissions, temperature, speed). | ||
| 1.092 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall collect special event data. | ||
| 1.093 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall collect data from Transit Agencies about current and planned transit operations, including information about transit routes, services, and ridership. | ||
| 1.094 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall collect data from vehicle payment devices being carried on-board the vehicle and used as a payment instrument. | ||
| 1.095 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall collect data entered by personnel operating the system. | ||
| N1.027 | Low Emissions Zone Management needs to process current and historical data from multiple sources in order to provide low emissions zone operations. | 1.050 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall use data collected from vehicles to determine violations for individual vehicles that illegally entered the Low Emissions Zone. |
| 1.051 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall maintain a log of all fee and incentive transactions carried out by the system. | ||
| 1.096 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall synthesize traffic data from multiple sources (e.g., fixed sensors, connected vehicle roadway equipment, other centers) to provide traffic analyses aggregated at different levels (e.g., intersection, corridor, and regional levels). | ||
| 1.097 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall use historical and processed traffic data to predict traffic conditions aggregated at different levels (e.g., intersection, corridor, and regional levels). Low Emissions Zone Management needs to collect traffic data from other systems, or produce and continually update, a predictive model of the traffic flow conditions on the road network. | ||
| 1.098 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall synthesize environmental data from multiple sources (e.g., fixed sensors, connected vehicle roadside equipment, and other centers) to provide emissions analyses aggregated at different levels (e.g., intersection, corridor, and regional levels). | ||
| 1.099 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall synthesize environmental data from multiple sources (e.g., sensors, connected vehicle roadside equipment, and other centers) to generate predicted emissions aggregated at different levels (e.g., intersection, corridor, and regional levels). | ||
| 1.100 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall create and decommission Low Emissions Zones. | ||
| 1.101 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall use data collected from vehicles to determine fees for vehicles to enter the Low Emissions Zone. | ||
| 1.102 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall use data collected from individual vehicles to determine incentives for individual vehicles in the Low Emissions Zone. | ||
| N1.028 | Low Emissions Zone Management needs to share information to other centers in support of low emission zone operations. | 1.052 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall disseminate traffic conditions to other centers to enable coordination of operational strategies for a corridor or a region. |
| 1.054 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall disseminate environmental data (e.g., regional and/or local air quality, temperature, precipitation) to other centers. | ||
| 1.056 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall provide parameters about the Low Emissions Zone to other centers. | ||
| 1.059 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall make requests for payment from Financial Institutions. | ||
| 1.063 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall notify enforcement agencies of a violation. | ||
| N1.029 | Low Emissions Zone Management needs to share information with vehicles in support of emission zone operations. | 1.057 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall provide parameters about the Low Emissions Zone to vehicles. |
| 1.058 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall disseminate information specific to individual vehicles for electronic payment of tolls. | ||
| 1.060 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall use vehicle specific data collected from vehicles to provide an individual vehicle an incentive. | ||
| 1.061 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall provide confirmation of payment or incentive to individual vehicles. | ||
| 1.062 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall provide individual vehicles notice of a violation. | ||
| N1.030 | Low Emissions Zone Management needs to archive data that improves the low emissions zone operations in the future and stores financial data. | 1.064 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall archive traffic data, environmental data, Low Emissions Zone parameters (e.g., geographic limits, fee structure), and event logs (e.g., time the Low Emissions Zone was implemented, time it was decommissioned, etc.). |
| 1.065 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall archive all financial data for toll transactions. | ||
| 1.066 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall determine performance measures and make them available to the operator. | ||
| N1.031 | Low Emissions Zone Management vehicle based systems needs to receive data from the vehicle itself, payment information and driver inputs in support of low emissions zone operations. | 1.069 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall collect diagnostics data from onboard systems and onboard sensors located on the vehicle to obtain vehicle status and vehicle emissions data. |
| 1.070 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall receive parameters about Low Emissions Zones that have been created and decommissioned. | ||
| 1.071 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall receive payment requests. | ||
| 1.072 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall receive confirmation of payment. | ||
| 1.073 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall receive a notice of a violation. | ||
| 1.074 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall collect data from the driver so the driver can configure parameters of the system or override certain vehicle characteristics. | ||
| N1.032 | Low Emissions Zone Management vehicle based systems needs to process data from the vehicle itself, payment information and driver inputs in order to support low emissions zone operations and driver recommendations. | 1.075 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall calculate estimates of tailpipe emissions and fuel consumption if these data cannot be collected directly from the vehicle. |
| 1.076 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall determine if the vehicle meets the criteria for entering the Low Emissions Zone. | ||
| 1.077 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall process requests for payment. | ||
| N1.033 | Low Emissions Zone Management Vehicle System needs to provide actionable information and low emissions zone direction to the driver to drive in a more environmentally friendly manner as well as broadcast vehicle information from the vehicle. | 1.080 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall broadcast vehicle status data or data that is currently included in the SAE J2735 basic safety message (BSM) (e.g., data about the vehicle's location, heading, speed, acceleration, braking status, and size). |
| 1.081 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall broadcast environmental data messages based on data collected from sensors located on-board the vehicle, or data that it processed. | ||
| 1.084 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall provide Low Emissions Zone parameters to the driver. | ||
| 1.085 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall provide payment information so that the account associated with the vehicle can be debited for the amount required to enter the Low Emissions Zone. | ||
| N1.034 | Low Emissions Zone Management Vehicle System needs to provide a user interface through which pertinent traveler information and driver recommendations are provided to the driver. | 1.088 | Low Emissions Zone Management shall provide a user interface through which traffic conditions, environmental conditions, driving recommendations, confirmation of payment, notice of violation, and feedback on driving behavior can be provided to the driver. |
Related Sources
- AERIS Transformative Concepts, Draft, 7/13/2011
- Dynamic Low Emissions Zones: Operational Concept, Final v1.1, 8/1/2012
Security
In order to participate in this application, each physical object should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Physical Object Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Object | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability | Security Class |
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | ||||
In order to participate in this application, each information flow triple should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Information Flow Security | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Destination | Information Flow | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability |
| Basis | Basis | Basis | |||
| Security levels have not been defined yet. | |||||